Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of glycocalyx in cell membranes?
What is the main function of glycocalyx in cell membranes?
- Prevents contact with inappropriate substances
- Facilitates passive diffusion of ions through the lipid bilayer
- Binds antigens and enzymes to the cell surface (correct)
- Aids in attachment of epithelial cells to the extracellular matrix
In what way does glycocalyx assist T-cells and antigen-presenting cells?
In what way does glycocalyx assist T-cells and antigen-presenting cells?
- Maintaining electrical potential differences
- Facilitating passive diffusion of lipids
- Preventing enzymatic cleavage of receptors and ligands (correct)
- Aiding in cell-cell recognition
How thick can the glycocalyx layer be on the outer surface of the cell membrane?
How thick can the glycocalyx layer be on the outer surface of the cell membrane?
- Up to 70 nm
- Up to 50 nm (correct)
- Up to 30 nm
- Up to 10 nm
Which substance can pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane by simple diffusion?
Which substance can pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane by simple diffusion?
What is the composition of glycocalyx mainly comprised of?
What is the composition of glycocalyx mainly comprised of?
Where is the glycocalyx located in relation to the plasmalemma?
Where is the glycocalyx located in relation to the plasmalemma?
What is the process that occurs down an electrochemical gradient and does not require metabolic energy?
What is the process that occurs down an electrochemical gradient and does not require metabolic energy?
Which scientist is associated with the concept of the Nernst Potential?
Which scientist is associated with the concept of the Nernst Potential?
What type of transport mechanism is not carrier-mediated and occurs down an electrochemical gradient?
What type of transport mechanism is not carrier-mediated and occurs down an electrochemical gradient?
Which factor is directly proportional to the permeability of the cell membrane?
Which factor is directly proportional to the permeability of the cell membrane?
What is the potential inside the membrane that exactly opposes the net diffusion of a particular ion known as?
What is the potential inside the membrane that exactly opposes the net diffusion of a particular ion known as?
Which type of transport mechanism has limitations beyond a certain point?
Which type of transport mechanism has limitations beyond a certain point?
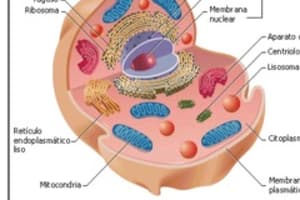
What organelle contains hydrolytic enzymes like acid hydrolases, proteases, and nucleases?
What organelle contains hydrolytic enzymes like acid hydrolases, proteases, and nucleases?
Which organelle is primarily responsible for the extraction of energy from nutrients and ATP production?
Which organelle is primarily responsible for the extraction of energy from nutrients and ATP production?
What is the main function of peroxisomes in liver cells?
What is the main function of peroxisomes in liver cells?
Which vesicle fuses with lysosomes to form digestive vesicles?
Which vesicle fuses with lysosomes to form digestive vesicles?
In which step of ATP production do carbohydrates get converted into glucose?
In which step of ATP production do carbohydrates get converted into glucose?
Which organelle requires a trigger for secretion to occur?
Which organelle requires a trigger for secretion to occur?
What happens when inhibition of Na+, K+ ATPase occurs?
What happens when inhibition of Na+, K+ ATPase occurs?
Which type of transport exhibits stereospecificity, saturation, and competition?
Which type of transport exhibits stereospecificity, saturation, and competition?
What is the term for solutes moving in opposite directions across cell membranes?
What is the term for solutes moving in opposite directions across cell membranes?
Which of the following is an example of a symporter or cotransporter?
Which of the following is an example of a symporter or cotransporter?
What is another term for the Na+ Ca2+ exchanger?
What is another term for the Na+ Ca2+ exchanger?
Which special type of active transport involves moving molecules out of the cell?
Which special type of active transport involves moving molecules out of the cell?
Which type of nerve fibres are large & medium-sized myelinated fibres of spinal nerves?
Which type of nerve fibres are large & medium-sized myelinated fibres of spinal nerves?
What is the function of Type-C Fibres?
What is the function of Type-C Fibres?
At what velocity do the smallest fibers transmit impulses?
At what velocity do the smallest fibers transmit impulses?
What is the main function of Type-A Fibres?
What is the main function of Type-A Fibres?
What is a characteristic of Type-C Fibres?
What is a characteristic of Type-C Fibres?
Which type of nerve fibers are the smallest and can transmit impulses at low velocities?
Which type of nerve fibers are the smallest and can transmit impulses at low velocities?