Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary consideration when a mother is about to give birth and delivery is imminent?
What is the primary consideration when a mother is about to give birth and delivery is imminent?
- To provide emotional support and let the mother assume a comfortable position (correct)
- To suction the baby's mouth and nose during delivery
- To restrain or delay delivery to prepare the OB pack
- To immediately clamp and cut the umbilical cord
What is the recommended position for the mother during delivery?
What is the recommended position for the mother during delivery?
- Prone position with a wedge under the abdomen
- Supine position with legs straight
- Semi-sitting position with head up 30° and knees bent (correct)
- Left lateral decubitus position with a pillow under the abdomen
What should be done if the amniotic sac is still intact during delivery?
What should be done if the amniotic sac is still intact during delivery?
- Leave the membrane intact to prevent infection
- Gently twist or tear the membrane (correct)
- Gently tear the membrane with forceps
- Quickly clamp and cut the umbilical cord
What should be done if meconium is present during delivery?
What should be done if meconium is present during delivery?
What should be done to prevent vagal stimulation and fetal bradycardia during delivery?
What should be done to prevent vagal stimulation and fetal bradycardia during delivery?
What should be done if a nuchal cord is present during delivery?
What should be done if a nuchal cord is present during delivery?
What should be done to deliver the upper shoulder during delivery?
What should be done to deliver the upper shoulder during delivery?
What should be done if shoulder dystocia occurs during delivery?
What should be done if shoulder dystocia occurs during delivery?
What is the recommended fluid management strategy for a postpartum hemorrhage patient with blood loss exceeding 500 mL?
What is the recommended fluid management strategy for a postpartum hemorrhage patient with blood loss exceeding 500 mL?
What should you do during a breech birth if the baby is delivered to the shoulders?
What should you do during a breech birth if the baby is delivered to the shoulders?
Why is it important to anticipate the need for fluid challenges in a breech birth?
Why is it important to anticipate the need for fluid challenges in a breech birth?
What should you do if the umbilical cord is accessible during a breech birth?
What should you do if the umbilical cord is accessible during a breech birth?
When should you transport a postpartum hemorrhage patient with ongoing blood loss and a systolic blood pressure below 90?
When should you transport a postpartum hemorrhage patient with ongoing blood loss and a systolic blood pressure below 90?
What is the recommended method for supporting the baby's body during a breech birth after the legs are delivered?
What is the recommended method for supporting the baby's body during a breech birth after the legs are delivered?
Why is breastfeeding contraindicated during transport of a postpartum hemorrhage patient?
Why is breastfeeding contraindicated during transport of a postpartum hemorrhage patient?
What is a critical time for the infant during a breech birth?
What is a critical time for the infant during a breech birth?
What is the normal range of SpO2 expected in a newborn infant after 5 to 10 minutes of birth?
What is the normal range of SpO2 expected in a newborn infant after 5 to 10 minutes of birth?
What is the first step in resuscitation of a newborn infant?
What is the first step in resuscitation of a newborn infant?
What is the target SpO2 at 2 minutes after birth?
What is the target SpO2 at 2 minutes after birth?
What is the purpose of the first breath in neonatal resuscitation?
What is the purpose of the first breath in neonatal resuscitation?
What is the recommended peak inflation pressure when using a BVM during neonatal resuscitation?
What is the recommended peak inflation pressure when using a BVM during neonatal resuscitation?
What is the indication for positioning a newborn infant supine with a 1" pad under back/shoulders?
What is the indication for positioning a newborn infant supine with a 1" pad under back/shoulders?
What is the recommended rate of PPV/neonatal BVM during neonatal resuscitation?
What is the recommended rate of PPV/neonatal BVM during neonatal resuscitation?
What is the recommended action if a newborn infant is dusky, RR > 40, and has adequate breathing effort?
What is the recommended action if a newborn infant is dusky, RR > 40, and has adequate breathing effort?
What is the maximum dosage of magnesium that can be administered to a patient experiencing a seizure during pregnancy?
What is the maximum dosage of magnesium that can be administered to a patient experiencing a seizure during pregnancy?
Which intervention is NOT advisable for a patient in eclamptic seizure status?
Which intervention is NOT advisable for a patient in eclamptic seizure status?
If a patient has received magnesium for preeclampsia, what is the additional magnesium dosage if a seizure occurs?
If a patient has received magnesium for preeclampsia, what is the additional magnesium dosage if a seizure occurs?
Which of the following should always be done when a patient is over 20 weeks gestation?
Which of the following should always be done when a patient is over 20 weeks gestation?
In the case of seizures in a pregnant patient, what is the preferred route for administering Midazolam if IV/IO is not feasible?
In the case of seizures in a pregnant patient, what is the preferred route for administering Midazolam if IV/IO is not feasible?
What is recommended to relieve discomfort during IV magnesium administration?
What is recommended to relieve discomfort during IV magnesium administration?
What condition does generalized tonic-clonic seizure during pregnancy without any known cause represent?
What condition does generalized tonic-clonic seizure during pregnancy without any known cause represent?
What is the maximum allowable total dose for Midazolam in a pregnant patient after the initial dosing?
What is the maximum allowable total dose for Midazolam in a pregnant patient after the initial dosing?
According to the provided text, when is it considered reasonable to limit or not initiate neonatal resuscitation?
According to the provided text, when is it considered reasonable to limit or not initiate neonatal resuscitation?
Which of the following factors are mentioned as influencing the survivability of peri-viable births?
Which of the following factors are mentioned as influencing the survivability of peri-viable births?
Based on the text, what is the recommended action when a newborn exhibits cyanosis with spontaneous ventilations, a slow heart beat, and spontaneous movements?
Based on the text, what is the recommended action when a newborn exhibits cyanosis with spontaneous ventilations, a slow heart beat, and spontaneous movements?
Which of the following is NOT mentioned as a general caveat regarding newborn resuscitation?
Which of the following is NOT mentioned as a general caveat regarding newborn resuscitation?
What is the primary purpose of the text's recommendation to apply saline-moistened sterile towels or dressings around the uterus?
What is the primary purpose of the text's recommendation to apply saline-moistened sterile towels or dressings around the uterus?
What is the significance of the Apgar score being 6 or less?
What is the significance of the Apgar score being 6 or less?
Which of the following is a characteristic of central cyanosis?
Which of the following is a characteristic of central cyanosis?
What is the implication of the statement "Majority of newborns require no resuscitation beyond drying, warming, mild stimulation, and airway suctioning"?
What is the implication of the statement "Majority of newborns require no resuscitation beyond drying, warming, mild stimulation, and airway suctioning"?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
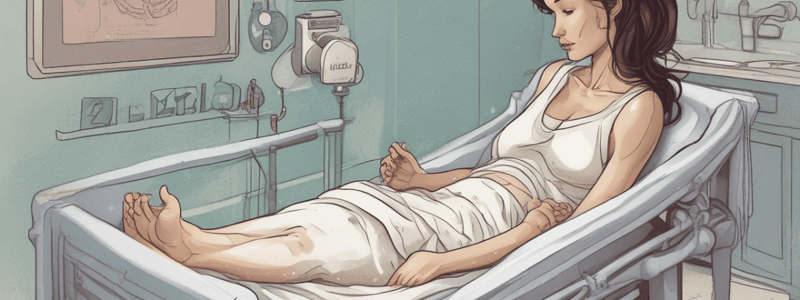
Emergency Childbirth
- Assume the most comfortable position and transport to a hospital with OB services if delivery is imminent.
- Do not attempt to restrain or delay delivery unless there is a prolapsed cord present.
Delivery Procedure
- Allow the head to deliver passively and control the rate of descent by placing the palm of one hand gently over the occiput.
- Protect the perineum with pressure from the other hand.
- If the amniotic sac is still intact, gently twist or tear the membrane.
- After the head is delivered:
- If there is no meconium, do not suction during delivery to avoid vagal stimulation and fetal bradycardia.
- If meconium is present, gently suction the mouth and then the nose with a bulb syringe.
- Anticipate the need for resuscitation of a non-vigorous infant after delivery.
- Feel around the neck for the umbilical cord (nuchal cord) and if present, attempt to gently lift it over the baby's head.
- If unsuccessful, double clamp and cut the cord between the clamps.
Shoulder Delivery
- Gently guide the head downwards to deliver the upper shoulder first.
- Support and lift the head and neck slightly to deliver the lower shoulder.
- If shoulder dystocia occurs, gently flex the mother's knees alongside her abdomen and attempt to rotate the anterior shoulder under the symphysis pubis.
Post-Delivery Complications
- If blood loss exceeds 500 mL or if there are signs and symptoms of shock/hypoperfusion, administer IV NS fluid challenges in 200 mL increments titrated to patient response up to 1 L.
- Massage the fundus until it becomes firm; breastfeeding may increase uterine tone.
Breech Birth
- A footling/frank breech generally delivers in three stages: legs, abdomen, and head.
- The most dangerous times for the infant are after delivery to the abdomen (cord can become compressed against the pelvic inlet as the head descends) and after delivery of the torso and shoulders, awaiting delivery of the head.
Newborn Resuscitation
- Majority of newborns require no resuscitation beyond drying, warming, mild stimulation, and airway suctioning.
- Those who do may be critically ill and need expeditious transport to a hospital with OB capabilities.
- Acrocyanosis is peripheral cyanosis around the mouth, hands, and feet, often seen in healthy newborns and differentiated from central cyanosis.
Steps in Resuscitation
- Assess respiratory rate/distress, motor tone, and heart rate; do not wait for APGAR score to begin resuscitating if obvious distress is present.
- Warm, dry, and stimulate the newborn by flicking the soles of the feet and/or rubbing the back.
- If weak cry, ineffective breathing, poor tone, or preterm, position supine with a 1" pad under the back/shoulders to align the head and neck in a neutral position.
- Suction mouth and then nose with a bulb syringe and monitor heart rate.
- If dusky, respiratory rate > 40, and adequate effort, or heart rate ≥ 100, place neonatal NRM 1" from the baby's face and blow-by oxygen at 10 L/min.
- If apneic, respiratory rate < 40, or ineffective breathing, and heart rate ≥ 100, initiate PPV/neonatal BVM at 40-60 BPM on room air.
Eclampsia
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizure during pregnancy with no other known cause.
- Administer magnesium (50%) 2 g in 16 mL NS (slow IVP/IO) or in 50 mL NS (IVPB) over 10 minutes; max 1 g/5 minutes.
- Begin on scene and continue en route; cover IV site with cold, moist gauze or cold pack to relieve burning.
- If seizure persists after magnesium, administer midazolam 2 mg increments IVP/IO q. 30-60 sec (0.2 mg/kg IN) up to 10 mg IVP/IO/IN titrated to stop seizure.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.