Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the structure and function of the phospholipid bilayer in the cell membrane?
What is the structure and function of the phospholipid bilayer in the cell membrane?
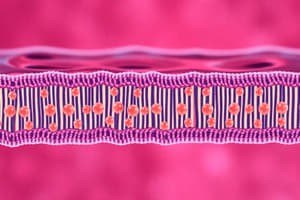
The phospholipid bilayer is composed of two layers of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails facing inward. It acts as a semi-permeable barrier that controls what enters and exits the cell.
Distinguish between integral and peripheral proteins in the cell membrane.
Distinguish between integral and peripheral proteins in the cell membrane.
Integral proteins span the membrane and facilitate transport and communication, while peripheral proteins are loosely attached and provide support or signaling.
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane structure?
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane structure?
Cholesterol helps maintain membrane fluidity and stability, ensuring the membrane does not become too rigid or too fluid under varying temperatures.
How do carbohydrates contribute to the functions of the cell membrane?
How do carbohydrates contribute to the functions of the cell membrane?
Explain how the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids relate to the function of the cell membrane.
Explain how the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids relate to the function of the cell membrane.
What is the significance of membrane proteins in cell signaling?
What is the significance of membrane proteins in cell signaling?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cell Membrane Structure and Functions
-
Phospholipid Bilayer:
- Comprises two layers of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads directed outward and hydrophobic tails facing inward.
- Functions as a semi-permeable barrier, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
-
Proteins:
- Integral Proteins: Span the entire membrane and play critical roles in molecular transport (e.g., channels and pumps) and cell signaling (as receptors).
- Peripheral Proteins: Loosely affixed to the membrane, contributing to structural support and facilitating communication between cells.
-
Cholesterol:
- Vital for maintaining membrane fluidity and stability, preventing excess rigidity or fluidity across varying temperatures.
-
Carbohydrates:
- Typically attached to proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids), crucial for cell recognition, signaling, and mediating interactions among cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.