Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary form in which structural proteins are present within the cell?
What is the primary form in which structural proteins are present within the cell?
- As simple amino acids
- As mobile enzymes
- As glucose molecules
- As long filaments (correct)
Which of the following is a major role of functional proteins in the cell?
Which of the following is a major role of functional proteins in the cell?
- Catalyzing chemical reactions (correct)
- Storing fat
- Forming cell membranes
- Providing structural support
Which lipids are primarily involved in forming the cell membrane?
Which lipids are primarily involved in forming the cell membrane?
- Phospholipids and cholesterol (correct)
- Fatty acids and phospholipids
- Saturated fats and triglycerides
- Triglycerides and cholesterol
What percentage of total cell mass do phospholipids and cholesterol constitute?
What percentage of total cell mass do phospholipids and cholesterol constitute?
In which cellular organelles do microtubules primarily provide structural support?
In which cellular organelles do microtubules primarily provide structural support?
What is the main stored form of energy in fat cells?
What is the main stored form of energy in fat cells?
Which of the following components primarily plays a role in cell nutrition rather than structural function?
Which of the following components primarily plays a role in cell nutrition rather than structural function?
What type of proteins are primarily found as fibrillar proteins in connective tissues?
What type of proteins are primarily found as fibrillar proteins in connective tissues?
What role do integral proteins primarily serve in the cell membrane?
What role do integral proteins primarily serve in the cell membrane?
What is one function of peripheral proteins in the cell membrane?
What is one function of peripheral proteins in the cell membrane?
How do carbohydrate molecules function on the cell membrane?
How do carbohydrate molecules function on the cell membrane?
What is the function of the selective properties of integral protein channels?
What is the function of the selective properties of integral protein channels?
What triggers conformational changes in integral membrane receptors?
What triggers conformational changes in integral membrane receptors?
What term describes the process of transporting substances against their natural direction of diffusion?
What term describes the process of transporting substances against their natural direction of diffusion?
What type of protein is most commonly found as a part of the membrane lipids?
What type of protein is most commonly found as a part of the membrane lipids?
What are proteoglycans primarily composed of?
What are proteoglycans primarily composed of?
What form of carbohydrate is predominantly available in the surrounding extracellular fluid for cells?
What form of carbohydrate is predominantly available in the surrounding extracellular fluid for cells?
What is the main structural component of the cell membrane?
What is the main structural component of the cell membrane?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the cell membrane?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the cell membrane?
What property of phospholipids allows them to form a bilayer in the cell membrane?
What property of phospholipids allows them to form a bilayer in the cell membrane?
Which type of substances can easily penetrate the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane?
Which type of substances can easily penetrate the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane?
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane?
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane?
What percentage of the cell membrane is composed of carbohydrates?
What percentage of the cell membrane is composed of carbohydrates?
Membrane proteins that have carbohydrates attached to them are referred to as what?
Membrane proteins that have carbohydrates attached to them are referred to as what?
What percentage of the adult human body is primarily made up of fluid?
What percentage of the adult human body is primarily made up of fluid?
Which of the following components are part of protoplasm?
Which of the following components are part of protoplasm?
Which type of proteins primarily provide structural support in cells?
Which type of proteins primarily provide structural support in cells?
What role do ions play in cellular function?
What role do ions play in cellular function?
What types of fluids exist outside of cells?
What types of fluids exist outside of cells?
Which of the following substances constitutes the highest percentage of a typical cell's composition?
Which of the following substances constitutes the highest percentage of a typical cell's composition?
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
Which of the following ions is least mentioned as important for cellular functions?
Which of the following ions is least mentioned as important for cellular functions?
Flashcards
What is a cell?
What is a cell?
The fundamental building block of the body, capable of carrying out essential life functions.
Structural Proteins: What are they?
Structural Proteins: What are they?
Long filaments formed by polymers of many individual protein molecules. They provide structural support for cellular components such as cilia and the mitotic spindle.
Functional Proteins: What are they?
Functional Proteins: What are they?
They are mainly responsible for the cell's metabolic processes, acting as catalysts in chemical reactions.
What is intracellular fluid?
What is intracellular fluid?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lipids: What are they?
Lipids: What are they?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is extracellular fluid?
What is extracellular fluid?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the nucleus of a cell?
What is the nucleus of a cell?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lipids: What is their function?
Lipids: What is their function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lipids (Triglycerides): How are they important for energy?
Lipids (Triglycerides): How are they important for energy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the cytoplasm?
What is the cytoplasm?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbohydrates: What is their function?
Carbohydrates: What is their function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the cell membrane?
What is the cell membrane?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are structural proteins?
What are structural proteins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a glycoprotein?
What is a glycoprotein?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the mitotic spindle?
What is the mitotic spindle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are functional proteins?
What are functional proteins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Integral proteins
Integral proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral proteins
Peripheral proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein channels
Protein channels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carrier proteins
Carrier proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active transport
Active transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell membrane receptors
Cell membrane receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycolipids
Glycolipids
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are phospholipids?
What are phospholipids?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is cholesterol?
What is cholesterol?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are membrane proteins?
What are membrane proteins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is glycogen?
What is glycogen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is carbohydrate stored in cells?
How is carbohydrate stored in cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is permeability?
What is permeability?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the cell membrane regulate permeability?
How does the cell membrane regulate permeability?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
The Cell
- The cell is the basic living unit of the body.
- Each organ is made up of many different cells held together by intercellular structures.
- Individual cells are adapted to perform specific functions.
- Although cells vary, they share common characteristics and the ability to reproduce.
Body Fluid Composition
- Approximately 60% of the adult human body is fluid, primarily water with dissolved ions and other substances.
- Most of this fluid is intracellular fluid (inside cells).
- A smaller portion is extracellular fluid (outside cells), containing ions and nutrients necessary for cell function.
- Composition of extracellular fluid:
- Intravascular fluid (blood plasma): 7%.
- Interstitial fluid: 26%.
- Cerebrospinal fluid: less than 1%.
Intracellular Fluid
- Intracellular fluid is crucial for cell function.
- Proper concentrations of oxygen, glucose, ions, amino acids, fatty substances, and other nutrients are needed for cell survival, growth, and function. These are found in the extracellular fluid surrounding cells.
Cell Structure
- Cells have two main parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
- The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane.
- The cytoplasm is separated from the surrounding fluids by a cell membrane (plasma membrane).
- Protoplasm is a collective term for the substances that make up the cell.
- Protoplasm is primarily composed of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates.
Water in Cells
- Water is the primary fluid medium within most cells.
- Water content ranges from 70 to 85% for most cells (excluding fat cells).
- Many cell chemicals are dissolved in this water.
- Other cell chemicals are suspended in the water as solid particulates.
Ions in Cells
- Important ions in cells include potassium, magnesium, phosphate, sulfate, bicarbonate, sodium, chloride, and calcium.
- These ions are crucial for cellular chemical reactions.
- Ions acting on cell membranes are required for transmitting electrochemical impulses in nerves and muscles.
Proteins in Cells
- Proteins are the most abundant substances in cells after water, commonly comprising 10-20% of cell mass.
- Proteins can be categorized into structural proteins and functional proteins.
- Structural proteins provide the framework and support for various cellular structures.
- Functional proteins include enzymes, crucial for catalyzing cellular chemical reactions (e.g., glucose breakdown).
Structural Proteins
- Structural proteins are predominantly filamentous molecules.
- They form microtubules that act as the "cytoskeletons" of various cellular components (e.g., cilia, nerve axons, mitotic spindles).
- Extracellularly, they are found in collagen and elastin fibers, connective tissue, blood vessel walls, tendons, ligaments, etc., providing structure, support, and strength.
Functional Proteins (enzymes)
- Functional proteins (enzymes) are often mobile within the cell fluid; they catalyze specific cellular chemical reactions
- Examples of their activities include breaking down glucose and combining it with oxygen to produce energy-rich molecules for cell function.
Lipids
- Lipids are various substances grouped by their solubility in fat solvents.
- Key lipids are phospholipids and cholesterol, comprising about 2% of cell mass.
- Their primary function is forming cell membranes and intracellular membrane barriers for compartmentalization. They are hydrophobic ("water-fearing").
- Some cells contain triglycerides (neutral fat) that store energy.
Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates play a crucial role in cell nutrition, though with limited structural roles in most cells.
- Dissolved glucose (a sugar) is available in extracellular fluid for rapid uptake.
- Glycogen, another form of carbohydrate, is stored to provide energy when needed.
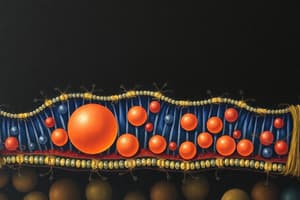
Cell Membrane
- The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, encloses the cell and is a thin, elastic structure (7.5-10 nanometers thick).
- It primarily consists of lipids (mostly phospholipids) and proteins in a bilayer arrangement.
- Phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, other lipids, and carbohydrates are present in specific proportions in the cell membrane.
Cell Membrane Structure
- The cell membrane's basic structure is a lipid bilayer.
- One end of each phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic ("water-loving") and soluble in water.
- The other end is hydrophobic (“water-fearing”); it's soluble in fat.
- The hydrophobic portion of the membrane is impermeable to common water-soluble substances but permeable to fat-soluble substances (e.g., oxygen).
- The hydrophilic regions ("heads") face the aqueous environments inside and outside of the cell.
Cell Membrane Proteins
- Membrane proteins are globular masses embedded in the phospholipid bilayer.
- Many are glycoproteins (proteins with carbohydrate components).
- Two main types of membrane proteins are:
- Integral proteins: span the entire membrane, acting as channels or carriers for substance transport.
- Peripheral proteins: are attached to one side of the membrane and do not penetrate the entire structure; mostly enzymes or transport controllers.
Membrane Protein Functions
- Many integral proteins form channels for molecules to pass between intracellular and extracellular fluids (e.g., water, ions).
- Some transport specific substances across, even against, their concentration gradient (active transport).
- Other proteins act as receptors, binding to hormones or other substances, initiating internal signals.
Cell Membrane Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are often attached to proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids) at the cell surface.
- The carbohydrate components are often arranged on the outer surface of the membrane.
- The carbohydrate-rich layer on the cell surface is called the glycocalyx, and it performs various roles (e.g., cell-to-cell recognition, cell surface characteristics).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.