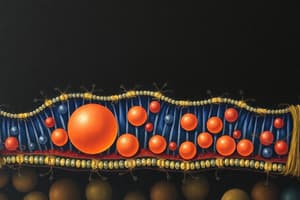
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of lipids in the cell membrane?
What is the primary function of lipids in the cell membrane?
- Provide structural support
- Create a semi-permeable barrier (correct)
- Facilitate communication between cells
- Transport substances across the membrane
Which component of the cell membrane is responsible for selective passage of substances?
Which component of the cell membrane is responsible for selective passage of substances?
- Cholesterol
- Protein channel (correct)
- Cytoskeletal filaments
- Peripheral membrane protein
In the Davson-Danielli model, what is positioned between the outer layers of protein?
In the Davson-Danielli model, what is positioned between the outer layers of protein?
- Carbohydrate chains
- Phospholipid monolayer
- Lipid bilayer (correct)
- Integral membrane proteins
Which statement accurately describes glycoproteins?
Which statement accurately describes glycoproteins?
What structural feature of the cell membrane helps in maintaining its shape and integrity?
What structural feature of the cell membrane helps in maintaining its shape and integrity?
What is the main characteristic of the Davson-Danielli Model of the cell membrane?
What is the main characteristic of the Davson-Danielli Model of the cell membrane?
Which statement best describes the Singer-Nicolson Fluid Mosaic Model?
Which statement best describes the Singer-Nicolson Fluid Mosaic Model?
How does temperature affect the fluidity of the cell membrane?
How does temperature affect the fluidity of the cell membrane?
Which factor contributes to increased fluidity of a cell membrane?
Which factor contributes to increased fluidity of a cell membrane?
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane?
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane?
Flashcards
Davson-Danielli Model
Davson-Danielli Model
A model of the cell membrane, also called the sandwich model, proposing a phospholipid bilayer between two protein layers.
Singer-Nicolson Model
Singer-Nicolson Model
A modern model describing the cell membrane as a mosaic of proteins embedded in a fluid phospholipid bilayer.
Phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid bilayer
A two-layered structure forming the basic framework of the cell membrane, with hydrophobic tails facing inward.
Membrane Fluidity
Membrane Fluidity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluidity Increase
Fluidity Increase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semi-permeable Barrier
Semi-permeable Barrier
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why are lipids in the cell membrane?
Why are lipids in the cell membrane?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do membrane proteins do?
What do membrane proteins do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are carbohydrates in membranes for?
What are carbohydrates in membranes for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cell Membrane Structure
- The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is a vital structure for transport mechanisms and separates the living cell from its surroundings.
- To perform these roles, the cell membrane needs lipids, which make a semi-permeable barrier between the cell and its environment, proteins, involved in cross-membrane transport and cell communication, and carbohydrates attach to the proteins or lipids, enabling cells to recognize each other.
Structural Components of the Cell Membrane
-
Lipids: Form the primary structure of the membrane, acting as a semi-permeable barrier to prevent water-soluble molecules from entering or exiting the cell.
-
Proteins: Embedded within the lipid bilayer. These proteins assist in transport of specific molecules across the membrane, support structural integrity, and act as recognition sites for other cells.
-
Carbohydrates: Attached to proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids) on the outer surface of the membrane. They play a vital role in cell-cell recognition and communication.
-
In 1935, the Davson-Danielli model of the membrane proposed that the membrane consisted of a phospholipid bilayer sandwiched between two protein layers.
-
In 1972, Singer and Nicolson proposed the fluid mosaic model. This model describes the membrane as a mosaic of proteins dispersed within a phospholipid bilayer; only the hydrophilic regions of the proteins are exposed to water.
Membrane Fluidity
- Membrane fluidity is influenced by temperature, the configuration of the unsaturated fatty acid tails, and the presence of cholesterol.
- Unsaturated fatty acids increase fluidity.
- Cholesterol reduces fluidity at high temperatures but maintains fluidity at lower temperatures.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.