Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the radius of the Earth?
What is the radius of the Earth?
6,378 km
What is the name of the project that involves drilling deep into the ocean floor?
What is the name of the project that involves drilling deep into the ocean floor?
Integrated Ocean Drilling Project
Where are the deepest gold mines located?
Where are the deepest gold mines located?
South Africa.
The Earth's gravitational force is the same at all latitudes.
The Earth's gravitational force is the same at all latitudes.
Signup and view all the answers
Seismic activity is a minor source of information about the Earth's interior.
Seismic activity is a minor source of information about the Earth's interior.
Signup and view all the answers
A tsunami is directly caused by an earthquake.
A tsunami is directly caused by an earthquake.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the instrument that records earthquake waves?
What is the name of the instrument that records earthquake waves?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a type of earthquake wave?
Which of the following is NOT a type of earthquake wave?
Signup and view all the answers
The shadow zone for S-waves is smaller than the shadow zone for P-waves.
The shadow zone for S-waves is smaller than the shadow zone for P-waves.
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a direct source of information about the Earth's interior?
Which of the following is a direct source of information about the Earth's interior?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the uppermost, solid layer of the Earth?
What is the name of the uppermost, solid layer of the Earth?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name for the soft, partially molten layer of the Earth's mantle?
What is the name for the soft, partially molten layer of the Earth's mantle?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best describes the crust?
Which of the following best describes the crust?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following types of volcanoes is characterized by low-explosivity and forms a broad, gently sloping cone?
Which of the following types of volcanoes is characterized by low-explosivity and forms a broad, gently sloping cone?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of volcanic landform is a large, dome-shaped intrusion of magma that has cooled and solidified within the Earth's crust?
What type of volcanic landform is a large, dome-shaped intrusion of magma that has cooled and solidified within the Earth's crust?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best describes the lithosphere?
Which of the following best describes the lithosphere?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the difference between a sill and a dyke?
What is the difference between a sill and a dyke?
Signup and view all the answers
The Earth's core is primarily composed of nickel and iron.
The Earth's core is primarily composed of nickel and iron.
Signup and view all the answers
Volcanoes are only found on land.
Volcanoes are only found on land.
Signup and view all the answers
The most destructive earthquake waves are called surface waves.
The most destructive earthquake waves are called surface waves.
Signup and view all the answers
The shadow zone for S-waves is caused by the Earth's liquid outer core.
The shadow zone for S-waves is caused by the Earth's liquid outer core.
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following types of earthquakes is most common?
Which of the following types of earthquakes is most common?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a feature that is typically associated with composite volcanoes?
Which of the following is NOT a feature that is typically associated with composite volcanoes?
Signup and view all the answers
The Earth's crust is thicker beneath the oceans than beneath the continents.
The Earth's crust is thicker beneath the oceans than beneath the continents.
Signup and view all the answers
The Earth's outer core is liquid, while its inner core is solid.
The Earth's outer core is liquid, while its inner core is solid.
Signup and view all the answers
The most destructive volcanic eruptions are those that occur in flood basalt provinces.
The most destructive volcanic eruptions are those that occur in flood basalt provinces.
Signup and view all the answers
What is a caldera?
What is a caldera?
Signup and view all the answers
What causes the movement of tectonic plates?
What causes the movement of tectonic plates?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of these is NOT a direct source of information about the Earth's interior?
Which of these is NOT a direct source of information about the Earth's interior?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Interior of the Earth
- Earth's radius is approximately 6,378 km
- Direct sources of information include surface rocks, mining areas, and deep drilling projects (Deep Ocean Drilling Project and Integrated Ocean Drilling Project).
- Deep drilling has reached up to 12 km
- Volcanic eruptions provide molten material (magma) for analysis
- Indirect sources include analysis of matter properties, meteors, gravitation, magnetic fields, and seismic activity.
- Temperature and pressure increase with depth, and so does density.
- Scientists estimate interior characteristics based on estimates and inferences to describe the interior.
Earthquake
- Earthquakes are the shaking of the earth, caused by energy release along a fault.
- Faults are breaks in the crustal rocks.
- Energy release causes waves that travel in all directions.
- Earthquake focus (hypocentre) is where energy is released.
- Earthquake epicentre is the point on the surface nearest to the focus.
- Earthquake waves are body and surface waves, recorded by seismographs.
- Body waves (P and S waves) travel through the earth.
Earthquake Waves
- P-waves (primary waves) are faster and travel through all materials.
- S-waves (secondary waves) travel only through solids.
- Shadow zones indicate areas where certain waves are not detected, this helps understand the Earth's interior structure.
- P-wave shadow zone is between 105° and 145° from the epicentre.
- S-wave shadow zone is larger and extends beyond 105° from the epicentre.
Effects of Earthquake
- Ground shaking, differential ground settlement, land and mud slides, soil liquefaction, and ground lurching.
- Avalanches, ground displacement, floods from dams, fires, structural collapse, and falling objects are also common effects.
- Tsunami occurs when the earthquake's epicenter is below the ocean.
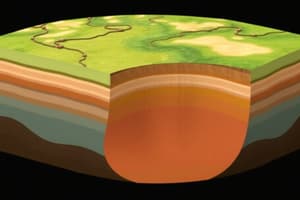
Structure of the Earth
- Crust: The outermost solid part, thinner under oceans, thicker in mountain regions, ranging from 5 km to 70 km.
- Mantle: The layer below the crust, extends to a depth of 2,900 km. The upper part (asthenosphere) is weaker than the rest of the mantle.
- Core: The innermost layer, made mainly of nickel and iron, with an outer liquid and inner solid part.
Volcanoes
- Volcanoes are classified based on eruption types and shape.
- Important types include shield volcanoes and composite volcanoes.
- Shield volcanoes are large, gently sloping, formed from fluid lava flows.
- Composite volcanoes are steep-sided, formed from explosive eruptions.
- Flood basalts describe large areas covered by lava flows.
- Intrusive forms are intrusive rocks that cool within the Earth's crust.
Volcanic Landforms
- Intrusive forms like batholiths, laccoliths, and sills are different types.
- Features like dykes, lapoliths, phacoliths, and volcanic necks are other examples.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge of the Earth's layers and tectonic processes with this informative quiz. From the radius of the Earth to the types of volcanic landforms, explore intriguing facts and concepts that shape our planet. Ideal for students studying Earth Science or related fields.