Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the nuclear matrix within the nucleoplasm?
What is the function of the nuclear matrix within the nucleoplasm?
- It acts as a scaffold that aids in organizing the nucleoplasm. (correct)
- It serves as a site for ribosome assembly.
- It encapsulates the nucleolus to regulate its activities.
- It isolates chromatin from RNA synthesis.
What characterizes heterochromatin in terms of its location and structure?
What characterizes heterochromatin in terms of its location and structure?
- It is dispersed evenly throughout the nucleoplasm.
- It is primarily found in the nucleolar matrix.
- It is tightly packed and located around the nucleolus and nucleus periphery. (correct)
- It consists solely of active, RNA-synthesizing regions.
Which component of the nucleoplasm contains interchromatin and perichromatin granules?
Which component of the nucleoplasm contains interchromatin and perichromatin granules?
- Nuclear Particles (correct)
- Nuclear Matrix
- Nucleolar Regions
- Nuclear Membrane
Which of the following best describes the structure of the nuclear pore complex?
Which of the following best describes the structure of the nuclear pore complex?
What distinguishes the four distinct regions of the nucleolus?
What distinguishes the four distinct regions of the nucleolus?
What is the typical diameter of interchromatin granules found in the nuclear particles?
What is the typical diameter of interchromatin granules found in the nuclear particles?
What is the primary function of integral proteins in the membrane?
What is the primary function of integral proteins in the membrane?
What is the composition of the glyocalyx?
What is the composition of the glyocalyx?
Which type of transport requires no energy and occurs along the concentration gradient?
Which type of transport requires no energy and occurs along the concentration gradient?
Which small molecule is primarily transported through simple diffusion?
Which small molecule is primarily transported through simple diffusion?
What characteristic distinguishes peripheral proteins from integral proteins?
What characteristic distinguishes peripheral proteins from integral proteins?
How is facilitated diffusion different from simple diffusion?
How is facilitated diffusion different from simple diffusion?
Which type of lysosome is formed by the fusion of a phagocytic vacuole and a late endosome?
Which type of lysosome is formed by the fusion of a phagocytic vacuole and a late endosome?
What is the primary function of peroxisomes?
What is the primary function of peroxisomes?
What structure is responsible for forming a small aqueous pore across the membrane?
What structure is responsible for forming a small aqueous pore across the membrane?
What structural component is involved in the formation of autophagolysosomes?
What structural component is involved in the formation of autophagolysosomes?
What feature characterizes the appearance of the glycalyx?
What feature characterizes the appearance of the glycalyx?
Which type of molecules are primarily moved via ion channel proteins?
Which type of molecules are primarily moved via ion channel proteins?
What is the typical lifespan of a peroxisome?
What is the typical lifespan of a peroxisome?
Which of the following components do residual bodies contain?
Which of the following components do residual bodies contain?
Which of these is NOT a type of lysosome mentioned?
Which of these is NOT a type of lysosome mentioned?
What process primarily identifies peroxisomes in cells?
What process primarily identifies peroxisomes in cells?
Which enzyme is NOT typically found in peroxisomes?
Which enzyme is NOT typically found in peroxisomes?
What type of lysosome is characterized by containing undegraded material such as lipofuscin?
What type of lysosome is characterized by containing undegraded material such as lipofuscin?
What is the primary acid pH maintained by ATP-powered proton pumps in lysosomes?
What is the primary acid pH maintained by ATP-powered proton pumps in lysosomes?
What type of transport involves the movement of a molecule against its electrochemical gradient?
What type of transport involves the movement of a molecule against its electrochemical gradient?
Which of the following correctly describes the function of carrier proteins?
Which of the following correctly describes the function of carrier proteins?
Osmosis is best described as which of the following processes?
Osmosis is best described as which of the following processes?
Which type of endocytosis involves the engulfing of particulate material?
Which type of endocytosis involves the engulfing of particulate material?
What is the primary function of the Na+-K+ pump?
What is the primary function of the Na+-K+ pump?
What is the defining feature of receptor-mediated endocytosis?
What is the defining feature of receptor-mediated endocytosis?
Which type of transport is characterized by the bulk movement of substances out of the cell?
Which type of transport is characterized by the bulk movement of substances out of the cell?
Which statement about vesicular transport is incorrect?
Which statement about vesicular transport is incorrect?
Pinocytosis is best defined as which of the following?
Pinocytosis is best defined as which of the following?
What is a key characteristic that distinguishes active transport from passive transport?
What is a key characteristic that distinguishes active transport from passive transport?
What is the role of the pericentriolar cloud in the centrosome?
What is the role of the pericentriolar cloud in the centrosome?
Which statement correctly describes microtubules?
Which statement correctly describes microtubules?
What role does the cytoskeleton play in a cell?
What role does the cytoskeleton play in a cell?
How do microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) contribute to microtubules?
How do microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) contribute to microtubules?
During which phase does the centrosome form a pole for the mitotic spindle?
During which phase does the centrosome form a pole for the mitotic spindle?
Which component is NOT considered part of the cytoskeleton?
Which component is NOT considered part of the cytoskeleton?
What do kinesin and cytoplasmic dynein specifically act upon in the cell?
What do kinesin and cytoplasmic dynein specifically act upon in the cell?
Which of the following is a primary function of microtubules?
Which of the following is a primary function of microtubules?
What distinguishes microtubules from intermediate filaments?
What distinguishes microtubules from intermediate filaments?
Which of the following best describes the structure of tubulin dimers?
Which of the following best describes the structure of tubulin dimers?
Study Notes
Glycocalyx
- A fuzzy material outside the cell membrane formed by carbohydrate side chains of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
- Thickness is approximately 50 nm.
- Composed of polar oligosaccharides linked covalently to proteins and some lipids; also contains proteoglycans.
Membrane Proteins
- Integral (Transmembrane) Proteins: Function as membrane receptors and transport proteins, span the lipid bilayer.
- Peripheral Proteins: Located on the cytoplasm surface, do not extend into the lipid bilayer; involved in the cytoskeleton and intracellular signaling.
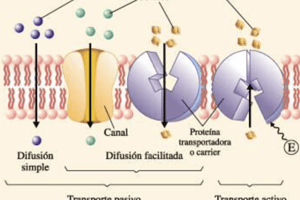
Plasma Membrane Transport Processes
-
Passive Transport: Moves molecules from higher to lower concentration without energy; includes:
- Simple Diffusion: Small non-polar molecules (e.g., O2, N2) and small unchanged polar molecules (e.g., H2O, CO2) diffuse based on concentration gradient.
- Facilitated Diffusion: Involves specific ion channels or carrier proteins allowing selective transport.
- Osmosis: The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane until equilibrium is achieved.
-
Active Transport: Requires energy to move molecules against their electrochemical gradient; includes:
- Na+-K+ Pump: Anti-port transport of Na+ and K+, mediated by ATPase.
- Glucose Transport: Involves symport transport across epithelial cells (transepithelial transport).
-
Vesicular Transport: Involves vesicle formation for transporting materials in and out of the cell; includes:
- Exocytosis: Bulk movement of substances out of the cell via secretory vesicles.
- Endocytosis: Bulk uptake of substances into the cell; includes phagocytosis (cell eating) and pinocytosis (cell drinking).
- Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis: Involves specific binding of substances to receptors before uptake.
Cytoplasm
- Composed of organelles, inclusions, and ATP-powered proton pumps in lysosomes maintaining an acidic pH (≈5).
Lysosomes
- Include different types:
- Multivesicular Bodies: Formed by fusion of endosomes.
- Phagolysosomes: Formed by fusion of phagocytic vacuoles and lysosomes.
- Autophagolysosomes: Result from fusion of autophagic vacuoles with lysosomes, involved in degrading cellular components.
- Residual Bodies: Lysosomes that cannot degrade material contain undegraded substances.
Peroxisomes
- Membrane-bound organelles involved in the oxidation of long-chain fatty acids, cholesterol synthesis, and detoxification of substances like ethanol.
- Contains enzymes and undergoes fission; lifespan of approximately 5-6 days.
Cytoskeleton
- Structural framework maintaining cell shape, stabilizing attachments, and facilitating transport and cell motility.
- Major components include:
- Microtubules: Hollow tubes made of tubulin, aiding in transport and maintaining shape.
- Microfilaments: Thin filaments involved in muscle contraction and cell movement.
- Intermediate Filaments: Provide structural support and cell integrity.
Nuclear Structure
- Nuclear Pore Complex: Composed of cytoplasmic and nucleoplasmic rings, facilitating transport between nucleus and cytoplasm.
- Nucleolus: Contains four regions (fibrillar center, pars fibrosa, pars granulosa, nucleolar matrix) involved in ribosome production.
- Nucleoplasm: The substance within the nuclear envelope, includes the nuclear matrix for organization and particles containing RNA and enzymes.
Chromatin
- Contains double-stranded DNA complexed with histones, exists as heterochromatin (inactive) and euchromatin (active).
- Responsible for RNA synthesis, with heterochromatin concentrated around the nucleus.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers essential concepts regarding cell membrane structures, focusing on membrane proteins and the glycocalyx. Understand the roles of integral and peripheral proteins as well as the significance of the carbohydrate side chains in glycocalyx formation. Test your knowledge on membrane functionality and structural components.