Podcast
Questions and Answers
In a patient diagnosed with acromegaly exhibiting signs of cardiac dysfunction, which constellation of pathophysiological changes is most likely contributing to the development of heart failure?
In a patient diagnosed with acromegaly exhibiting signs of cardiac dysfunction, which constellation of pathophysiological changes is most likely contributing to the development of heart failure?
- Decreased myocardial contractility secondary to prolonged exposure to elevated growth hormone levels, coupled with reduced ventricular afterload due to systemic vasodilation.
- Myocardial hypertrophy leading to diastolic dysfunction and reduced ventricular filling, compounded by increased peripheral vascular resistance and hypertension. (correct)
- Atrial fibrillation induced by direct growth hormone stimulation of atrial myocytes, leading to impaired atrial emptying and subsequent pulmonary congestion.
- Coronary artery vasospasm induced by elevated growth hormone levels combined with increased blood viscosity, leading to myocardial ischemia and subsequent systolic dysfunction.
A pediatric endocrinologist is evaluating a 7-year-old male presenting with accelerated linear growth, advanced bone age, and elevated IGF-1 levels. Which of the following diagnostic modalities would provide the MOST definitive information regarding the etiology of the patient's condition?
A pediatric endocrinologist is evaluating a 7-year-old male presenting with accelerated linear growth, advanced bone age, and elevated IGF-1 levels. Which of the following diagnostic modalities would provide the MOST definitive information regarding the etiology of the patient's condition?
- Provocative testing with clonidine or arginine stimulation to assess the dynamic secretory capacity of the pituitary gland.
- Serial measurements of growth hormone levels throughout a 24-hour period, correlated with sleep patterns and activity levels.
- Genetic testing for mutations in the _GNAS1_ gene, associated with McCune-Albright syndrome and autonomous endocrine hyperfunction.
- High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland with contrast enhancement to visualize potential structural abnormalities. (correct)
Following a transsphenoidal resection of a pituitary adenoma in a patient with acromegaly, which postoperative finding would necessitate the MOST urgent intervention to prevent life-threatening complications?
Following a transsphenoidal resection of a pituitary adenoma in a patient with acromegaly, which postoperative finding would necessitate the MOST urgent intervention to prevent life-threatening complications?
- Serum sodium level of 120 mEq/L with associated confusion, lethargy, and depressed deep tendon reflexes. (correct)
- A persistent cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak from the nasal cavity, accompanied by a severe headache and photophobia.
- Development of bilateral lower extremity deep vein thrombosis (DVT) with associated shortness of breath and pleuritic chest pain.
- Urine output of 8 liters over a 24-hour period with a corresponding serum osmolality of 260 mOsm/kg and a urine specific gravity of 1.001.
A 28-year-old female diagnosed with hypopituitary dwarfism expresses concern about her ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term. Which intervention, considering the complexities of hormonal deficiencies, offers the MOST comprehensive approach to address her fertility challenges?
A 28-year-old female diagnosed with hypopituitary dwarfism expresses concern about her ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term. Which intervention, considering the complexities of hormonal deficiencies, offers the MOST comprehensive approach to address her fertility challenges?
In a patient with central diabetes insipidus, which of the following therapeutic interventions would MOST directly address the underlying pathophysiology of the disorder?
In a patient with central diabetes insipidus, which of the following therapeutic interventions would MOST directly address the underlying pathophysiology of the disorder?
A patient with Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH) develops severe hyponatremia (Na+ < 115 mEq/L) accompanied by altered mental status and seizures. Which of the following interventions is MOST critical in this situation?
A patient with Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH) develops severe hyponatremia (Na+ < 115 mEq/L) accompanied by altered mental status and seizures. Which of the following interventions is MOST critical in this situation?
A patient undergoing treatment for Graves' disease with propylthiouracil (PTU) develops a fever, sore throat, and oral ulcers. Which of the following laboratory findings would be MOST concerning and warrant immediate discontinuation of the medication?
A patient undergoing treatment for Graves' disease with propylthiouracil (PTU) develops a fever, sore throat, and oral ulcers. Which of the following laboratory findings would be MOST concerning and warrant immediate discontinuation of the medication?
During a thyroidectomy for Graves' disease, the surgical team inadvertently damages the recurrent laryngeal nerve bilaterally. What is the MOST IMMEDIATE and critical intervention required to ensure the patient's airway patency?
During a thyroidectomy for Graves' disease, the surgical team inadvertently damages the recurrent laryngeal nerve bilaterally. What is the MOST IMMEDIATE and critical intervention required to ensure the patient's airway patency?
Post-thyroidectomy, a patient exhibits carpopedal spasms and a positive Chvostek's sign. Ignoring other potential complications, what additional electrolyte abnormality should be suspected and confirmed via lab testing?
Post-thyroidectomy, a patient exhibits carpopedal spasms and a positive Chvostek's sign. Ignoring other potential complications, what additional electrolyte abnormality should be suspected and confirmed via lab testing?
A patient experiencing a thyroid storm exhibits hyperpyrexia (temperature > 104°F), severe tachycardia, and agitation. Beyond standard cooling measures and beta-blockers, which of the following pharmacological interventions is MOST crucial to directly inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis and release?
A patient experiencing a thyroid storm exhibits hyperpyrexia (temperature > 104°F), severe tachycardia, and agitation. Beyond standard cooling measures and beta-blockers, which of the following pharmacological interventions is MOST crucial to directly inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis and release?
In a patient with acromegaly presenting with persistent headaches and visual disturbances, which diagnostic imaging technique would be MOST effective in identifying the underlying cause?
In a patient with acromegaly presenting with persistent headaches and visual disturbances, which diagnostic imaging technique would be MOST effective in identifying the underlying cause?
A patient with acromegaly is scheduled for transsphenoidal surgery. What preoperative nursing intervention is MOST important to minimize the risk of post-operative complications?
A patient with acromegaly is scheduled for transsphenoidal surgery. What preoperative nursing intervention is MOST important to minimize the risk of post-operative complications?
A 35-year-old female with acromegaly is considering pregnancy. Which of the following hormonal considerations is MOST critical to address before conception?
A 35-year-old female with acromegaly is considering pregnancy. Which of the following hormonal considerations is MOST critical to address before conception?
Which of the following assessment findings would MOST strongly suggest the development of diabetes insipidus following transsphenoidal surgery for a pituitary adenoma?
Which of the following assessment findings would MOST strongly suggest the development of diabetes insipidus following transsphenoidal surgery for a pituitary adenoma?
A patient with central diabetes insipidus is prescribed desmopressin (DDAVP). Which instruction is MOST critical for the nurse to emphasize regarding potential adverse effects?
A patient with central diabetes insipidus is prescribed desmopressin (DDAVP). Which instruction is MOST critical for the nurse to emphasize regarding potential adverse effects?
In a patient with SIADH, which of the following physiological mechanisms is MOST directly responsible for the development of hyponatremia?
In a patient with SIADH, which of the following physiological mechanisms is MOST directly responsible for the development of hyponatremia?
A patient with SIADH is being treated with hypertonic saline. Which assessment finding would indicate that the treatment is effective and should be potentially de-escalated?
A patient with SIADH is being treated with hypertonic saline. Which assessment finding would indicate that the treatment is effective and should be potentially de-escalated?
A patient with Graves' disease is being treated with methimazole. Which of the following signs and symptoms should prompt the nurse to immediately assess for agranulocytosis?
A patient with Graves' disease is being treated with methimazole. Which of the following signs and symptoms should prompt the nurse to immediately assess for agranulocytosis?
Following a total thyroidectomy, a patient reports tingling around the mouth and fingertips. Which electrolyte imbalance is MOST likely responsible for these symptoms?
Following a total thyroidectomy, a patient reports tingling around the mouth and fingertips. Which electrolyte imbalance is MOST likely responsible for these symptoms?
During the management of a thyroid storm, what is the PRIMARY rationale for administering potassium iodide solution?
During the management of a thyroid storm, what is the PRIMARY rationale for administering potassium iodide solution?
In the management of giantism, what is the MOST significant long-term complication to monitor, irrespective of the primary treatment modality?
In the management of giantism, what is the MOST significant long-term complication to monitor, irrespective of the primary treatment modality?
For a child diagnosed with hypopituitary dwarfism, which assessment parameter requires the MOST urgent attention during routine follow-up visits?
For a child diagnosed with hypopituitary dwarfism, which assessment parameter requires the MOST urgent attention during routine follow-up visits?
What is the MOST critical instruction to provide to a patient newly diagnosed with diabetes insipidus regarding fluid management at home?
What is the MOST critical instruction to provide to a patient newly diagnosed with diabetes insipidus regarding fluid management at home?
Which intervention is MOST appropriate for preventing complications associated with chronic SIADH?
Which intervention is MOST appropriate for preventing complications associated with chronic SIADH?
In a patient experiencing a thyroid storm, which intervention takes PRIORITY over all others in the initial management?
In a patient experiencing a thyroid storm, which intervention takes PRIORITY over all others in the initial management?
When providing dietary education to a patient with hyperthyroidism, what is the MOST important consideration regarding caloric intake?
When providing dietary education to a patient with hyperthyroidism, what is the MOST important consideration regarding caloric intake?
A patient post-thyroidectomy exhibits signs of hypocalcemia. What is the PRIMARY rationale for having calcium gluconate readily available?
A patient post-thyroidectomy exhibits signs of hypocalcemia. What is the PRIMARY rationale for having calcium gluconate readily available?
For a patient with acromegaly, which sleep-related problem is MOST likely to increase their risk for cardiovascular complications?
For a patient with acromegaly, which sleep-related problem is MOST likely to increase their risk for cardiovascular complications?
A patient with known diabetes insipidus is scheduled for a diagnostic water deprivation test. Which finding would necessitate IMMEDIATE termination of the test?
A patient with known diabetes insipidus is scheduled for a diagnostic water deprivation test. Which finding would necessitate IMMEDIATE termination of the test?
What is the BEST way to assist a child with dwarfism with adaptation during adolescence?
What is the BEST way to assist a child with dwarfism with adaptation during adolescence?
In caring for a patient with SIADH, what is the MOST accurate method to assess the effectiveness of fluid restriction in managing the condition?
In caring for a patient with SIADH, what is the MOST accurate method to assess the effectiveness of fluid restriction in managing the condition?
A patient with Graves' disease who is undergoing radioactive iodine therapy requires which of the following precautions in the immediate post-treatment period?
A patient with Graves' disease who is undergoing radioactive iodine therapy requires which of the following precautions in the immediate post-treatment period?
Following a thyroidectomy, a patient reports increasing anxiety, palpitations, and a subjective feeling of heat intolerance despite normal thyroid hormone levels. Which complication should the nurse suspect?
Following a thyroidectomy, a patient reports increasing anxiety, palpitations, and a subjective feeling of heat intolerance despite normal thyroid hormone levels. Which complication should the nurse suspect?
In a patient with acromegaly, which comorbidity is MOST likely to have the greatest impact on long-term mortality?
In a patient with acromegaly, which comorbidity is MOST likely to have the greatest impact on long-term mortality?
Considering ethical implications, what is the MOST appropriate approach when discussing growth hormone therapy with the parents of a child with hypopituitary dwarfism who express unrealistic expectations about the potential height gain?
Considering ethical implications, what is the MOST appropriate approach when discussing growth hormone therapy with the parents of a child with hypopituitary dwarfism who express unrealistic expectations about the potential height gain?
A patient with acromegaly exhibits persistent peripheral neuropathy, displaying decreased nerve conduction velocity and sensory loss in a stocking-glove distribution. Which of the following underlying mechanisms MOST directly contributes to this neurological complication?
A patient with acromegaly exhibits persistent peripheral neuropathy, displaying decreased nerve conduction velocity and sensory loss in a stocking-glove distribution. Which of the following underlying mechanisms MOST directly contributes to this neurological complication?
A patient diagnosed with giantism presents with progressive bitemporal hemianopsia and panhypopituitarism. Which of the following surgical approaches offers the MOST comprehensive and direct access to address the likely underlying pathology while minimizing iatrogenic damage?
A patient diagnosed with giantism presents with progressive bitemporal hemianopsia and panhypopituitarism. Which of the following surgical approaches offers the MOST comprehensive and direct access to address the likely underlying pathology while minimizing iatrogenic damage?
In the context of managing a pediatric patient with hypopituitary dwarfism undergoing recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) therapy, which of the following strategies is MOST critical for optimizing long-term skeletal development and minimizing the risk of premature epiphyseal closure?
In the context of managing a pediatric patient with hypopituitary dwarfism undergoing recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) therapy, which of the following strategies is MOST critical for optimizing long-term skeletal development and minimizing the risk of premature epiphyseal closure?
A patient with long-standing, untreated diabetes insipidus develops nephrogenic insensitivity to vasopressin, further exacerbating polyuria and hypernatremia. Which of the following therapeutic interventions is MOST likely to improve urine concentrating ability in this patient?
A patient with long-standing, untreated diabetes insipidus develops nephrogenic insensitivity to vasopressin, further exacerbating polyuria and hypernatremia. Which of the following therapeutic interventions is MOST likely to improve urine concentrating ability in this patient?
A patient with SIADH secondary to small cell lung cancer develops profound hyponatremia (serum sodium 110 mEq/L) and exhibits signs of central nervous system herniation. Which of the following represents the MOST appropriate and evidence-based approach to rapidly correct the hyponatremia while mitigating the risk of osmotic demyelination syndrome?
A patient with SIADH secondary to small cell lung cancer develops profound hyponatremia (serum sodium 110 mEq/L) and exhibits signs of central nervous system herniation. Which of the following represents the MOST appropriate and evidence-based approach to rapidly correct the hyponatremia while mitigating the risk of osmotic demyelination syndrome?
A patient with Graves' disease develops thyroid storm following radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy. In addition to standard supportive measures, which of the following pharmacological interventions is MOST critical for rapidly inhibiting peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 and reducing the acute hyperadrenergic symptoms?
A patient with Graves' disease develops thyroid storm following radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy. In addition to standard supportive measures, which of the following pharmacological interventions is MOST critical for rapidly inhibiting peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 and reducing the acute hyperadrenergic symptoms?
During a total thyroidectomy, intraoperative neuromonitoring indicates injury to the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (EBSLN). What is the MOST likely clinical consequence the patient will experience postoperatively, affecting vocal function?
During a total thyroidectomy, intraoperative neuromonitoring indicates injury to the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (EBSLN). What is the MOST likely clinical consequence the patient will experience postoperatively, affecting vocal function?
A patient post-thyroidectomy develops severe hypocalcemia refractory to intravenous calcium gluconate administration. Which of the following underlying conditions should be MOST strongly suspected as contributing to this resistance to calcium replacement therapy?
A patient post-thyroidectomy develops severe hypocalcemia refractory to intravenous calcium gluconate administration. Which of the following underlying conditions should be MOST strongly suspected as contributing to this resistance to calcium replacement therapy?
A patient experiencing thyroid storm develops atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. In addition to standard antiarrhythmic therapy, which of the following interventions is MOST crucial for addressing the underlying cause of the arrhythmia and preventing thromboembolic complications?
A patient experiencing thyroid storm develops atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. In addition to standard antiarrhythmic therapy, which of the following interventions is MOST crucial for addressing the underlying cause of the arrhythmia and preventing thromboembolic complications?
In the long-term management of giantism, which of the following surveillance strategies is MOST critical for detecting and mitigating the development of acromegaly-related cardiomyopathy and its associated complications?
In the long-term management of giantism, which of the following surveillance strategies is MOST critical for detecting and mitigating the development of acromegaly-related cardiomyopathy and its associated complications?
For a child with hypopituitary dwarfism being treated with growth hormone, which of the following assessment parameters would warrant IMMEDIATE modification of the growth hormone dosage to prevent potential complications?
For a child with hypopituitary dwarfism being treated with growth hormone, which of the following assessment parameters would warrant IMMEDIATE modification of the growth hormone dosage to prevent potential complications?
A patient with diabetes insipidus is prescribed desmopressin (DDAVP) intranasally. Which of the following instructions is MOST critical to emphasize to the patient to minimize the risk of developing hyponatremia and water intoxication?
A patient with diabetes insipidus is prescribed desmopressin (DDAVP) intranasally. Which of the following instructions is MOST critical to emphasize to the patient to minimize the risk of developing hyponatremia and water intoxication?
Which of the following interventions is MOST likely to provide SUSTAINED long-term benefit in managing chronic SIADH secondary to ectopic ADH production from a non-resectable malignancy?
Which of the following interventions is MOST likely to provide SUSTAINED long-term benefit in managing chronic SIADH secondary to ectopic ADH production from a non-resectable malignancy?
In the initial management of a patient experiencing a thyroid storm, which of the following interventions should be prioritized to DIRECTLY address the excessive thyroid hormone production and reduce its impact on end-organs?
In the initial management of a patient experiencing a thyroid storm, which of the following interventions should be prioritized to DIRECTLY address the excessive thyroid hormone production and reduce its impact on end-organs?
When providing nutritional counseling to a patient with hyperthyroidism, what is the MOST important consideration regarding micronutrient intake to prevent complications associated with increased metabolic demand?
When providing nutritional counseling to a patient with hyperthyroidism, what is the MOST important consideration regarding micronutrient intake to prevent complications associated with increased metabolic demand?
Post-thyroidectomy, a patient exhibits signs of hypocalcemia, including circumoral paresthesia and muscle cramping. What is the PRIMARY rationale for administering intravenous calcium gluconate SLOWLY, with continuous cardiac monitoring?
Post-thyroidectomy, a patient exhibits signs of hypocalcemia, including circumoral paresthesia and muscle cramping. What is the PRIMARY rationale for administering intravenous calcium gluconate SLOWLY, with continuous cardiac monitoring?
For a patient with acromegaly, which sleep-related disturbance is MOST likely to contribute to the development of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance, independent of other known risk factors?
For a patient with acromegaly, which sleep-related disturbance is MOST likely to contribute to the development of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance, independent of other known risk factors?
A patient with known central diabetes insipidus is undergoing a diagnostic water deprivation test. Which of the following findings would necessitate IMMEDIATE termination of the test due to potential complications?
A patient with known central diabetes insipidus is undergoing a diagnostic water deprivation test. Which of the following findings would necessitate IMMEDIATE termination of the test due to potential complications?
What psychosocial intervention strategy would be MOST effective in assisting a child with dwarfism in developing a positive self-image and adapting to social challenges during adolescence?
What psychosocial intervention strategy would be MOST effective in assisting a child with dwarfism in developing a positive self-image and adapting to social challenges during adolescence?
In the management of a patient with SIADH, which diagnostic or monitoring technique provides the MOST ACCURATE assessment of the effectiveness of fluid restriction in alleviating intracellular cerebral edema?
In the management of a patient with SIADH, which diagnostic or monitoring technique provides the MOST ACCURATE assessment of the effectiveness of fluid restriction in alleviating intracellular cerebral edema?
A patient with Graves' disease undergoing radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy requires which of the following specific precautions to minimize radiation exposure to household contacts, particularly pregnant women and young children?
A patient with Graves' disease undergoing radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy requires which of the following specific precautions to minimize radiation exposure to household contacts, particularly pregnant women and young children?
Following a thyroidectomy, a patient reports increasing anxiety, palpitations, and heat intolerance despite normal thyroid hormone levels on recent laboratory tests. Which of the following complications should the nurse suspect, and what is the MOST appropriate initial intervention?
Following a thyroidectomy, a patient reports increasing anxiety, palpitations, and heat intolerance despite normal thyroid hormone levels on recent laboratory tests. Which of the following complications should the nurse suspect, and what is the MOST appropriate initial intervention?
In a patient with acromegaly, which of the following comorbidities is MOST likely to have the greatest impact on long-term mortality due to its insidious progression and frequent underdiagnosis?
In a patient with acromegaly, which of the following comorbidities is MOST likely to have the greatest impact on long-term mortality due to its insidious progression and frequent underdiagnosis?
When discussing growth hormone therapy with the parents of a child with hypopituitary dwarfism who express unrealistic expectations about the potential height gain, what is the MOST ethically appropriate approach for the healthcare provider?
When discussing growth hormone therapy with the parents of a child with hypopituitary dwarfism who express unrealistic expectations about the potential height gain, what is the MOST ethically appropriate approach for the healthcare provider?
A 40-year-old male with a history of acromegaly presents with progressive proximal muscle weakness, particularly in the lower extremities, and elevated creatine kinase levels. Electromyography (EMG) reveals myopathic changes. Which of the following mechanisms is MOST likely contributing to this patient's myopathy?
A 40-year-old male with a history of acromegaly presents with progressive proximal muscle weakness, particularly in the lower extremities, and elevated creatine kinase levels. Electromyography (EMG) reveals myopathic changes. Which of the following mechanisms is MOST likely contributing to this patient's myopathy?
A 10-year-old child with giantism is found to have impaired glucose tolerance but normal fasting glucose levels. Which of the following diagnostic tests would be MOST sensitive in detecting early pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in this patient?
A 10-year-old child with giantism is found to have impaired glucose tolerance but normal fasting glucose levels. Which of the following diagnostic tests would be MOST sensitive in detecting early pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in this patient?
A 6-year-old child with hypopituitary dwarfism is being evaluated for growth hormone therapy. Which of the following pre-treatment assessments is MOST critical to rule out contraindications and ensure the safety of growth hormone administration?
A 6-year-old child with hypopituitary dwarfism is being evaluated for growth hormone therapy. Which of the following pre-treatment assessments is MOST critical to rule out contraindications and ensure the safety of growth hormone administration?
A patient with diabetes insipidus develops severe dehydration and hypernatremia (serum sodium 165 mEq/L). Which of the following intravenous fluid regimens is MOST appropriate for initial management to gradually correct the hypernatremia while avoiding cerebral edema?
A patient with diabetes insipidus develops severe dehydration and hypernatremia (serum sodium 165 mEq/L). Which of the following intravenous fluid regimens is MOST appropriate for initial management to gradually correct the hypernatremia while avoiding cerebral edema?
A patient with SIADH secondary to small cell lung cancer develops symptomatic hyponatremia (serum sodium 120 mEq/L) despite fluid restriction. Which of the following pharmacological interventions is MOST appropriate for managing this patient's hyponatremia while minimizing the risk of rapid overcorrection?
A patient with SIADH secondary to small cell lung cancer develops symptomatic hyponatremia (serum sodium 120 mEq/L) despite fluid restriction. Which of the following pharmacological interventions is MOST appropriate for managing this patient's hyponatremia while minimizing the risk of rapid overcorrection?
A patient with Graves' disease is being treated with methimazole and develops bilateral lower extremity edema, proteinuria, and elevated blood pressure. Which of the following complications should be MOST strongly suspected?
A patient with Graves' disease is being treated with methimazole and develops bilateral lower extremity edema, proteinuria, and elevated blood pressure. Which of the following complications should be MOST strongly suspected?
During a thyroidectomy, inadvertent injury to all parathyroid glands occurs. What is the MOST IMMEDIATE and effective strategy to prevent symptomatic hypocalcemia in the immediate postoperative period?
During a thyroidectomy, inadvertent injury to all parathyroid glands occurs. What is the MOST IMMEDIATE and effective strategy to prevent symptomatic hypocalcemia in the immediate postoperative period?
A patient in thyroid storm develops hyperthermia (temperature >105°F) unresponsive to acetaminophen and cooling blankets. Which intervention is MOST crucial to reduce the patient's temperature and prevent end-organ damage?
A patient in thyroid storm develops hyperthermia (temperature >105°F) unresponsive to acetaminophen and cooling blankets. Which intervention is MOST crucial to reduce the patient's temperature and prevent end-organ damage?
In a patient with acromegaly who has undergone transsphenoidal surgery, which finding is MOST suggestive of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage requiring immediate intervention?
In a patient with acromegaly who has undergone transsphenoidal surgery, which finding is MOST suggestive of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage requiring immediate intervention?
In a child with hypopituitary dwarfism, which of the following complications is MOST likely to directly impair cardiovascular function and reduce exercise tolerance?
In a child with hypopituitary dwarfism, which of the following complications is MOST likely to directly impair cardiovascular function and reduce exercise tolerance?
Flashcards
Acromegaly
Acromegaly
Overproduction of growth hormone after puberty, when growth plates are sealed, leading to irreversible changes.
Giantism
Giantism
Oversecretion of growth hormone before the closure of growth plates, leading to overgrowth of long bones and increased height.
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Insipidus
A metabolic disorder of the posterior pituitary with ADH deficiency causing excessive urination and thirst.
SIADH
SIADH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid crisis/storm
Thyroid crisis/storm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Giantism
Giantism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dwarfism
Dwarfism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Insipidus
Signup and view all the flashcards
SIADH
SIADH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromegaly: Craniofacial Changes
Acromegaly: Craniofacial Changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromegaly: Fingertip Changes
Acromegaly: Fingertip Changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromegaly Diagnosis
Acromegaly Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromegaly Treatments
Acromegaly Treatments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromegaly Nursing Interventions
Acromegaly Nursing Interventions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Giantism: Weakness
Giantism: Weakness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dwarfism Diagnosis
Dwarfism Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dwarfism: Reproduction
Dwarfism: Reproduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dwarfism: Nursing Care
Dwarfism: Nursing Care
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Insipidus: Complications
Diabetes Insipidus: Complications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Insipidus: Nursing
Diabetes Insipidus: Nursing
Signup and view all the flashcards
SIADH Treatments
SIADH Treatments
Signup and view all the flashcards
SIADH Nursing Interventions
SIADH Nursing Interventions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperthyroidism: Swallowing Problems
Hyperthyroidism: Swallowing Problems
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperthyroidism: Temperature Regulation
Hyperthyroidism: Temperature Regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperthyroidism Treatments
Hyperthyroidism Treatments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Thyroidectomy Care
Post-Thyroidectomy Care
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypocalcemia Signs
Hypocalcemia Signs
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is acromegaly?
What is acromegaly?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes dwarfism?
What causes dwarfism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How to monitor kidney output in DI?
How to monitor kidney output in DI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does water retention occur in SIADH?
Where does water retention occur in SIADH?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decomycin or Lithium Carbonate action?
Decomycin or Lithium Carbonate action?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does radioactive iodine work?
How does radioactive iodine work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subtotal thyroidectomies downsides?
Subtotal thyroidectomies downsides?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chvostek sign indicates?
Chvostek sign indicates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Acromegaly
- Overproduction of growth hormone occurs after puberty, when growth plates are sealed.
- Changes from acromegaly are irreversible.
- Possible causes are idiopathic hyperplasia or tumor growth.
- Signs and symptoms develop gradually, often starting in the third or fourth decade of life.
- Diagnosis can take 7 to 9 years from the onset of symptoms.
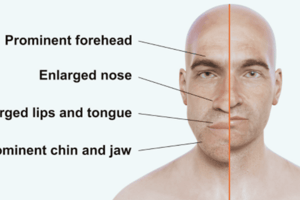
- Enlargement of the cranium and lower jaw are characteristic signs.
- Other signs include teeth separation, bulging forehead, bulbous nose, thick lips, and coarse facial features.
- Hands and feet enlarge.
- The heart, liver, and spleen also enlarge, which can impair their functioning.
- Muscle weakness and painful joint hypertrophy can occur.
- Males may experience impotence, while females may develop a deepened voice, increased facial hair, and amenorrhea.
- A tumor can put pressure on the optic nerve, potentially leading to partial or complete blindness.
- Visual changes and severe headaches may be early indicators.
- Fingertips may become tufted, showing a clubbed appearance.
- Heart failure can develop due to heart enlargement.
- Diagnosis involves assessing history, clinical manifestations, CT scan, MRI, cranial radiographic evaluation, and visual exam.
- The definitive lab test is an oral glucose challenge, where growth hormone levels do not fall as expected.
- Treatments include dopamine agonists to suppress growth hormone.
- Surgical removal of the pituitary gland or tumor is a treatment option.
- Post-surgery, there's an increased risk of diabetes insipidus.
- Proton beam therapy (gamma knife radio surgery) is a less destructive radiation option.
- Complications from organ enlargement include hypertension, heart failure, and cardiomyopathy.
- Nursing interventions focus on supporting ADLs, providing a soft and easy to chew diet, and encouraging fluids.
- Pain relief is managed with non-opioid analgesics.
- Address psychological distress, assess fluid status, and monitor for heart failure.
- Encourage a healthy weight, exercise, and range of motion to maintain joint flexibility.
Giantism
- Oversecretion of growth hormone occurs before the closure of growth plates.
- Results from a defect in the hypothalamus, causing the anterior pituitary to release excess growth hormone.
- Overgrowth of long bones, muscles, and viscera organs occurs.
- Body proportions remain normal, but individuals become very tall.
- Weakness is common due to the stretching of bones, muscles, and organs.
- Diagnosis is through a growth hormone suppression test, revealing high baseline levels.
- Treatment includes surgical removal or irradiation of the anterior pituitary gland.
- Hormone replacement is necessary based on post-surgery needs.
- Observation for complications includes hypertension, heart failure, osteoporosis, thickened bones, and delayed sexual development.
- Self-esteem issues and a shorter lifespan are common.
Dwarfism
- Hypopituitary dwarfism is caused by genetic mutations or idiopathic factors.
- Individuals have a shorter stature than their peers.
- Underdeveloped jaws can lead to dental problems.
- Sexual development is normal but delayed.
- Individuals can produce normal-sized offspring.
- Normal intelligence is maintained.
- Treatment involves surgical removal if there's a tumor.
- Growth hormone replacement is administered via injection.
- Nurses monitor children's growth, reporting heights below the third percentile to providers for further evaluation.
- Self-esteem issues and potential musculoskeletal and cardiovascular complications may occur.
- Diagnosis involves radiographic evaluation of the skull and skeleton to assess bone age compared to chronological age.
- MRI and CT scans check for pituitary tumors.
- Decreased growth hormone levels after fasting confirm the diagnosis.
- Genetic counseling is recommended for family planning.
- Report headaches, visual disturbances, and behavior changes.
- Encourage age-appropriate clothing.
- Emphasize abilities and strengths, and address psychosocial needs.
- Musculoskeletal and cardiovascular issues may arise.
Diabetes Insipidus
- A metabolic disorder of the posterior pituitary with ADH deficiency.
- May be transient or permanent.
- Can be primary or secondary to head injuries, intracranial tumors, or infections.
- Characterized by marked polyuria (excessive urination) and intense polydipsia (thirst).
- ADH deficiency leads to excessive urine output.
- Urine is very dilute with a low specific gravity.
- Urine output can range from 5 to 20 liters in 24 hours.
- Minimum output of 200 mL/hour for >2 hours.
- Intense craving for ice water.
- Dehydration may still occur despite high fluid intake.
- Hypernatremia (elevated sodium levels) occurs due to dehydration.
- Hypothalamic shock can occur, marked by low blood pressure, elevated heart rate, and increased respirations with continued high urine output.
- Changes in level of consciousness (LOC) are related to electrolyte imbalances, particularly hypernatremia.
- Tachycardia and hypotension may develop.
- Nursing interventions include frequent checks of skin turgor.
- Assess weakness, tiredness, and lethargy, providing a bedside commode if needed for severe cases.
- Monitor urine color and specific gravity to track kidney output.
- High risk of constipation.
- Daily weights (before breakfast), noting nocturia occurrences, are important.
- Monitor dehydration through assessment of mucous membranes and vital signs.
- Avoid alcohol and caffeine due to their diuretic effects.
- Diagnosis: specific gravity below 1.003.
- Serum osmolality is greater than 300.
- Water deprivation test includes fluid restriction for 12 hours with frequent monitoring of urine specific gravity, serum osmolality, and orthostatic vital signs.
- Weight is measured before and after the test to assess fluid loss.
- CT scan of the sella turcica and urinary ADH measurements aid diagnosis.
Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)
- Characterized by excessive ADH release, leading to water retention by the kidneys and decreased urine output.
- Expands fluid volume in the vascular space, not the interstitial space.
- Leads to dilution hyponatremia and fluid overload without edema.
- Can cause water intoxication and cerebral edema.
- Early symptoms when sodium is less than 125 mEq/L include nausea, vomiting, tremors, cramping, anorexia, headaches, confusion, and irritability.
- Worsening condition may lead to seizures, stupor, coma, and pathologic reflexes.
- Fluid intake exceeds urine output.
- Serum becomes hypotonic, leading to brain cell swelling.
- Results in lethargy, personality changes, seizures, coma, and death.
- Sodium levels are less than 135.
- BUN and creatinine are usually normal.
- Urine specific gravity is greater than 1.032 and concentrated.
- Treatments include fluid restrictions, hypertonic saline IV (slow infusion), and diuretics.
- Demeclocycline or lithium carbonate inhibits ADH action.
- Surgical removal is indicated for tumors or malignant neoplasms.
- Nursing interventions: neuro exams.
- Hydration assessments and lung sound auscultation are important.
- Fluid restrictions may equal output.
- Monitor labs, daily weight, and intake/output.
- Avoid salty foods to reduce thirst; provide frequent mouth care.
Hyperthyroidism (Graves Disease)
- Also known as Graves' Disease, exophthalmic goiter, or thyrotoxicosis.
- Increased thyroid gland activity leads to increased T3 and T4 production.
- Thyroid edema of the anterior neck and bulging eyes from exophthalmos.
- Bulging eyes may lead to incomplete eye closure, corneal dryness/ulcers, and vision loss.
- Onset typically occurs between ages 20-50 in women.
- Trouble swallowing (dysphagia) or hoarseness can occur.
- Elevated metabolism, jitteriness, and nervousness are common.
- Weight loss despite good appetite.
- Insomnia and emotional lability; patients may overreact.
- Rapid pulse, elevated blood pressure, and a bruit over the thyroid gland.
- Heart palpitation and SOB.
- Difficulty with mental focus and concentration, and memory loss.
- Skin becomes warm and flushed.
- Elevated temperatures and profuse diaphoresis (sweating).
- Tremors of the hands, clumsiness/hyperactivity.
- Decreased TSH with high T3 and T4 levels.
- Treatment: radioactive iodine/drugs (PTU or methimazole/Tapazole).
- Radioactive iodine targets and kills thyroid tissue; results take 6-8 weeks.
- Could develop hypothyroidism.
- PTU or methimazole/Tapazole can suppress/block hormone function.
- Subtotal thyroidectomies are less popular due to increased hemorrhage and hypoparathyroidism risk.
- Diet should be high-calorie, high-protein/mineral, with increased carbs and snacks.
- Treatment sequence: PTU or methimazole/Tapazole, then radioactive iodine/tumorectomy.
- No radiation safety precautions needed.
- After subtotal thyroidectomy: patient needs teaching on head/neck support and to avoid side-to-side movements to not ruin sutures.
- Maintain neutral anatomic position.
- Maintain semi-Fowler's position.
- Encourage deep breathing (avoid constant coughing).
- Rest voice for up to 48 hrs; nurse voice checks every 2-4 hrs.
- Keep suction/trach tray on hand for respiratory distress.
- Maintain humidifier and check vitals, especially respirations.
- Check for hemorrhage, looking behind the neck.
- Hypocalcemia may develop and cause muscle spasms.
- Check for Chvostek's sign (tap face) or Trousseau's sign (pump cuff on arm to systolic +3 for 3 mins).
- Lethal arrhythmia can occur.
- Have calcium gluconate IV ready (tape on pole).
- Thyroid crisis/storm happens when manipulating thyroid gland post-surgery.
- Severe nausea/vomiting/tachycardia/hypotension/hyperthermia (up to 106)/restlessness/ cardiac dysrhythmias/delirium.
- Treatment is IV fluids/sodium iodide/corticosteroids/antipyretics/PTU and O2 PRN/Tapazole.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.