Podcast
Questions and Answers
¿Qué estudia la biología?
¿Qué estudia la biología?
La biología estudia los seres vivos y su relación con el entorno.
¿Cuáles son algunas características de los seres vivos?
¿Cuáles son algunas características de los seres vivos?
Algunas características de los seres vivos son su alta organización, la capacidad de interacción con el medio, la capacidad de autoconstrucción, la reproducción, la capacidad de respuesta a estímulos, la homeostasis y la adaptación al entorno.
¿Cuál es el primer nivel de organización de la materia en el cual se manifiestan y cumplen las características de los seres vivos?
¿Cuál es el primer nivel de organización de la materia en el cual se manifiestan y cumplen las características de los seres vivos?
El primer nivel de organización de la materia en el cual se manifiestan y cumplen las características de los seres vivos son las células.
¿Qué instrumentos se utilizan para observar las células debido a su tamaño?
¿Qué instrumentos se utilizan para observar las células debido a su tamaño?
¿Cuál es la teoría que postula que la materia viva está formada por células?
¿Cuál es la teoría que postula que la materia viva está formada por células?
¿Qué tipo de células se originan a partir de otras células y contienen la información hereditaria de los organismos?
¿Qué tipo de células se originan a partir de otras células y contienen la información hereditaria de los organismos?
¿Qué tipos de células se pueden identificar en los seres vivos?
¿Qué tipos de células se pueden identificar en los seres vivos?
¿En qué tipos de organismos se encuentran las células procariotas?
¿En qué tipos de organismos se encuentran las células procariotas?
¿Cuáles son algunos de los componentes orgánicos de las células?
¿Cuáles son algunos de los componentes orgánicos de las células?
¿Cuáles son algunos de los átomos que componen a los seres vivos?
¿Cuáles son algunos de los átomos que componen a los seres vivos?
¿Qué elementos se combinan de manera específica en la materia viva?
¿Qué elementos se combinan de manera específica en la materia viva?
¿Qué ciclo de vida cumplen las células?
¿Qué ciclo de vida cumplen las células?
¿Qué es la endocitosis?
¿Qué es la endocitosis?
¿Por qué es fundamental el conocimiento de la composición físico-química celular?
¿Por qué es fundamental el conocimiento de la composición físico-química celular?
¿Qué función tiene la clatrina en la endocitosis con receptores específicos?
¿Qué función tiene la clatrina en la endocitosis con receptores específicos?
¿Qué ocurre en la exocitosis?
¿Qué ocurre en la exocitosis?
¿Qué compone el citosol celular?
¿Qué compone el citosol celular?
¿Cuál es la función de los microtúbulos en la célula?
¿Cuál es la función de los microtúbulos en la célula?
¿Qué generan los microfilamentos, también conocidos como filamentos de actina?
¿Qué generan los microfilamentos, también conocidos como filamentos de actina?
¿Cuál es la función de los filamentos intermedios?
¿Cuál es la función de los filamentos intermedios?
¿Qué es la transcitosis?
¿Qué es la transcitosis?
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre la membrana celular específica y la inespecífica en el transporte de sustancias?
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre la membrana celular específica y la inespecífica en el transporte de sustancias?
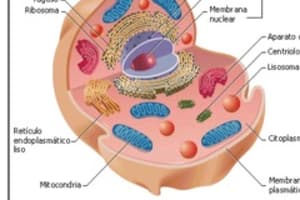
¿Qué son los orgánulos membranosos en el citoplasma celular?
¿Qué son los orgánulos membranosos en el citoplasma celular?
¿Cuáles son las subetapas de la interfase en el ciclo celular?
¿Cuáles son las subetapas de la interfase en el ciclo celular?
¿Qué ocurre en la subetapa G2 del ciclo celular?
¿Qué ocurre en la subetapa G2 del ciclo celular?
¿En qué subetapa de la interfase ocurre la replicación del ADN?
¿En qué subetapa de la interfase ocurre la replicación del ADN?
¿Qué implica la fase de división del ciclo celular?
¿Qué implica la fase de división del ciclo celular?
¿Qué comprende el límite celular en células eucariotas animales?
¿Qué comprende el límite celular en células eucariotas animales?
¿Cómo se define la membrana plasmática en células eucariotas animales?
¿Cómo se define la membrana plasmática en células eucariotas animales?
¿Qué plantea el Modelo de mosaico fluido en relación a las membranas?
¿Qué plantea el Modelo de mosaico fluido en relación a las membranas?
¿Qué tipo de estructura presenta la bicapa lipídica en la membrana plasmática?
¿Qué tipo de estructura presenta la bicapa lipídica en la membrana plasmática?
¿Cuáles son las funciones específicas de las proteínas en la membrana plasmática?
¿Cuáles son las funciones específicas de las proteínas en la membrana plasmática?
¿Qué es el glucocáliz o cubierta celular?
¿Qué es el glucocáliz o cubierta celular?
¿Cuáles son las funciones del glucocáliz?
¿Cuáles son las funciones del glucocáliz?
¿Qué es el glucocálix y de qué está compuesto?
¿Qué es el glucocálix y de qué está compuesto?
¿Cuáles son las funciones del glucocálix?
¿Cuáles son las funciones del glucocálix?
¿Qué papel tiene el ácido siálico en los oligosacáridos de las glucoproteínas?
¿Qué papel tiene el ácido siálico en los oligosacáridos de las glucoproteínas?
¿Cuáles son los mecanismos de movimiento de agua y solutos a través de la membrana celular?
¿Cuáles son los mecanismos de movimiento de agua y solutos a través de la membrana celular?
¿Qué papel desempeña la difusión en el transporte de sustancias en organismos multicelulares?
¿Qué papel desempeña la difusión en el transporte de sustancias en organismos multicelulares?
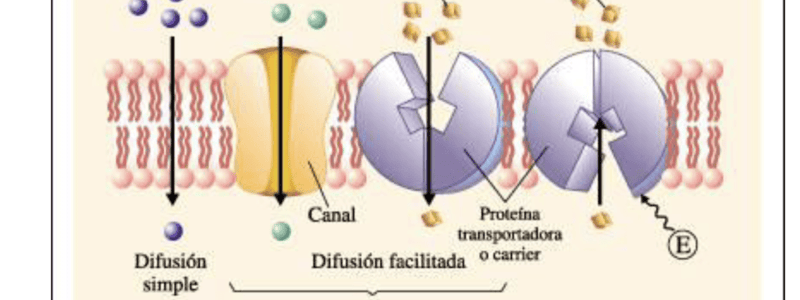
¿Cómo se clasifican los mecanismos de difusión?
¿Cómo se clasifican los mecanismos de difusión?
¿Qué permite la difusión simple?
¿Qué permite la difusión simple?
¿Qué es la ósmosis y en qué consiste?
¿Qué es la ósmosis y en qué consiste?
¿Qué incluyen las difusiones mediadas por proteínas?
¿Qué incluyen las difusiones mediadas por proteínas?
¿Qué requiere el transporte activo o bombas y qué mantenimiento realiza?
¿Qué requiere el transporte activo o bombas y qué mantenimiento realiza?
¿En qué consiste el transporte en masa y qué implica?
¿En qué consiste el transporte en masa y qué implica?
Flashcards
What does Biology study?
What does Biology study?
Biology studies living organisms and their relationship with the environment.
What are some characteristics of living organisms?
What are some characteristics of living organisms?
Living organisms are highly organized, interact with their environment, have self-construction abilities, reproduce, respond to stimuli, maintain homeostasis, and adapt to their surroundings.
What is the first level of organization where living characteristics appear?
What is the first level of organization where living characteristics appear?
The first level of organization where living characteristics appear is the cell.
What tools are used to observe cells?
What tools are used to observe cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What theory states that living matter is made of cells?
What theory states that living matter is made of cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What types of cells arise from other cells and contain hereditary information?
What types of cells arise from other cells and contain hereditary information?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main types of cells found in living organisms?
What are the main types of cells found in living organisms?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where can prokaryotic cells be found?
Where can prokaryotic cells be found?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some organic components of cells?
What are some organic components of cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What atoms make up living organisms?
What atoms make up living organisms?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the cell life cycle?
What is the cell life cycle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is endocytosis?
What is endocytosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is understanding cell physio-chemical composition crucial?
Why is understanding cell physio-chemical composition crucial?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of clathrin in receptor-mediated endocytosis?
What is the function of clathrin in receptor-mediated endocytosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens during exocytosis?
What happens during exocytosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the composition of the cytosol?
What is the composition of the cytosol?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of microtubules?
What is the function of microtubules?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do microfilaments, also known as actin filaments, generate?
What do microfilaments, also known as actin filaments, generate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of intermediate filaments?
What is the function of intermediate filaments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is transcytosis?
What is transcytosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the difference between specific and non-specific cell membrane transport?
What is the difference between specific and non-specific cell membrane transport?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are membranous organelles in the cell cytoplasm?
What are membranous organelles in the cell cytoplasm?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the sub-stages of interphase in the cell cycle?
What are the sub-stages of interphase in the cell cycle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens during the G2 sub-stage of the cell cycle?
What happens during the G2 sub-stage of the cell cycle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
During what sub-stage of interphase does DNA replication occur?
During what sub-stage of interphase does DNA replication occur?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the division phase of the cell cycle involve?
What does the division phase of the cell cycle involve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What comprises the cell boundary in animal eukaryotic cells?
What comprises the cell boundary in animal eukaryotic cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is the plasma membrane defined in animal eukaryotic cells?
How is the plasma membrane defined in animal eukaryotic cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the Fluid Mosaic Model propose about membranes?
What does the Fluid Mosaic Model propose about membranes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What type of structure does the lipid bilayer in the plasma membrane have?
What type of structure does the lipid bilayer in the plasma membrane have?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the specific functions of proteins in the plasma membrane?
What are the specific functions of proteins in the plasma membrane?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the glycocalyx or cell covering?
What is the glycocalyx or cell covering?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the functions of the glycocalyx?
What are the functions of the glycocalyx?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the glycocalyx made of?
What is the glycocalyx made of?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the functions of the glycocalyx?
What are the functions of the glycocalyx?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What role does sialic acid play in glycoprotein oligosaccharides?
What role does sialic acid play in glycoprotein oligosaccharides?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the mechanisms of water and solute movement across the cell membrane?
What are the mechanisms of water and solute movement across the cell membrane?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What role does diffusion play in substance transportation in multicellular organisms?
What role does diffusion play in substance transportation in multicellular organisms?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are diffusion mechanisms classified?
How are diffusion mechanisms classified?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does simple diffusion allow?
What does simple diffusion allow?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is osmosis and what does it involve?
What is osmosis and what does it involve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are protein-mediated diffusions?
What are protein-mediated diffusions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does active transport or pumps require and maintain?
What does active transport or pumps require and maintain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does bulk transport consist of and what does it involve?
What does bulk transport consist of and what does it involve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Funciones y tipos de transporte a través del glucocálix y la membrana celular
- El glucocálix es un revestimiento continuo en la membrana plasmática de células eucariotas animales, compuesto principalmente por glucoproteínas y glucolípidos.
- Tiene funciones de filtración, protección mecánica, adhesión celular, creación de microambientes favorables, función enzimática y función inmunológica.
- Participa en el reconocimiento molecular e intercelular, permitiendo la distinción entre células propias y extrañas.
- El ácido siálico en los oligosacáridos de las glucoproteínas tiene un papel crucial en la función inmunológica.
- Existen dos mecanismos de movimiento de agua y solutos: flujo global y difusión.
- La difusión mueve moléculas e iones de forma independiente y al azar, desempeñando un papel importante en el transporte de sustancias en organismos multicelulares.
- Los mecanismos de difusión se clasifican como activos o pasivos, dependiendo del uso de energía celular y cambios en la estructura de la membrana.
- La difusión simple permite el pasaje de moléculas pequeñas, no polares y solubles en lípidos a favor de su gradiente de concentración.
- La ósmosis es un caso particular de difusión que realiza el paso de agua a través de una membrana selectivamente permeable.
- Las difusiones mediadas por proteínas incluyen proteínas formadoras de canales y transportadoras, permitiendo el pasaje de iones y moléculas hidrofílicas a favor o en contra de los gradientes.
- El transporte activo o bombas requiere el gasto de energía celular y mantiene la polarización de la membrana.
- El transporte en masa implica la formación o fusión de vesículas a la membrana plasmática y consume energía celular (ATP).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Funciones y mecanismos de transporte a través del glucocálix y la membrana celular. Aprende sobre la composición y funciones del glucocálix, así como los distintos tipos de transporte celular, incluyendo difusión, ósmosis, transporte activo y transporte en masa.