Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which treatment is considered appropriate for a patient with severe weakness due to dysarthria?
Which treatment is considered appropriate for a patient with severe weakness due to dysarthria?
- Pharyngeal flap surgery
- Lip puckering exercises
- Jaw muscle strengthening exercises (correct)
- Prosthetic palatal lift
Which of the following is a consequence of damage to the Facial Nerve?
Which of the following is a consequence of damage to the Facial Nerve?
- Resonance deficit
- Diminished vocal pitch
- Increased pitch variability
- Decreased lip strength and movement (correct)
What is one method to manage hypernasality in speech modification?
What is one method to manage hypernasality in speech modification?
- Using a nasal voice
- Increasing loudness (correct)
- Encouraging rapid speech
- Reducing breath support
Which surgical or prosthetic option is noted for having inconsistent effects on patients?
Which surgical or prosthetic option is noted for having inconsistent effects on patients?
What is the main benefit of performing pushing and pulling procedures during phonation training?
What is the main benefit of performing pushing and pulling procedures during phonation training?
Which cranial nerve damage necessitates lip puckering exercises during treatment?
Which cranial nerve damage necessitates lip puckering exercises during treatment?
Which treatment aims to address the resonance deficit from Vagus Nerve damage?
Which treatment aims to address the resonance deficit from Vagus Nerve damage?
What should a patient do while practicing lip puckering to improve their strength?
What should a patient do while practicing lip puckering to improve their strength?
What is the primary goal of the yawning-sighing exercise in the treatment of spastic dysarthria?
What is the primary goal of the yawning-sighing exercise in the treatment of spastic dysarthria?
Which of the following describes the effect of unilateral upper motor neuron damage on speech?
Which of the following describes the effect of unilateral upper motor neuron damage on speech?
In articulation treatment, what is the purpose of using a pacing board?
In articulation treatment, what is the purpose of using a pacing board?
Which treatment method involves providing the patient with auditory feedback after a delay?
Which treatment method involves providing the patient with auditory feedback after a delay?
Which exercise is NOT typically associated with articulation treatment for spastic dysarthria?
Which exercise is NOT typically associated with articulation treatment for spastic dysarthria?
What role does careful movement play in tongue stretching exercises?
What role does careful movement play in tongue stretching exercises?
What is a common etiological factor for unilateral upper motor neuron damage?
What is a common etiological factor for unilateral upper motor neuron damage?
Which technique is designed to focus on improving the intelligibility of speech?
Which technique is designed to focus on improving the intelligibility of speech?
What is the purpose of holding breath during vocal fold exercises?
What is the purpose of holding breath during vocal fold exercises?
What does a hard glottal attack involve?
What does a hard glottal attack involve?
What kind of exercises can help with tongue weakness and imprecise consonant production?
What kind of exercises can help with tongue weakness and imprecise consonant production?
Which technique is used to improve articulation of phonemes?
Which technique is used to improve articulation of phonemes?
What are minimal contrast drills designed to practice?
What are minimal contrast drills designed to practice?
Which of the following is NOT a method for increasing tongue awareness during exercises?
Which of the following is NOT a method for increasing tongue awareness during exercises?
Which treatment method decreases velar hypertonicity?
Which treatment method decreases velar hypertonicity?
What does the use of a tongue depressor in resonance treatment aim to achieve?
What does the use of a tongue depressor in resonance treatment aim to achieve?
Flashcards
Vocal Fold Adduction
Vocal Fold Adduction
The process of bringing the vocal folds together.
Hard Glottal Attack
Hard Glottal Attack
A technique used to increase vocal fold adduction by building up air pressure below the vocal folds and then releasing it forcefully.
Head Turning and Lateral Pressure
Head Turning and Lateral Pressure
A treatment strategy for vocal fold paralysis where pressure is applied to the larynx to compensate for weakness.
Pitch Range Exercises
Pitch Range Exercises
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tongue Strengthening Exercises
Tongue Strengthening Exercises
Signup and view all the flashcards
Traditional Articulation Treatment
Traditional Articulation Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minimal Contrast Drills
Minimal Contrast Drills
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resonance Treatment
Resonance Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerve Strengthening Exercises
Cranial Nerve Strengthening Exercises
Signup and view all the flashcards
Jaw Muscle Strengthening
Jaw Muscle Strengthening
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lip Strengthening Exercises
Lip Strengthening Exercises
Signup and view all the flashcards
Velopharyngeal Closure Techniques
Velopharyngeal Closure Techniques
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharyngeal Flap Surgery
Pharyngeal Flap Surgery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Teflon Injection
Teflon Injection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prosthetic Palatal Lift
Prosthetic Palatal Lift
Signup and view all the flashcards
Speech Modification Techniques
Speech Modification Techniques
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unilateral Upper Motor Neuron Damage
Unilateral Upper Motor Neuron Damage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tongue Stretching Exercise
Tongue Stretching Exercise
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phonetic Placement
Phonetic Placement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slow and Controlled Exhalation
Slow and Controlled Exhalation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pacing Board
Pacing Board
Signup and view all the flashcards
Delayed Auditory Feedback
Delayed Auditory Feedback
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Dysarthria Assessment and Treatment
- Dysarthria treatment approaches vary between clinicians.
- A combination of therapies is usually recommended.
- Treatments might focus on the damaged cranial nerve.
- Strengthening exercises are best for patients with significant weakness.
Damage to the Trigeminal Nerve
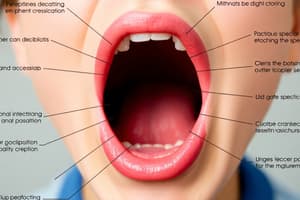
- Jaw muscle strengthening:
- Three sets of opening and closing the mouth.
- Focus on increasing bite strength.
- Resistance exercises (opening, resisting closure).
Damage to the Facial Nerve
- Lip strengthening exercises:
- Lip puckering (hold fully puckered for 10 seconds, then move side-to-side). Repeat 10 times.
- Holding a wide smile for 5-10 seconds.
- Impacts bilabial and labiodental phonemes (sounds).
Damage to the Vagus Nerve
- Resonance deficit treatment:
- Surgical/prosthetic:
- Using a pharyngeal flap to ensure velopharyngeal closure.
- Injecting Teflon into the pharynx where the soft palate makes contact.
- Prosthetic palatal lift to push the velum upward (most successful).
- Note: The effectiveness of surgical/prosthetic methods isn't consistent across all patients.
- Surgical/prosthetic:
Modification of Speech
- Increase loudness: Masking nasal sounds with increased volume.
- Reducing speech rate: Increases intelligibility and reduces perceived hypernasality.
Phonation Deficit
- Pushing and pulling exercises: Patient uses upper body strength to aid vocal fold adduction.
- Holding breath to fully adduct vocal folds.
- Hard glottal attack: Rapid adduction with subglottic air pressure, followed by a "burst" of phonation.
- Head turning/sideways pressure: Helps with unilateral laryngeal weakness/paralysis.
Prosodic Deficit (Treatment)
- Pitch range variation:
- Prolonging "ah" at low and high pitches.
- Reading sentences with pitch arrows to demonstrate variation.
Damage to the Hypoglossal Nerve
- Tongue strengthening:
- Resistance: Resist lateralization (clinician pushes toward the middle).
- Elevation: Using a tongue depressor to elevate the tongue's back.
- Mirror practice: Improves awareness and accuracy of tongue movement.
- Imprecise consonants are a common result.
Traditional Articulation Treatment
- Intelligibility drills: Patient reads words/sentences without clinician feedback.
- If unintelligible, patient repeats, or clinician provides feedback.
- Phonetic placement: Instruct patient on correct articulator positions for improved speech.
- Minimal contrast drills: Emphasize phonetic differences (e.g., voicing, manner, place, vowels).
- Example: 'park' vs. 'bark'.
Resonance Treatment
- Reduction of velar hypertonicity:
- Stimulate tongue & velum with objects in mouth
- Massage velum with depressor
- Press velum upwards with depressor
- Increased loudness: Improve intelligibility by masking hypernasality.
Treatment of Spastic Dysarthria
- Phonation:
- Head and neck relaxation (tilting, massage).
- Yawn exercise: Promotes relaxation of the neck muscles.
- Articulation:
- Tongue stretching.
- Lip stretching (smiling, kissing, puffing cheeks).
Unilateral Upper Motor Neuron
- Definition: Damage to one side of the upper motor neurons causes weakness on the opposite side of the mouth, face, lips, tongue.
- Etiologies: Stroke, tumors, TBI.
Further Treatment Approaches
- Intelligibility drills, Phonetic placement, Minimal consonant drills, and Oral motor exercises are key aspects of speech therapy for dysarthria.
- Respiration techniques: Slow, controlled exhalation with subsequent speech.
- Pacing board for improved rate.
- Delayed auditory feedback (DAF) for practice and reinforcement.
- Treatment plan: Detailed, individualized treatment plan developed prior to therapy commencement. This plan should include factors from diagnostic reports as applicable.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.