Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a common application of remote sensing?
Which of the following is NOT a common application of remote sensing?
What is the primary function of the Earth's mantle?
What is the primary function of the Earth's mantle?
What does one full rotation of the Earth on its axis result in?
What does one full rotation of the Earth on its axis result in?
What is the length of time it takes Earth to complete one revolution around the sun?
What is the length of time it takes Earth to complete one revolution around the sun?
Signup and view all the answers
In a social studies context, which of the following would geospatial mapping tools be least useful for?
In a social studies context, which of the following would geospatial mapping tools be least useful for?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main difference between a rotation and a revolution?
What is the main difference between a rotation and a revolution?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of Earth's layers is composed of both solid and liquid components?
Which of Earth's layers is composed of both solid and liquid components?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the purpose of adding a leap day every four years?
What is the purpose of adding a leap day every four years?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT considered a major physical subsystem of Earth?
Which of the following is NOT considered a major physical subsystem of Earth?
Signup and view all the answers
Approximately what percentage of Earth's surface is covered by water?
Approximately what percentage of Earth's surface is covered by water?
Signup and view all the answers
Which layer of the Earth is primarily made up of liquid?
Which layer of the Earth is primarily made up of liquid?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a key difference between weathering and erosion?
Which of the following is a key difference between weathering and erosion?
Signup and view all the answers
The Earth's surface is made up of huge slabs called:
The Earth's surface is made up of huge slabs called:
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following landforms is characterized by flat, elevated regions with steep sides?
Which of the following landforms is characterized by flat, elevated regions with steep sides?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is primarily part of the hydrosphere?
Which of the following is primarily part of the hydrosphere?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is considered part of the biosphere?
Which of the following is considered part of the biosphere?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary focus of climate change mitigation strategies?
What is the primary focus of climate change mitigation strategies?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a typical 'sink' for greenhouse gases?
Which of the following is NOT a typical 'sink' for greenhouse gases?
Signup and view all the answers
The primary goal of climate change adaptation is to:
The primary goal of climate change adaptation is to:
Signup and view all the answers
What does population geography primarily study?
What does population geography primarily study?
Signup and view all the answers
How is population density calculated?
How is population density calculated?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement best describes global population distribution?
Which statement best describes global population distribution?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the timeframe goal of mitigation, according to the content?
What is the timeframe goal of mitigation, according to the content?
Signup and view all the answers
What could be considered a benefit from climate change in some regions, according to the content?
What could be considered a benefit from climate change in some regions, according to the content?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best describes permanent migration?
Which of the following best describes permanent migration?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the key difference between voluntary and forced migration?
What is the key difference between voluntary and forced migration?
Signup and view all the answers
Which option accurately describes the purpose of push and pull factors in migration?
Which option accurately describes the purpose of push and pull factors in migration?
Signup and view all the answers
What constitutes an internal migration?
What constitutes an internal migration?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is considered a national barrier to migration?
Which of the following is considered a national barrier to migration?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following can be classified as a social pull factor?
Which of the following can be classified as a social pull factor?
Signup and view all the answers
How do personal barriers to migration mainly affect potential migrants?
How do personal barriers to migration mainly affect potential migrants?
Signup and view all the answers
An individual is considering leaving a country due to political instability, this is considered a _____ factor.
An individual is considering leaving a country due to political instability, this is considered a _____ factor.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary driver of voluntary migration?
What is the primary driver of voluntary migration?
Signup and view all the answers
Which population group is typically not identified using population pyramids?
Which population group is typically not identified using population pyramids?
Signup and view all the answers
A population pyramid with a concave shape is most typical of which type of country?
A population pyramid with a concave shape is most typical of which type of country?
Signup and view all the answers
Which demographic indicator is decreasing in a country that has a convex population pyramid, like Nepal?
Which demographic indicator is decreasing in a country that has a convex population pyramid, like Nepal?
Signup and view all the answers
Which characteristic is typical of a country with a column-shaped population pyramid, such as the USA?
Which characteristic is typical of a country with a column-shaped population pyramid, such as the USA?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a defining characteristic of a country whose population pyramid is shaped like a pentagon with a narrow base, such as Japan?
What is a defining characteristic of a country whose population pyramid is shaped like a pentagon with a narrow base, such as Japan?
Signup and view all the answers
In the context of population pyramids, what is the 'dependency ratio'?
In the context of population pyramids, what is the 'dependency ratio'?
Signup and view all the answers
What is one implication of an ageing population as highlighted in the text?
What is one implication of an ageing population as highlighted in the text?
Signup and view all the answers
Which cause is most closely associated with involuntary migration?
Which cause is most closely associated with involuntary migration?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most likely consequence of a low birth rate in a developed country and an increasing older population?
What is the most likely consequence of a low birth rate in a developed country and an increasing older population?
Signup and view all the answers
Which physical factor most significantly influences population density through its impact on agriculture?
Which physical factor most significantly influences population density through its impact on agriculture?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the presence of natural resources typically affect population density?
How does the presence of natural resources typically affect population density?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary challenge that mountainous areas pose to population density?
What is the primary challenge that mountainous areas pose to population density?
Signup and view all the answers
Which economic factor primarily impacts population density by influencing job availability?
Which economic factor primarily impacts population density by influencing job availability?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most relevant impact of government investment on population density?
What is the most relevant impact of government investment on population density?
Signup and view all the answers
How can cultural factors influence population density?
How can cultural factors influence population density?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a typical consequence of low population density?
Which of the following is a typical consequence of low population density?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a common impact of low population density?
Which of the following is NOT a common impact of low population density?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
- Social science study notes cover guidelines for creating wordboxes, highlighting important terms, and addressing unclear concepts.
Chapter 1: What is Geography?
- Geography studies the Earth's surface, features, and its inhabitants.
- It analyzes physical characteristics like landforms, climate, and resources.
- Human activities and the interactions between them and the environment are also significant aspects of study.
2. Types of Geography
- Physical geography focuses on natural features such as mountains, rivers, oceans, and climate.
3. Themes of Geography
-
Location:
- Absolute location describes an exact position using latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Relative location describes a place's position in comparison to other locations.
- Place: This considers physical characteristics (landforms, water bodies, climate, etc.) and human characteristics (culture, language, religion, etc.)
-
Human-Environment Interaction: This theme investigates how human activities adapt to and modify the environment.
- Adaptation: Adjusting to the environment (building igloos in cold climates).
- Modification: Changing the environment (building dams, cutting trees).
-
Movement: This theme examines movements of people, goods, and ideas across Earth's surface.
- Migration: The movement of people.
4. Types of Maps
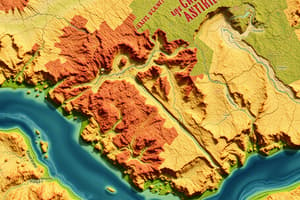
- Topographic/Relief Maps: Show the Earth's surface features, including mountains, valleys, hills, and plains. They utilize contour lines for elevation representation.
- Political Maps: Depict boundaries of countries, states, and other political divisions; they might highlight capital cities, major cities, and other significant locations.
- Thematic/Choropleth Maps: Display specific information visually using colors or patterns (e.g., population density, climate).
- Climate Maps: Represent average weather conditions like temperature and precipitation in specific regions.
- Nautical Charts: Special maps used for sea navigation, displaying depths, currents, and navigational hazards.
- Digital Maps: Electronic maps on computers or mobile devices, often incorporating GPS for real-time location information.
5. Geospatial Mapping Tools
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): A tool that combines maps, satellite images, and geographic data for detailed maps.
- Analytical tool for patterns, migration, resources, impact of natural disasters, climate change, and urbanization.
- Global Positioning Systems (GPS): Uses satellites to pinpoint locations on Earth’s surface. Widely used for navigation, surveying, and tracking the movement of people, animals, and vehicles.
6. Remote Sensing
- Remote sensing involves collecting data about Earth's surface from a distance (e.g., using satellites or aircraft).
- Data used to monitor changes in land use, deforestation, pollution and weather patterns, and natural disasters.
Topic 2: Earth's Physical Geography
- Earth has four major layers: crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
- The sun is the center of the solar system, with Earth orbiting it.
- Earth's spin on its axis causes day and night; one rotation lasts 24 hours.
Topic 3: Landforms
- Landforms include mountains, hills, plateaus, plains, deserts, forests, and islands.
- Landforms are shaped by various forces including erosion, deposition, tectonic activity, and volcanic activity.
- Erosion is the displacement of solids by wind, water, and ice.
Topic 5: Types of Mountains
- Mountains are formed through tectonic plate collisions, resulting in folded or upwarped formations or through volcanic activity.
- Fault block mountains are created by the movement of large crust blocks along fault lines.
Topic 6: The Hydrosphere
- The hydrosphere comprises all Earth's water (oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, groundwater, ice).
- The hydrological cycle describes the continuous circulation of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface. Processes include evaporation, transpiration, condensation, and precipitation.
Topic 7: Climate
- Factors Affecting Regional Climate: Latitude, Elevation, Proximity to Water Bodies (oceans and currents) significantly influence climate.
Topic 8: What is Climate Change?
- Climate change refers to long-term shifts in weather patterns, influenced by human activities (burning fossil fuels, deforestation) leading to climate change.
- Greenhouse gasses contribute to warming by trapping the sun's heat.
- Main greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide and methane.
- Sectors like energy, industry, transport, buildings, agriculture, and land use are major contributors for greenhouse gases.
- Mitigation and adaptation strategies are employed to address climate change.
Topic 9: Population Geography
- Population geography studies the spatial distribution and characteristics of human populations, including population growth and decline and migration.
- Population density varies across the world depending on physical factors like climate, water supply, natural resources, and relief, and human factors like economic opportunities and social and cultural factors.
Topic 10: What are the main types of migration?
- Migration is the movement of people across a boundary, can be permanent, temporary, voluntary, or forced, international, or internal.
- Push factors (factors pushing people away from their homes) and pull factors (factors attracting people to a new location) influence migration decisions.
Topic 11: Population Pyramids
- Population pyramids are graphical representations of a population’s age and gender structure.
- They are used to analyze population distributions and demographics to understand needs, and trends.
Topic 12: Economic Geography
- Economic Principles govern use of limited resources to satisfy human needs and wants. -Renewable resources are replenished naturally. -Non-renewable resources exist in limited quantities and take a long time to replenish.
- Economic systems (traditional, market, command, mixed) are different ways economies are organized, and each has its unique characteristics.
- Economic activity can be classified into primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary, and quinary sectors.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge of Earth science concepts, including the layers of the Earth, the difference between rotation and revolution, and the application of remote sensing tools. This quiz covers fundamental aspects of Earth's physical systems and geospatial mapping.