Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following organs is NOT part of the alimentary canal?
Which of the following organs is NOT part of the alimentary canal?
- Small intestine
- Esophagus
- Pancreas (correct)
- Stomach
What is the primary function of the tongue in the digestive system?
What is the primary function of the tongue in the digestive system?
- Produces saliva
- Initiates swallowing (correct)
- Absorbs nutrients
- Breaks down food chemically
Which part of the digestive system is primarily responsible for nutrient absorption?
Which part of the digestive system is primarily responsible for nutrient absorption?
- Small intestine (correct)
- Stomach
- Mouth
- Large intestine
Which of the following statements about the stomach is correct?
Which of the following statements about the stomach is correct?
How many permanent teeth do adults typically have?
How many permanent teeth do adults typically have?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
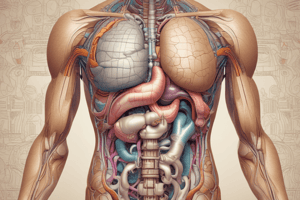
Components of the Digestive System
- Alimentary Canal: Comprises the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
- Digestive Glands: Includes the liver, pancreas, and salivary glands.
Mouth (Oral Cavity)
- Functions: Primary site for food intake and initial digestion.
- Parts:
- Vestibule: Area between the cheeks and lips on the outside, and the gums and teeth on the inside.
- Mouth Cavity Proper: Surrounded by gums and teeth, contains the tongue, teeth, and openings of salivary glands.
Tongue
- Characteristics: Muscular organ responsible for manipulating food.
- Functions:
- Aids in chewing and swallowing.
- Houses receptors for general and taste sensations.
- Facilitates speech.
Teeth
- Types:
- Deciduous (Milk) Teeth: 20 teeth in children.
- Permanent Teeth: 32 teeth in adults.
Salivary Glands
- Types:
- Parotid Gland: Largest, watery secretion, located on the side of the face.
- Submandibular Gland: Intermediate in size, produces viscid secretion, located below the mandible.
- Sublingual Gland: Smallest, viscid secretion, situated on the floor of the mouth.
Pharynx
- Function: Serves as a common pathway for air and food.
Esophagus
- Structure: Hollow muscular tube about 25 cm long.
- Function: Transports food from the pharynx to the stomach.
Stomach
- Location: Upper left part of the abdominal cavity.
- Shape: J-shaped and most dilated part of the alimentary canal.
- Anatomy:
- Ends: Cardiac (upper) and Pyloric (lower).
- Curvatures: Lesser (right) and Greater (left).
- Divisions: Cardiac part (including fundus and body) and Pyloric part.
Small Intestine
- Length: Approximately 6 meters long, coiled tube.
- Parts:
- Duodenum: 25 cm, proximal part.
- Jejunum: Middle section, accounts for 2/5 of the small intestine's length.
- Ileum: Distal part, makes up 3/5 of the small intestine's length, ends at the cecum.
Large Intestine
- Length: About 1.5 meters long.
- Location: Surrounds small intestine in the abdominal cavity.
- Characteristics: Notable presence of sacculations.
- Parts:
- Cecum (widest part)
- Vermiform appendix (narrowest part)
- Ascending colon
- Right colic flexure
- Transverse colon
- Left colic flexure
- Descending colon
- Pelvic (sigmoid) colon
- Rectum
- Anal canal
Liver
- Description: Largest gland in the body, weighing about 1.5 kg.
- Location: Upper right part of the abdominal cavity.
- Functions:
- Secretion of bile for fat digestion.
- Synthesis of albumin and clotting factors.
- Detoxification of metabolites like bilirubin and estrogen.
Gall Bladder
- Shape: Small, pear-shaped sac.
- Location: Inferior surface of the liver.
- Function: Stores and concentrates bile, which is released into the duodenum via the bile duct.
Pancreas
- Location: Lies transversely across the posterior abdominal wall.
- Parts: Head, neck, body, and tail.
- Functions:
- Endocrine: Secretes insulin and glucagon to regulate blood glucose levels.
- Exocrine: Produces pancreatic enzymes that enter the duodenum through the pancreatic duct.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.