Podcast
Questions and Answers
What role does the glycocalyx play in cellular activity?
What role does the glycocalyx play in cellular activity?
- It facilitates the exchange of nutrients and waste between the cell and its environment.
- It acts solely as a barrier to prevent substances from entering the cell.
- It serves as a molecular identifier for the immune system to differentiate between healthy and diseased cells. (correct)
- It allows for unrestricted movement of particles in and out of the cell.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the glycocalyx?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the glycocalyx?
- Immunity to infection by recognizing foreign organisms.
- Protection of the plasma membrane from chemical injury.
- Enhancement of nutrient absorption into the cell. (correct)
- Defense against cancer through immune recognition.
How does the glycocalyx contribute to transplant compatibility?
How does the glycocalyx contribute to transplant compatibility?
- By providing identification markers that the immune system uses to assess foreignness. (correct)
- By promoting the growth of new cells in the donor site.
- By creating an impermeable barrier to pathogens.
- By enabling cells to absorb nutrients more efficiently.
What property of the plasma membrane allows certain substances to pass while restricting others?
What property of the plasma membrane allows certain substances to pass while restricting others?
What is the significance of membrane potential in a cell?
What is the significance of membrane potential in a cell?
Which statement accurately describes non-cellular organisms?
Which statement accurately describes non-cellular organisms?
What characterizes unicellular organisms that live in colonies?
What characterizes unicellular organisms that live in colonies?
Which type of organisms are considered to have eukaryotic cells?
Which type of organisms are considered to have eukaryotic cells?
What is the primary function of the endocrine and nervous systems in multicellular organisms?
What is the primary function of the endocrine and nervous systems in multicellular organisms?
Which statement correctly describes the hierarchy of living systems?
Which statement correctly describes the hierarchy of living systems?
What is the primary reason that a cell must be an open system?
What is the primary reason that a cell must be an open system?
Which component allows cells to adapt to their environment?
Which component allows cells to adapt to their environment?
Which of the following elements is classified as a macroelement necessary for cell survival?
Which of the following elements is classified as a macroelement necessary for cell survival?
What type of compounds are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids considered?
What type of compounds are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids considered?
Which of the following is NOT a similarity between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
Which of the following is NOT a similarity between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
Which form of communication is primarily associated with cell signaling?
Which form of communication is primarily associated with cell signaling?
What is the role of the semi-permeable membrane in a cell?
What is the role of the semi-permeable membrane in a cell?
Which of the following is true regarding microelements in cells?
Which of the following is true regarding microelements in cells?
What role do membrane proteins play in transport within the cell membrane?
What role do membrane proteins play in transport within the cell membrane?
Which of the following statements about membrane fluidity is true?
Which of the following statements about membrane fluidity is true?
What is one function of membrane compartments within eukaryotic cells?
What is one function of membrane compartments within eukaryotic cells?
How do glycolipids contribute to cell interaction?
How do glycolipids contribute to cell interaction?
What is a characteristic of intramembrane domains of membrane proteins?
What is a characteristic of intramembrane domains of membrane proteins?
What are the consequences of having unsaturated fatty acids in the membrane?
What are the consequences of having unsaturated fatty acids in the membrane?
Which membrane protein function involves initiating a cellular response to external signals?
Which membrane protein function involves initiating a cellular response to external signals?
How does the fluid-mosaic model describe the arrangement of cellular membranes?
How does the fluid-mosaic model describe the arrangement of cellular membranes?
What is the primary function of G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)?
What is the primary function of G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)?
What happens to receptor tyrosine kinases upon ligand binding?
What happens to receptor tyrosine kinases upon ligand binding?
What is the primary driving force behind osmosis?
What is the primary driving force behind osmosis?
Which subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins is responsible for GTPase activity?
Which subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins is responsible for GTPase activity?
How does ligand binding affect ligand-gated ion channels?
How does ligand binding affect ligand-gated ion channels?
Which type of channel is regulated by specific ligand binding?
Which type of channel is regulated by specific ligand binding?
What describes an isotonic solution in relation to cytosol?
What describes an isotonic solution in relation to cytosol?
What is the role of adenylyl cyclase in signaling pathways?
What is the role of adenylyl cyclase in signaling pathways?
What is a key characteristic of primary active transport?
What is a key characteristic of primary active transport?
What type of receptors are primarily responsible for mediating insulin signaling?
What type of receptors are primarily responsible for mediating insulin signaling?
Which of the following describes a hypertonic solution?
Which of the following describes a hypertonic solution?
Which of the following best describes the function of integrins?
Which of the following best describes the function of integrins?
How does secondary active transport differ from primary active transport?
How does secondary active transport differ from primary active transport?
Which pathway does phospholipase C activate in response to thrombin signaling?
Which pathway does phospholipase C activate in response to thrombin signaling?
What is the primary function of vesicular transport?
What is the primary function of vesicular transport?
Which mechanism moves sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell?
Which mechanism moves sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell?
Flashcards
Virus Structure
Virus Structure
Viruses are composed of a nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) and a protein coat (capsid). Their structure can be helical, icosahedral, or complex.
Viral Reproduction
Viral Reproduction
Viruses need a host cell to reproduce, as they cannot reproduce on their own. They hijack the host cell's mechanisms.
Unicellular Organism Types
Unicellular Organism Types
Unicellular organisms include prokaryotes (bacteria, archaea) and eukaryotes (protozoa, algae, some fungi).
Multicellular Organization
Multicellular Organization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organ Systems Coordination
Organ Systems Coordination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open System
Open System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Entropy
Entropy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genetic Material
Genetic Material
Signup and view all the flashcards
Environmental Information
Environmental Information
Signup and view all the flashcards
Signaling Pathways
Signaling Pathways
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes
Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Composition (Organic)
Chemical Composition (Organic)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intramembrane Domains
Intramembrane Domains
Signup and view all the flashcards
Membrane Protein Functions
Membrane Protein Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does 'Fluid Mosaic' mean?
What does 'Fluid Mosaic' mean?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the factors that affect membrane fluidity?
What are the factors that affect membrane fluidity?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are membrane compartments?
What are membrane compartments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why are compartments important?
Why are compartments important?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What stabilizes membrane compartments?
What stabilizes membrane compartments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the plasma membrane do?
What does the plasma membrane do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the glycocalyx help with?
What does the glycocalyx help with?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semi-permeable membrane
Semi-permeable membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Membrane potential
Membrane potential
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to the glycocalyx in cancer cells?
What happens to the glycocalyx in cancer cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uniporter
Uniporter
Signup and view all the flashcards
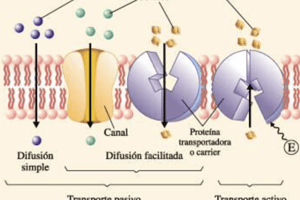
Passive membrane transport
Passive membrane transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osmosis
Osmosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tonicity
Tonicity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Isotonic Solution
Isotonic Solution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active transport
Active transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary active transport
Primary active transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary active transport
Secondary active transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ligand-Gated Ion Channel
Ligand-Gated Ion Channel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enzyme-Linked Receptor
Enzyme-Linked Receptor
Signup and view all the flashcards
G Protein-Coupled Receptor
G Protein-Coupled Receptor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heterotrimeric G Protein
Heterotrimeric G Protein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adenylyl Cyclase Pathway
Adenylyl Cyclase Pathway
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phospholipase C Pathway
Phospholipase C Pathway
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Adhesion
Cell Adhesion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Integrins
Integrins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Biological Organization
- A fundamental basis in medical sciences
- Hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems define life
- Each level of complexity builds on the units of the previous level
Hierarchy of Living Systems
- Organisms differ by their organizational complexity.
- Non-cellular organisms: viruses
- Simple structure: one molecule of nucleic acid (NA) and one type of protein
- Complex structure: one molecule of NA, several types of proteins and other chemical compounds (mostly lipids)
- Viruses rely on host cells for reproduction
- Unicellular organisms
- Prokaryotes (bacteria, archaea)
- Simple cells, lacking membrane-bound organelles
- Precursors to modern eukaryotes
- Eukaryotes (protozoa, unicellular algae, fungi)
- More complex cells with membrane-bound organelles
- Prokaryotes (bacteria, archaea)
- Multicellular organisms
- Most animal and plant species
- Cells with specific functions
- Tissues formed by similar cells
- Organs formed by combinations of tissues
- Organ systems formed from combinations of organs
Cell Theory
- All living things are composed of one or more cells
- Cells are the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms
- Cells come from pre-existing cells (Omnis cellula e cellula).
Cells
- Open systems focused on self-maintenance and reproduction
- Exchange of matter and energy with the environment
- Obtain energy to maintain a stable state
- Genetic material (inherited from the parent cell) stores information for structure and function
- Cells adapt to environmental changes (e.g., chemical composition, presence of nutrients, toxins)
Biochemical Assemblies
- Nucleo-proteins: Association of nucleic acid and protein
- Glyco-proteins: Consist of both proteins and carbohydrates
- Lipo-proteins: Consist of proteins and lipids.
Protein Denaturation
- A protein loses its function when it's denatured.
- Denaturation involves changes to secondary and tertiary structure (but not peptide bonds)
- Denaturation can be reversible or irreversible depending on the conditions.
Enzymes
- Proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions
- Lower activation energy => increased reaction rate
- Are highly specific to their substrates
- Isozymes catalyze the same reaction but differ in amino acid sequence.
- Allosteric Regulation: Enzymes can be regulated.
Cell Signaling
- Govern basic cellular activities and coordinates cell actions
- Signals include hormones, neurotransmitters, and cytokines
- Signals bind to receptors to initiate cascade of cellular responses.
Biomembranes
- Selectively permeable barrier
- Consist of a phospholipid bilayer
- Various proteins embedded (integral and peripheral) for specialized functions
- Cholesterol modulates fluidity.
- Lipids and proteins arranged asymmetrically in the bilayer.
Cell Adhesion and Communication
- Integrins, cadherins, tight, adherens, and gap junctions connect cells and the extracellular matrix.
- Junctions determine cell shape and movement.
Cell Organelles
- Detailed descriptions of various cell organelles, including their structure, functions, and roles in cellular processes.
- Rough ER: protein synthesis.
- Smooth ER: lipid synthesis.
- Golgi apparatus: modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids.
- Lysosomes: contain digestive enzymes.
- Mitochondria: produce energy (ATP) via oxidative phosphorylation.
- Cytoskeleton (microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments): maintaining cell shape and movement.
Cell Division: The Cell Cycle
- Interphase: G1, S, G2 (growth, DNA replication, and preparation for division)
- Mitosis (nuclear division), cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division)
- Control mechanisms (e.g., checkpoints) ensure accuracy and prevent uncontrolled cell growth
DNA and Chromosomes
- Details about chromosome structure, including nucleosomes and chromatin organization
- Various types of chromosomal aberrations
Gametogenesis
- Formation of egg and sperm
- Meiosis (reductional division) produces haploid gametes
- Spermatogenesis (male) and oogenesis (female) pathways
Fertilization
- Union of egg and sperm
- Steps of fertilization
Cell Death
- Apoptosis: programmed cell death, important for development & homeostasis
- Necrosis: uncontrolled cell death, often caused by infections, injuries
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.