Podcast
Questions and Answers
The fluid mosaic model describes the ever-changing nature of proteins within the cell membrane.
The fluid mosaic model describes the ever-changing nature of proteins within the cell membrane.
True (A)
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a selectively permeable membrane?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a selectively permeable membrane?
The generation of a proton motive force (PMF) is an important function of the ______ membrane.
The generation of a proton motive force (PMF) is an important function of the ______ membrane.
cytoplasmic
What is the main difference in the composition of archaeal cytoplasmic membranes compared to bacterial and eukaryotic membranes?
What is the main difference in the composition of archaeal cytoplasmic membranes compared to bacterial and eukaryotic membranes?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of transport moves substances from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration?
Which type of transport moves substances from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration?
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following types of passive transport with their descriptions:
Match the following types of passive transport with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Give an example of a molecule that moves across a membrane via simple diffusion?
Give an example of a molecule that moves across a membrane via simple diffusion?
Signup and view all the answers
During osmosis, water moves from an area of ______ water concentration to an area of ______ water concentration.
During osmosis, water moves from an area of ______ water concentration to an area of ______ water concentration.
Signup and view all the answers
Active transport requires energy expenditure to move solutes against their concentration gradient.
Active transport requires energy expenditure to move solutes against their concentration gradient.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the force generated by the influx of water during osmosis?
What is the name of the force generated by the influx of water during osmosis?
Signup and view all the answers
The rigid ______ of bacterial cells protects them from rupturing due to high osmotic pressure.
The rigid ______ of bacterial cells protects them from rupturing due to high osmotic pressure.
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following solutions would cause water to move into a cell?
Which of the following solutions would cause water to move into a cell?
Signup and view all the answers
In an isotonic solution, there is no net movement of water across the cell membrane.
In an isotonic solution, there is no net movement of water across the cell membrane.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the energy-rich compound used by some cells to drive active transport?
What is the name of the energy-rich compound used by some cells to drive active transport?
Signup and view all the answers
The proton motive force (PMF) is an example of a form of ______ used in active transport.
The proton motive force (PMF) is an example of a form of ______ used in active transport.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following types of transport systems with their corresponding descriptions:
Match the following types of transport systems with their corresponding descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
What are the structures that assist swimming in Bacteria?
What are the structures that assist swimming in Bacteria?
Signup and view all the answers
Archaea have flagella.
Archaea have flagella.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name for the directed movement of bacteria in response to chemical stimuli?
What is the name for the directed movement of bacteria in response to chemical stimuli?
Signup and view all the answers
The rotation of flagella is powered by the ______ force.
The rotation of flagella is powered by the ______ force.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the flagellar arrangements with their descriptions:
Match the flagellar arrangements with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
What does the term "serovar" refer to?
What does the term "serovar" refer to?
Signup and view all the answers
The capillary tube assay is a reliable method for measuring chemotaxis.
The capillary tube assay is a reliable method for measuring chemotaxis.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name for the directed movement of bacteria in response to light?
What is the name for the directed movement of bacteria in response to light?
Signup and view all the answers
Inclusions serve as ______ reserves, ______ or ______ reservoirs, and/or have special functions.
Inclusions serve as ______ reserves, ______ or ______ reservoirs, and/or have special functions.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
Signup and view all the answers
Both mitochondria and chloroplasts likely originated from endosymbiosis.
Both mitochondria and chloroplasts likely originated from endosymbiosis.
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is not a type of taxis?
Which of the following is not a type of taxis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the folded internal membranes found within mitochondria?
What is the name of the folded internal membranes found within mitochondria?
Signup and view all the answers
The process of converting sunlight energy into chemical energy in the form of sugar is called ______.
The process of converting sunlight energy into chemical energy in the form of sugar is called ______.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following structures with their descriptions:
Match the following structures with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the bacterial cell wall?
What is the primary function of the bacterial cell wall?
Signup and view all the answers
The cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria is thicker than that of Gram-negative bacteria.
The cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria is thicker than that of Gram-negative bacteria.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the unique compound found in bacterial cell walls that is responsible for its rigidity?
What is the name of the unique compound found in bacterial cell walls that is responsible for its rigidity?
Signup and view all the answers
The two alternating subunits in peptidoglycan are ______ and ______.
The two alternating subunits in peptidoglycan are ______ and ______.
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following antibiotics targets the formation of peptide cross-links in peptidoglycan?
Which of the following antibiotics targets the formation of peptide cross-links in peptidoglycan?
Signup and view all the answers
Teichoic acids are found exclusively in Gram-negative bacteria.
Teichoic acids are found exclusively in Gram-negative bacteria.
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures is found exclusively in Gram-negative bacteria?
Which of the following structures is found exclusively in Gram-negative bacteria?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the protein channels found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria that allow the passage of solutes?
What is the name of the protein channels found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria that allow the passage of solutes?
Signup and view all the answers
The outer leaflet of the outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria is composed of ______, not phospholipids.
The outer leaflet of the outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria is composed of ______, not phospholipids.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following bacterial cell wall components with their respective functions:
Match the following bacterial cell wall components with their respective functions:
Signup and view all the answers
Flashcards
Fluid Mosaic Model
Fluid Mosaic Model
A model describing the plasma membrane as flexible and dynamic, with proteins floating in or on the fluid lipid bilayer.
Selectively Permeable
Selectively Permeable
A property of the cytoplasmic membrane that allows certain molecules to pass while blocking others.
Passive Transport
Passive Transport
Movement of substances across a membrane from high to low concentration without using energy.
Simple Diffusion
Simple Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active Transport
Active Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transport Proteins
Transport Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osmosis
Osmosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Isotonic solution
Isotonic solution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic solution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic solution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proton motive force (PMF)
Proton motive force (PMF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
ABC transport system
ABC transport system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Group translocation
Group translocation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple transport
Simple transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mitosis
Mitosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meiosis
Meiosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mitochondria
Mitochondria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endosymbiosis
Endosymbiosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bacterial Cell Wall
Bacterial Cell Wall
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peptidoglycan (PTG)
Peptidoglycan (PTG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gram-positive Cell Wall
Gram-positive Cell Wall
Signup and view all the flashcards
Teichoic Acids
Teichoic Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gram-negative Cell Wall
Gram-negative Cell Wall
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outer Membrane
Outer Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Porins
Porins
Signup and view all the flashcards
O-polysaccharide
O-polysaccharide
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antibiotic Mechanism (Penicillin)
Antibiotic Mechanism (Penicillin)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coli O157
Coli O157
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pili
Pili
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prokaryotic Cell Morphology
Prokaryotic Cell Morphology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flagella
Flagella
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flagellar Rotation
Flagellar Rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Flagellar Arrangements
Types of Flagellar Arrangements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Measuring Chemotaxis
Measuring Chemotaxis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phototaxis
Phototaxis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Inclusions
Cell Inclusions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Microbial Cell Structure and Function
- The cell envelope is a series of layered structures surrounding the cytoplasm, governing interactions with the environment.
- The cytoplasmic membrane transports nutrients into the cell and waste products out.
- The cell wall provides rigidity and structure to the cell.
- Peptidoglycan.
- The outer membrane (LPS).
- Archaeal cell walls.
- There is a diversity of cell envelope structures.
Morphology of a Prokaryotic Cell
- Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus.
- Capsule: a sticky outer coat
- Plasmids: small rings of DNA
- Cytoplasm: the cell interior
- Cell wall: a rigid outer layer
- Plasma membrane: regulates passage
- Ribosomes: build proteins
- Nucleoid: coiled DNA (no membrane)
- Flagellum: aids in movement
- Pili: short projections
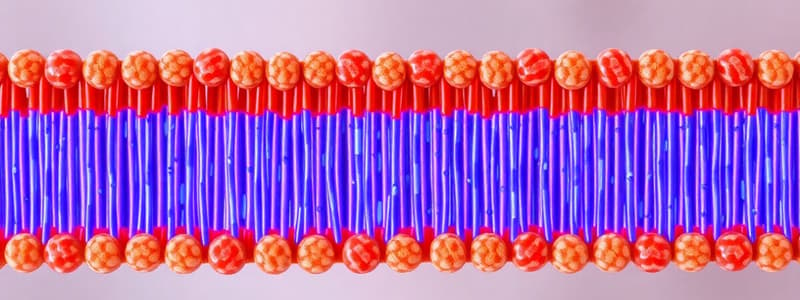
Plasma (Cytoplasmic) Membrane
-
Surrounds the cytoplasm, separating it from the environment.
-
Main function: selective permeability (transports nutrients in and waste products out).
-
Membrane proteins facilitate these reactions and energy metabolism.
-
General structure: phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
-
Phospholipids: contain both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components.
- Hydrophilic heads (glycerol + phosphate).
- Hydrophobic tails (fatty acids).
- Fatty acids associate inward to form a hydrophobic environment.
- Hydrophilic heads remain exposed to the external environment or the cytoplasm.
-
Peripheral membrane proteins: located on the inner or outer surface of the plasma membrane, loosely attached.
-
Embedded proteins: integral/transmembrane proteins.
- Extend completely across the membrane.
- Some form channels.
-
"Fluid mosaic model":
- The cytoplasmic membrane is as viscous as olive oil.
- The membrane is embedded with numerous proteins.
- More than 200 different proteins are possible.
- Proteins function as receptors, transport gates, and a mechanism to sense surroundings, etc.
- Proteins are not stationary, constantly changing position for various functions.
-
Cytoplasmic membrane is "selectively permeable", determining which molecules pass into or out of the cell.
-
Few molecules pass through freely.
-
Molecules pass through the membrane via simple diffusion or transport mechanisms, possibly requiring carrier proteins and energy.
-
Transport proteins accumulate solutes against their concentration gradient.
-
Protein anchor: Holds proteins in place.
-
Energy conservation and consumption (METABOLISM)
- Generation of proton motive force (PMF)
- Cell membrane contains enzymes for ATP production
-
Archaeal cytoplasmic membranes:
- Ether linkages in phospholipids.
- Ester linkages in phospholipids of Bacteria & Eukarya.
- Archaeal lipids have isoprenes instead of fatty acids.
Nutrients transport across cell membrane
-
Passive transport
- Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis.
- Simple diffusion: movement of a molecule from high concentration to low concentration; no energy expenditure.
- Facilitated diffusion: integral membrane proteins serve as channels or carriers (transporters) to facilitate movement of ions or larger molecules across the membrane.
- Substances moves with the concentration gradient (from high to low concentration).
- Transporter proteins: some are nonspecific, others are more specialized
- Osmosis: net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to lower water concentration.
- Water flows to equalize solute concentrations.
- Influx of water exerts osmotic pressure on the membrane.
-
Active transport: substances move from low concentration to high concentration; energy expenditure.
Bacterial Cell Wall
-
Rigid structure, surrounds cytoplasmic membrane, determines shape of bacteria.
-
Prevents cell from bursting from osmotic/turgor pressure.
-
Unique chemical structure distinguishes Gram-positive from Gram-negative.
-
Gram stain reaction determined by cell wall thickness.
-
Peptidoglycan (PTG): rigidity of the cell wall.
-
Alternating series of two subunits: N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM).
-
Stabilized by horizontal and vertical peptide cross-links, often containing peptide interbridges.
-
Site of action for some antibiotics.
- Penicillin interferes with peptide cross-bridges formation, weakening the cell wall.
-
Gram-positive cell wall
- Relatively thick layer of peptidoglycan (PTG).
- As many as 30 layers of thickness.
- Peptidoglycan is permeable to numerous substances.
- Teichoic acid component of PTG
- Gram positive cells commonly have teichoic acids (acidic molecules) embedded in the cell wall and covalently linked to peptidoglycan.
- Gives cells a negative charge.
- Lipo-teichoic acids: teichoic acids covalently bound to membrane lipids.
-
Gram-negative cell wall
- Only contains thin layer of PTG.
- PTG sandwiched between outer membrane and cytoplasmic membrane.
- Porins: transmembrane protein channels for entrance and exit of solutes. Gram-negative Outer Membrane
-
Second lipid bilayer external to cell wall.
-
Much like cytoplasmic membrane but outer leaflet made of lipo-polysaccharides (LPS) instead of phospholipids
-
Covalently bound to lipids.
-
LPS: a barrier to large molecules and ions.
-
O-polysaccharide: used to identify certain species or strains (e.g., E. coli O157:H7).
-
Lipid A: an endotoxin, the toxic component of LPS, toxic and can cause pain, fever, and damage to blood vessels.
Diversity of Cell Envelope Structure
- S-layers: para-crystalline structure consisting of protein or glycoprotein.
- If present, always outermost layer.
- Functions: strength, protection from lysis, shape, periplasmic-like space, promoting adhesion, protection to host defenses.
- Alternative configurations of cell envelope:
- Outer S-layer surrounding Gram+ or Gram- bacterium.
- Many archaea have only S-layer outside cytoplasmic membrane.
- Pseuromurein cell walls in archaea with or without S-layer.
- Archaea with outer membrane
- Some bacteria and archaea lack cell walls, but have tough cytoplasmic membranes (e.g. sterols).
- Mycoplasmas (Bacteria)
- Thermoplasma (Archaea)
Why the external structure is important?
- Many antibiotics target the cell wall and other components of the cell envelope (e.g., cell membrane and outer membrane).
- An outer membrane complicates treatment with antibiotics
- Cell envelope toxins also complicate treatment.
- Attachment to certain surfaces.
- Structure to the organism.
Cell Surface Structures: Capsules and Slime Layers (Glycocalyx)
- Glycocalyx: external to cell envelope, sticky polysaccharide coat.
-Capsule: neatly organized, tightly attached, and visible by India ink
- Many bacteria produce it, but not all.
- Slime layer: unorganized, loosely attached
- Functions:
- Assists in attachment
- Prevents dehydration
- Contributes to virulence (protects from phagocytosis, allows microbes to adhere to body surfaces).
- Extracellular polymeric substance helps form biofilms.
Pili and Fimbriae
- Pili: thin filamentous protein structures (~2-10 nm wide), enables attachment to surfaces or form pellicles (thin sheets of cells on a liquid surface).
- Conjugation pili: involved in DNA transfer between cells.
- Electrically conductive pili: conduct electrons.
- Involved in motility (gliding, twitching motility).
- Fimbriae: short pili mediating attachment to body surfaces.
- Examples: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, E. coli O157
- Virulence factors
Flagella, Archaella, and Swimming Motility
- Flagella: structures that assist in swimming in bacteria, long, thin appendages (15-20 nm wide), anchored in the cell.
- Use propeller-like movements to push bacteria.
- Rotate more than 100,000 revolutions per minute.
- Can increase or decrease rotational speed related to the strength of the proton motive force.
- Flagellar arrangements:
- Monotrichous
- Amphitrichous
- Lophotrichous
- Peritrichous
Chemotaxis
- Taxis: directed movement in response to chemical or physical stimuli.
- Chemotaxis: response to chemicals.
- Monitor/sample environment with chemoreceptors & sense attractants and repellents.
- Phototaxis: response to light.
- Directed movement enhances access to resources or allows avoidance of damage/death.
- Chemotaxis: response to chemicals.
- Osmotaxis, hydrotaxis, and aerotaxis.
- Chemotaxis measured by inserting a capillary tube with attractant/repellent.
- Chemical concentration decreases with the distance from the tip.
- Chemotactic bacteria swarm toward the attractant, increasing the number of cells in the capillary.
Phototaxis of Phototrophic Bacteria
Cell Inclusions
- Inclusions function as energy, carbon, or phosphorus reservoirs and have special functions.
- Enclosed by thin protein membrane.
- Reduces osmotic stress.
- Carbon storage polymers are synthesized when carbon is in excess.
- Examples:
- Glycogen (glucose polymer).
- Elemental sulfur accumulates in periplasmic granules (oxidized to sulfate).
- Magnetosomes: allow bacteria to orient within the magnetic field; biomineralized magnetic iron oxides.
- Gas vesicles: confer buoyancy
- Conical-shaped gas-filled structures made of two proteins.
Endospores
- Produced inside certain bacterial cells when nutrients are depleted.
- Specialized spores are resistant to desiccation, heat, radiation, and chemicals.
- Survival structures to endure unfavorable growth conditions.
- A survival mechanism; not a reproductive process.
- Ideal for dispersal via wind, water, or animal gut.
- Produced by members of Bacillus and Clostridium (Gram-positive).
- Germination: triggered by nutrient availability, three steps: activation, germination, and outgrowth.
- Endospore formation (sporulation) is complex and ordered—triggered by limiting nutrient; vegetative cell converts to a non-growing and heat-resistant light refractive structure.
- Comparisons with vegetative cells:
- Calcium content, dipicolinic acid.
- Enzymatic activity, respiration rate
- Macromolecular synthesis, Heat resistance
- Radiation resistance, resistance to chemicals, lysozyme, water content.
- Small acid-soluble spore proteins
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
- Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex.
- Key eukaryotic organelles include the nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough), Golgi apparatus.
- Lysosomes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, cytoskeleton (microfilaments, microtubules, intermediate filaments).
- Flagella and cilia (motility).
- Eukaryotic plasma membrane contains sterols for support (e.g. cholesterol and ergosterol).
Eukaryotic Plasma Membrane
- Similar in chemical structure and function to prokaryotic cytoplasm membranes but have sterols.
- Phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins
- Transport
- Maintain cell integrity
- Receptors for cell signaling
- Animal cells contain cholesterol.
- Fungal cells contain ergosterol.
- Difference in sterols target for antifungal medications.
The Nucleus and Cell Division
-
Double membrane structure (nuclear envelope) encloses the cell's DNA.
-
DNA is complexed with histone to form chromatin/nucleosomes
-
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis cells.
- The nucleus have a darker area called nucleolus, where ribosomes are produced.
- DNA molecules are wrapped around proteins to form fibers called chromatin and nucleosomes.
-
Cell division
- Mitosis: results in two diploid daughter cells (somatic cells).
- Meiosis: specialized form of nuclear division, converts diploid into haploid cells, results in four haploid gametes.
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria: organelle for cellular respiration, Uses oxygen to harvest energy (ATP) form sugar molecules.
- Surrounded by two membranes (porous outer membrane, inner membrane with cristae).
- Cristae: folded internal membranes.
- Matrix: innermost area containing citric acid enzymes.
- Chloroplasts are chlorophyll-containing organelles found in phototrophic eukaryotes.
- Site of photosynthesis; use sunlight to create sugar from water and carbon dioxide.
- Double membrane, thylakoids, stroma, and RuBisCO.
- Endosymbiotic origin: Mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from free-living prokaryotes engulfed by another prokaryotic cell.
- Evidence: circular DNA genomes and ribosomes (70S) similar to those of bacteria.
- Eukarya hypothesized to have originated from symbiotic fusion of archaeal host and mitochondrial endosymbiont.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Network of membranes continuous with nuclear membrane; two types (rough & smooth).
- Rough ER: contains attached ribosomes
- Smooth ER: participates in lipid (fats, steroids, hormones), carbohydrate metabolism.
- Products new membrane material
Golgi Apparatus:
- Transport organelle that modifies, sorts, and ships proteins from rough ER via vesicles.
- Transports modified proteins via secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane and other regions.
- Produces glycoproteins, lipoproteins, glycolipids, and lysosomes.
Lysosomes
- Membrane-enclosed compartments containing digestive enzymes and recycling cellular components.
- Present in phagocytic cells (e.g., immune cells).
Flagella and Cilia
- Present on many eukaryotic microbe surfaces.
- Function in motility, allowing cells to move via swimming.
- Cilia are short flagella that beat in synchrony.
- Eukaryotic flagella are long appendages that propel through whiplike motion.
Other Eukaryotic Cell Structures
- Cytoskeleton: internal structural support network.
- Microtubules: hollow tubes composed of α- and β-tubulin, maintain cell shape, facilitate motility, move chromosomes, and organelles.
- Microfilaments: polymers of actin for maintaining and changing cell shape, involved in amoeboid motility and cell division.
- Intermediate filaments: fibrous keratin proteins for maintaining cell shape and position organelles.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge of the fluid mosaic model and the characteristics of selectively permeable membranes. This quiz covers key concepts related to membrane transport mechanisms, including passive and active transport, osmosis, and the differences in membrane compositions across various organisms.