Podcast
Questions and Answers
What primary function does the circulatory system serve in addition to transporting gases and nutrients?
What primary function does the circulatory system serve in addition to transporting gases and nutrients?
- Filtering blood
- Regulating body temperature (correct)
- Storing nutrients
- Regulating digestion
What is primarily responsible for the transport of blood throughout the body?
What is primarily responsible for the transport of blood throughout the body?
- Platelets
- The heart (correct)
- Lymphatic vessels
- White blood cells
In what sequence does blood flow through the circulatory system starting from the heart?
In what sequence does blood flow through the circulatory system starting from the heart?
- Heart → Veins → Arterioles
- Heart → Arterioles → Capillaries → Arteries
- Heart → Capillaries → Veins
- Heart → Arteries → Capillaries → Venules → Veins (correct)
What is the key characteristic of capillaries compared to other blood vessels?
What is the key characteristic of capillaries compared to other blood vessels?
How do vertebrates retain heat in cold environments?
How do vertebrates retain heat in cold environments?
What type of blood vessel carries blood back to the heart?
What type of blood vessel carries blood back to the heart?
What role does the circulatory system play in protection?
What role does the circulatory system play in protection?
What is a significant feature of arteries compared to veins?
What is a significant feature of arteries compared to veins?
What is the primary distinction between open and closed circulatory systems?
What is the primary distinction between open and closed circulatory systems?
Which animals are known to possess a closed circulatory system?
Which animals are known to possess a closed circulatory system?
What serves as the circulating fluid in an open circulatory system?
What serves as the circulating fluid in an open circulatory system?
Which statement correctly describes the function of arteries in a closed circulatory system?
Which statement correctly describes the function of arteries in a closed circulatory system?
What is the role of capillaries in the circulatory system?
What is the role of capillaries in the circulatory system?
Which of the following is a characteristic of an open circulatory system?
Which of the following is a characteristic of an open circulatory system?
What is a primary function of the circulatory system?
What is a primary function of the circulatory system?
In which type of organism would simple diffusion likely be sufficient for oxygen and nutrient exchange?
In which type of organism would simple diffusion likely be sufficient for oxygen and nutrient exchange?
What is the lifespan of a monocyte in blood?
What is the lifespan of a monocyte in blood?
Which type of blood cell is a precursor of plasma cells?
Which type of blood cell is a precursor of plasma cells?
What is the primary function of platelets?
What is the primary function of platelets?
What is the lifespan of eosinophils?
What is the lifespan of eosinophils?
What is the primary function of T lymphocytes?
What is the primary function of T lymphocytes?
Which component of the blood is involved in the initial response to inflammation?
Which component of the blood is involved in the initial response to inflammation?
What is the function of a monocyte in blood?
What is the function of a monocyte in blood?
How long do platelets typically live in the bloodstream?
How long do platelets typically live in the bloodstream?
What is the primary role of the diaphragm in the respiratory system?
What is the primary role of the diaphragm in the respiratory system?
Which structure does air pass through first when entering the respiratory system?
Which structure does air pass through first when entering the respiratory system?
How does air enter the lungs during inhalation?
How does air enter the lungs during inhalation?
What occurs during exhalation in the respiratory process?
What occurs during exhalation in the respiratory process?
What is the function of alveoli in the respiratory system?
What is the function of alveoli in the respiratory system?
What causes air to flow outward during exhalation?
What causes air to flow outward during exhalation?
Which part of the respiratory system houses the vocal cords?
Which part of the respiratory system houses the vocal cords?
What protein is responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood?
What protein is responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood?
What initiates the contraction of the atria in the heart?
What initiates the contraction of the atria in the heart?
What is the purpose of the atrioventricular (AV) node in heart contraction?
What is the purpose of the atrioventricular (AV) node in heart contraction?
Which component is responsible for the almost simultaneous contraction of the ventricles?
Which component is responsible for the almost simultaneous contraction of the ventricles?
How can the electrical activity of the heart be measured?
How can the electrical activity of the heart be measured?
What is the primary function of respiration in most animals?
What is the primary function of respiration in most animals?
Which type of respiratory organs do more advanced animal phyla possess?
Which type of respiratory organs do more advanced animal phyla possess?
During which phase does the signal from the SA node spread to the ventricles?
During which phase does the signal from the SA node spread to the ventricles?
Which structure carries the electrical signal to the ventricles after the AV node?
Which structure carries the electrical signal to the ventricles after the AV node?
What is the primary function of the left ventricle in the human heart?
What is the primary function of the left ventricle in the human heart?
Which valves are associated with the 'Lub' sound in the heart?
Which valves are associated with the 'Lub' sound in the heart?
What best describes the flow of blood returning from the lungs to the heart?
What best describes the flow of blood returning from the lungs to the heart?
What is measured using a sphygmomanometer?
What is measured using a sphygmomanometer?
Which of the following describes diastolic pressure?
Which of the following describes diastolic pressure?
Where does blood go after it leaves the right ventricle?
Where does blood go after it leaves the right ventricle?
What is a heart murmur indicative of?
What is a heart murmur indicative of?
What does the aorta do?
What does the aorta do?
Flashcards
Pulmonary Circulation
Pulmonary Circulation
The flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart, where blood picks up oxygen.
Systemic Circulation
Systemic Circulation
The flow of blood from the heart to the rest of the body and back to the heart, delivering oxygen.
Left Ventricle
Left Ventricle
The heart chamber that pumps oxygenated blood to the body.
Right Ventricle
Right Ventricle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart Valves
Heart Valves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systolic Pressure
Systolic Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diastolic Pressure
Diastolic Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basophil lifespan
Basophil lifespan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basophil function
Basophil function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Monocyte lifespan
Monocyte lifespan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Monocyte function
Monocyte function
Signup and view all the flashcards
B lymphocyte lifespan
B lymphocyte lifespan
Signup and view all the flashcards
B lymphocyte function
B lymphocyte function
Signup and view all the flashcards
T lymphocyte lifespan
T lymphocyte lifespan
Signup and view all the flashcards
T lymphocyte function
T lymphocyte function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Circulatory System
Circulatory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open Circulatory System
Open Circulatory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Countercurrent Heat Exchange
Countercurrent Heat Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Closed Circulatory System
Closed Circulatory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemolymph
Hemolymph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Vessels
Blood Vessels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries
Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries
Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillaries
Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillaries
Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood
Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Veins
Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart
Heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Circulatory System Function
Circulatory System Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Large Animals Circulatory System
Large Animals Circulatory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human Respiratory System
Human Respiratory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli
Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm
Diaphragm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inhalation
Inhalation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exhalation
Exhalation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breathing
Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange
Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart Contraction
Heart Contraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
SA Node
SA Node
Signup and view all the flashcards
AV Node
AV Node
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bundle of His
Bundle of His
Signup and view all the flashcards
Purkinje fibers
Purkinje fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
ECG/EKG
ECG/EKG
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiration
Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory organs
Respiratory organs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction to Circulation and Respiration
- Learning changes everything.
Chapter 24 Outline
- Circulation and Respiration
- Essentials of the Living World, Seventh Edition
- Authors: George Johnson, Joel Bergh
24.1 Open and Closed Circulatory Systems
- Unicellular protists obtain oxygen and nutrients through simple diffusion.
- Cnidarians and flatworms have cells that are directly exposed to the external environment or a gastrovascular cavity.
- Large animals have tissues several cell layers thick, making surface exchange inefficient.
- Oxygen and nutrients are transported from the environment/digestive cavity to body cells via an internal circulatory system.
- Two main types of circulatory systems exist: open and closed.
24.1 Open Circulatory Systems
- No distinction between circulating fluid (blood) and extracellular fluid (body tissues).
- This fluid is called hemolymph.
- Insects have a muscular tube (heart) that pumps hemolymph through a network of open-ended channels.
24.1 Closed Circulatory Systems
- Circulating fluid (blood) is always enclosed within blood vessels.
- Annelids (like earthworms) and vertebrates have closed circulatory systems.
- Blood travels away from the heart through arteries.
- Exchange of gases and nutrients occurs through thin-walled capillaries.
- Blood returns to the heart through veins.
Figure 24.1: Circulatory Systems in the Animal Kingdom
- Illustrates three types of circulatory systems found in animals.
- Shows examples of gastrovascular cavity (planaria), open circulation (insect), and closed circulation (earthworm).
24.1 Function of the Circulatory System
- Transportation: Gases, nutrients, wastes, and hormones are transported.
- Regulation: Cardiovascular system regulates body temperature; vertebrates use countercurrent heat exchange to regulate body temperature in cold environments.
- Protection: System protects against injury and foreign microbes or toxins.
Figure 24.2: Countercurrent Heat Exchange
- Illustrates countercurrent heat exchange in an animal as a mechanism for regulating body temperature.
- Warm blood in the arteries warms the cold blood in the veins within a capillary bed.
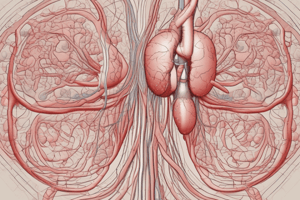
24.2 Architecture of the Vertebrate Circulatory System
- The system comprises three elements: heart, blood vessels, blood.
- The heart is a muscular pump that pushes blood throughout the body.
- Blood vessels are a network of tubes through which blood moves.
- Blood is the fluid that circulates through the vessels.
24.2 Blood Flow in Vertebrate Systems
- Blood leaves the heart via arteries.
- Blood moves into smaller arterioles.
- Tiny capillaries connect arterioles to venules (small veins).
- Venules and then veins carry blood back to the heart.
Figure 24.3: Blood Flow in the Circulatory System
- Illustrates the flow of blood, starting with arteries, moving through smaller arterioles and capillaries and back to the heart via venules, and then veins.
24.2 Capillary Structure
- Capillaries have the largest total cross-sectional area of any other blood vessel type.
- Capillary beds can open or close based on tissue physiological needs.
Figure 24.4: Capillary Network
- The network connects arteries with veins.
- Precapillary sphincters regulate blood flow through capillary beds.
24.2 Artery Structure
- Arteries are more than simple pipes.
- They need to expand with the pressure caused by heart contractions.
- Arterial walls contain several layers, including endothelial cells, elastic fibers, and smooth muscle surrounded by connective tissue.
Figure 24.5a: Artery Structure
- Illustrates the layered structure of an artery, highlighting the different tissue layers.
24.2 Capillary Function
- Capillaries are the site of material exchange between the blood and body cells.
- Capillaries are narrow and have thin walls to facilitate exchange.
- Almost all cells in the vertebrate body are within 100 micrometers of a capillary.
Figure 24.5b: Capillary Structure
- Illustrates the structure of a capillary.
24.2 Vein Function
- Veins return blood to the heart.
- Vein walls are thinner due to lower blood pressure as compared to arteries.
- Veins have unidirectional valves to prevent backflow.
Figure 24.5c: Vein Structure
- Shows the structure of blood vessels in detail, emphasizing the layers in a vein.
24.2 Blood Plasma
- Blood plasma is a complex water solution of various dissolved substances.
- Metabolites and wastes (e.g., glucose, vitamins, hormones) are dissolved in the plasma.
- Salts and ions (e.g., sodium, chloride, bicarbonate) are dissolved in the plasma.
- Proteins help maintain water balance in the plasma.
- Serum albumin maintains osmotic balance; other proteins include antibodies, globulins, and fibrinogen (involved in blood clotting).
Figure 24.9: Fibrin Threads
- Illustrates the presence of fibrin, a protein crucial for blood clotting.
24.3 Blood Cells
- Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets comprise the cellular components of blood.
- Hematocrit is the fraction of blood volume occupied by red blood cells (generally ~45% in humans).
- Red blood cells resemble flat disks.
- The interior is packed with hemoglobin for oxygen transport.
24.3 Red blood Cells
- Red blood cells are short-lived and replaced in the bone marrow.
24.3 White Blood Cells
- They are colorless and contain no hemoglobin; diverse cells responsible for the immune system.
24.3 Platelets
- Platelets are cell fragments from megakaryocytes (large cells in the bone marrow) crucial for blood clotting.
Figure 24.10: Types of Blood Cells
- Chart exhibiting different types of blood cells, their life spans, and functions.
24.4 Human Circulatory System
- Humans and other mammals have a four-chambered heart with two complete pumping circuits.
- One side pumps blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen; other side distributes oxygenated blood to the body.
24.4 Left Ventricle Function
- Oxygen-rich blood returns from the lungs via pulmonary veins to the left atrium.
- Blood flows passively to the left ventricle via the bicuspid (mitral) valve.
24.4 Aorta
- The thick-walled left ventricle contracts, sending oxygenated blood through the large artery called the aorta, distributing outwards into the body.
24.4 Right Ventricle Function
- Blood travels through the body via vena cavae, then to the right atrium.
- Blood moves from right atrium through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
- Right ventricle contracts, pushing blood through the pulmonary valve to pulmonary arteries (leading to the lungs).
Figure 24.11: The Heart and Circulation in Humans
- Shows the human heart's anatomy, including blood flow through the chambers and major vessels.
24.4 Heartbeat Monitoring
- Listening with a stethoscope: "Lub" (bikuspid and tricuspid valves closing -start of ventricular contraction); "Dub" (pulmonary and aortic valves closing- end of ventricular contraction).
- Heart murmurs indicate valve dysfunction.
24.4 Blood Pressure Monitoring
- Measurements made using a sphygmomanometer on the brachial artery.
- Systolic pressure (high) is recorded during ventricular contraction; diastolic pressure (low) is recorded during atrial filling.
Figure 24.12: Measuring Blood Pressure
- Diagram illustrates how blood pressure is measured using a sphygmomanometer and a stethoscope.
24.4 Heart Contraction
- Heart contraction involves coordinated muscular contractions (atria followed by ventricles).
- Sinoatrial (SA) node (pacemaker) initiates each heartbeat in the right atrium wall.
24.4 Heart Signal Transmission
- The signal from SA node delays for 0.1 sec through the atrioventricular (AV) node before reaching ventricles for contraction.
24.4 Electrical Conduction of the Ventricles
- Signal travels through the Bundle of His.
- Signal is then transferred to Purkinje fibers generating almost simultaneous contraction across the ventricles.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) captures electrical activity of the heart.
Figure 24.13: Mammalian Heart Contraction
- Illustration showing steps in mammalian heart contraction, indicating the sequence of events.
24.5 Respiratory Systems
- Respiration is the uptake of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide.
- Most primitive animal phyla obtain oxygen directly from the environment by diffusion.
- More advanced phyla possess specific respiratory organs (e.g., gills, tracheae, lungs).
Figure 24.14: Gas Exchange in Animals
- Diagram illustrating organisms using gills (fish), tracheae (insects), or lungs (mammals) for gas exchange.
24.6 Human Respiratory System: Introduction
- Lungs are adaptations for terrestrial habitat in mammals.
- A pair of lungs lies within the thoracic cavity.
24.6 Human Respiratory System: Airflow
- Air flows through nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe).
- Air travels through bronchi (in lungs), then to bronchioles.
- Bronchioles lead to alveoli where gas exchange occurs.
Figure 24.15: Human Respiratory System
- Diagram showing anatomy of the human respiratory system, from external structures like the nasal cavity to internal structures like alveoli.
24.6 Human Respiratory System: Mechanisms
- Diaphragm separates thoracic cavity from abdominal cavity.
- Lungs are covered by pleural membranes.
- Pleural membranes adhere to thoracic cavity to couple lungs to the thoracic walls.
- Air drawn into lungs by negative pressure.
24.6 Human Respiratory System: Breathing
- Inhalation: Muscular contractions expanding the chest cavity and diaphragm creating lower pressure in lungs causing air flow inward.
- Exhalation: Ribs and diaphragm return to their resting positions, increasing lung pressure and expelling air.
24.7 How Respiration Works - Gas Exchange
- Oxygen carried in blood by hemoglobin.
- Hemoglobin contains iron enabling reversible binding to oxygen.
Figure 24.16: Hemoglobin Molecule
- Shows hemoglobin's structure and how oxygen binds.
24.7 Hemoglobin and Oxygen Transport
- High oxygen levels at the lung cause hemoglobin molecules to carry a full load of O2.
- Low oxygen levels in tissues cause hemoglobin to release oxygen.
- CO2 presence in hemoglobin alters shape aiding oxygen release.
24.7 Carbon Dioxide Transport
- CO2 is transported by blood in various ways; about 8% dissolves in the plasma.
- 20% binds to hemoglobin (different site than oxygen).
- Remaining 72% diffuses into red blood cells to maintain gradient enabling CO2 exit the tissues and into the plasma.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.