Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the basement membrane?
What is the primary function of the basement membrane?
- It produces collagen fibers for tissue repair.
- It transports nutrients between cells.
- It supports the epithelium and connects it to underlying connective tissue. (correct)
- It serves as a barrier to pathogens.
Which of the following correctly describes the composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
Which of the following correctly describes the composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
- Contains a high percentage of water and large organic molecules. (correct)
- Contains only collagen and glycoproteins.
- Is primarily composed of lipids and proteins.
- Consists exclusively of fibers and cells.
Which type of fibers in connective tissue is considered the strongest?
Which type of fibers in connective tissue is considered the strongest?
- Reticular fibers.
- Glycosaminoglycan fibers.
- Collagen fibers. (correct)
- Elastic fibers.
Which of the following is NOT a major type of tissue in the human body?
Which of the following is NOT a major type of tissue in the human body?
What makes up the basal lamina layer of the basement membrane?
What makes up the basal lamina layer of the basement membrane?
What characteristic is unique to glandular epithelium compared to covering and lining epithelium?
What characteristic is unique to glandular epithelium compared to covering and lining epithelium?
Which component of the extracellular matrix helps to link cells and ECM components?
Which component of the extracellular matrix helps to link cells and ECM components?
What role do glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) play in the extracellular matrix?
What role do glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) play in the extracellular matrix?
What type of epithelium is characterized by a single layer of cells?
What type of epithelium is characterized by a single layer of cells?
Which feature do epithelial cells exhibit that contributes to their function?
Which feature do epithelial cells exhibit that contributes to their function?
Which of the following accurately characterizes reticular fibers in connective tissue?
Which of the following accurately characterizes reticular fibers in connective tissue?
Which statement is true regarding mature cells in connective tissue?
Which statement is true regarding mature cells in connective tissue?
What defines the polarity of epithelial cells?
What defines the polarity of epithelial cells?
Where are microvilli or cilia typically found?
Where are microvilli or cilia typically found?
What term encompasses various body tissues that connect, support, and bind other tissues together?
What term encompasses various body tissues that connect, support, and bind other tissues together?
Which epithelial tissue type is best suited for areas requiring rapid absorption?
Which epithelial tissue type is best suited for areas requiring rapid absorption?
Which of the following statements about elastic fibers is incorrect?
Which of the following statements about elastic fibers is incorrect?
Which arrangement of epithelial cells typically provides protection?
Which arrangement of epithelial cells typically provides protection?
What is the main reason epithelial tissue can heal rapidly?
What is the main reason epithelial tissue can heal rapidly?
What type of epithelium lines the upper respiratory passages and may contain cilia?
What type of epithelium lines the upper respiratory passages and may contain cilia?
What is the basement membrane's role in epithelial tissue?
What is the basement membrane's role in epithelial tissue?
Which structure primarily increases the surface area in simple columnar epithelium?
Which structure primarily increases the surface area in simple columnar epithelium?
Which type of epithelial cells are specifically defined as having dead, keratin-packed surface cells?
Which type of epithelial cells are specifically defined as having dead, keratin-packed surface cells?
What is the primary function of endothelium that lines blood vessels?
What is the primary function of endothelium that lines blood vessels?
What type of epithelium lines the urinary bladder and ureters?
What type of epithelium lines the urinary bladder and ureters?
Which of the following cells may be present in epithelial tissues, secreting mucus?
Which of the following cells may be present in epithelial tissues, secreting mucus?
Which description applies to nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which description applies to nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What characteristic distinguishes pseudostratified columnar epithelium from other epithelial types?
What characteristic distinguishes pseudostratified columnar epithelium from other epithelial types?
Which of these epithelia is likely to be classified as stratified but consists of a single layer of cells?
Which of these epithelia is likely to be classified as stratified but consists of a single layer of cells?
What classification would apply to a type of epithelium lining the esophagus?
What classification would apply to a type of epithelium lining the esophagus?
What distinguishes exocrine glands from endocrine glands?
What distinguishes exocrine glands from endocrine glands?
Which type of exocrine gland secretion involves cell rupture?
Which type of exocrine gland secretion involves cell rupture?
Which structural classification is NOT applicable to multicellular exocrine glands?
Which structural classification is NOT applicable to multicellular exocrine glands?
What is a characteristic feature of unicellular exocrine glands?
What is a characteristic feature of unicellular exocrine glands?
How are multicellular exocrine glands classified on a functional basis?
How are multicellular exocrine glands classified on a functional basis?
What distinguishes dense regular connective tissue from dense irregular connective tissue?
What distinguishes dense regular connective tissue from dense irregular connective tissue?
Which type of loose connective tissue is known for its protective role and energy storage?
Which type of loose connective tissue is known for its protective role and energy storage?
What is a key feature of cartilage that differentiates it from other types of connective tissue?
What is a key feature of cartilage that differentiates it from other types of connective tissue?
Which of the following connective tissues supports blood cells within lymphoid organs?
Which of the following connective tissues supports blood cells within lymphoid organs?
What characteristic is specific to elastic connective tissue?
What characteristic is specific to elastic connective tissue?
In which part of the body would you typically find areolar connective tissue?
In which part of the body would you typically find areolar connective tissue?
What is the role of chondrocytes in skeletal cartilage?
What is the role of chondrocytes in skeletal cartilage?
What are the two types of serosa in the abdominopelvic cavity?
What are the two types of serosa in the abdominopelvic cavity?
Which statement about the serosa is true?
Which statement about the serosa is true?
What is the function of collagenous fibers in the matrix of cartilage?
What is the function of collagenous fibers in the matrix of cartilage?
Which type of cartilage is known for its ability to withstand compression and serves as a precursor to bone?
Which type of cartilage is known for its ability to withstand compression and serves as a precursor to bone?
What is the primary function of serous membranes?
What is the primary function of serous membranes?
Which of the following types of connective tissue allows for flexibility and is typically found in structures that require stretch, such as the lungs?
Which of the following types of connective tissue allows for flexibility and is typically found in structures that require stretch, such as the lungs?
Which aspect distinguishes the parietal peritoneum from the visceral peritoneum?
Which aspect distinguishes the parietal peritoneum from the visceral peritoneum?
Where are serous membranes primarily found in the body?
Where are serous membranes primarily found in the body?
What type of tissue primarily makes up the serous membrane?
What type of tissue primarily makes up the serous membrane?
Which one of the following best describes the function of the serosa?
Which one of the following best describes the function of the serosa?
What is the role of the visceral peritoneum within the serous membranes?
What is the role of the visceral peritoneum within the serous membranes?
What is the primary composition of mucous membranes?
What is the primary composition of mucous membranes?
Which of the following best describes the main function of serous membranes?
Which of the following best describes the main function of serous membranes?
What type of tissue lines body cavities that are open to the exterior?
What type of tissue lines body cavities that are open to the exterior?
Which components primarily provide the lubricating effect of serous membranes?
Which components primarily provide the lubricating effect of serous membranes?
The lamina propria is associated with which type of membrane?
The lamina propria is associated with which type of membrane?
What distinguishes visceral serous membranes from parietal serous membranes?
What distinguishes visceral serous membranes from parietal serous membranes?
What type of fluid is secreted by mucous membranes for lubrication?
What type of fluid is secreted by mucous membranes for lubrication?
Which feature of mucous membranes helps prevent particles from entering the body?
Which feature of mucous membranes helps prevent particles from entering the body?
Which of the following is NOT a major type of serous membrane?
Which of the following is NOT a major type of serous membrane?
What is primarily responsible for the mucous coat in mucous membranes?
What is primarily responsible for the mucous coat in mucous membranes?
What type of cartilage is characterized by tough, shock-absorbing properties and is found between vertebrae?
What type of cartilage is characterized by tough, shock-absorbing properties and is found between vertebrae?
Which type of fibers are predominant in elastic cartilage providing flexible support?
Which type of fibers are predominant in elastic cartilage providing flexible support?
What is the main function of hyaline cartilage in the human body?
What is the main function of hyaline cartilage in the human body?
What type of membrane lines the inner surfaces of synovial joints and aids in reducing friction?
What type of membrane lines the inner surfaces of synovial joints and aids in reducing friction?
Which statement accurately describes the cutaneous membrane?
Which statement accurately describes the cutaneous membrane?
What role does the synovial membrane play in joint function?
What role does the synovial membrane play in joint function?
What type of cartilage forms the padding at the ends of joints?
What type of cartilage forms the padding at the ends of joints?
Which type of membrane is classified as the only dry membrane in the human body?
Which type of membrane is classified as the only dry membrane in the human body?
What characteristic defines the structure of mucous membranes?
What characteristic defines the structure of mucous membranes?
Which type of cartilage is the most abundant in the human body?
Which type of cartilage is the most abundant in the human body?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Major Tissue Types
- Four major tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue
- Tissue consists of similar cells functioning together.
Epithelial Tissue Characteristics
- Two main types: glandular and covering/lining epithelium
- Glandular epithelium specializes in secretion
- Covering and lining epithelium covers body surfaces both internally and externally
- Separated from connective tissue by a basement membrane
- Avascular: lacks blood vessels, but innervated: contains nerves
- Epithelial cells exhibit polarity with distinct apical and basal surfaces
- Rapid cell reproduction leads to quick healing and potential scarring
Classification of Epithelial Tissues
- Classified by layer number and cell shape
- Layer Number:
- Simple: single layer of cells
- Stratified: multiple layers of cells
- Cell Shape:
- Squamous: flat cells
- Cuboidal: square cells
- Columnar: rectangular cells
- Different arrangements of the same tissue type can perform distinct functions.
Locations and Functions of Epithelial Tissues
- Endothelium: lines blood vessels
- Alveoli: air sacs in the lungs for gas exchange
- Kidney Tubules: responsible for filtration
- Digestive Tract: can include goblet cells for mucus secretion
- Arrangement can include microvilli to enhance surface area
- Keratinized epithelium has dead, keratin-packed outer cells; found in skin.
- Non-keratinized type lines moist areas (mouth, esophagus) with living cells.
- Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: appears stratified but is a single layer; functions in mucus secretion and ciliary movement in the respiratory tract.
Structure of the Basement Membrane
- Thin, acellular structure part of the extracellular matrix (ECM)
- Located between epithelium and connective tissue
- Composed of two layers:
- Basal Lamina: includes lamina lucida and lamina densa
- Reticular Lamina: supports the basement membrane and connects to connective tissue
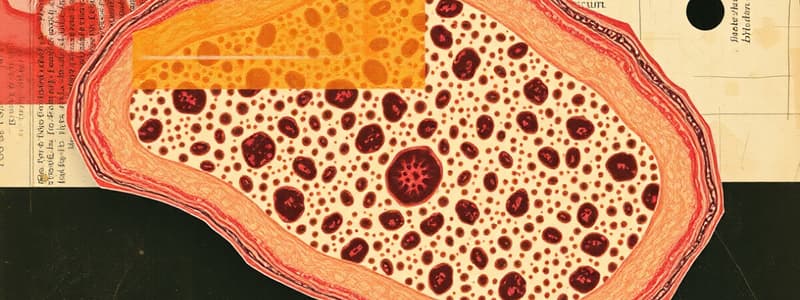
Structural Elements of Connective Tissue
- Connective tissue consists of an extracellular matrix (ECM)
- ECM contains a limited number of cell types (matrix-secreting blast cells and mature cyte cells)
- Matrix consists of long, thin fibers forming networks:
- Collagen Fibers: the strongest fibers providing tensile strength
- Elastic Fibers: allow tissues to return to original shape
- ECM comprised of approximately 10% large organic molecules and 90% interstitial fluid
- Contains glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and proteoglycans for structural support
- Adhesion proteins assist in connecting cells to ECM components
Body Cavities and Serous Membranes
- Serous membranes line body cavities and cover organs, reducing friction between moving organs.
- In the abdominopelvic cavity, serosa is categorized into parietal peritoneum (lining cavity) and visceral peritoneum (covering organs).
Exocrine Glands Structure and Function
- Exocrine glands release substances via ducts to epithelial surfaces.
- Classified on structural basis: unicellular (e.g., goblet cells) and multicellular glands (simple or compound).
- Multicellular glands can be tubular, alveolar, or tubuloalveolar.
- Functionally classified into merocrine (secrete via exocytosis) or holocrine (rupture to release secretion).
Types of Connective Tissue Proper
- Dense Regular: Fibers arranged in parallel bundles, resists tension, found in tendons and ligaments.
- Dense Irregular: Fibers packed in different planes, capable of withstanding tension from multiple directions, located in the dermis and fibrous capsules of joints.
- Elastic: Contains high elastic fiber content, allows recoil after stretching, found in walls of large arteries.
Loose Connective Tissue
- Areolar Tissue: Forms lamina propria in mucous membranes, supports organs and contains blood vessels.
- Adipose Tissue: Provides insulation and protects tissues, stores energy, characterized by a "bubble-like" appearance with little matrix.
- Reticular Tissue: Supports blood cells in lymphoid organs like lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen.
Composition and Types of Skeletal Cartilage
- Cartilage is dense connective tissue, composed of chondrocytes within lacunae embedded in a matrix.
- Lacks blood vessels (avascular) and does not contain nerve fibers.
Types of Cartilage in the Skeletal System
- Elastic Cartilage: Contains elastic fibers, providing flexibility; found in the external ear.
- Fibrocartilage: Tough and shock-absorbing; located between vertebrae.
- Hyaline Cartilage: Most abundant, provides support and padding, present in costal cartilages of ribs, nose, trachea, and joints.
Membranes in the Body
- Mucous Membranes (Mucosa): Line cavities open to the exterior (e.g., respiratory, digestive, urinary tracts). Contain goblet cells that produce mucus for protection and lubrication.
- Serous Membranes: Line closed body cavities and consist of a single layer of mesothelium over connective tissue. Secrete serous fluid for lubrication; examples include pericardium, pleural, and peritoneum.
- Cutaneous Membrane: The skin, thickest membrane, and is the only dry membrane.
- Synovial Membranes: Line the inner surfaces of joints, secrete synovial fluid for lubrication, reducing friction during movement, and cushioning impacts on bones.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.