Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is phagocytosis primarily responsible for?
What is phagocytosis primarily responsible for?
- Transporting small molecules across the membrane
- Engulfing large particles like debris or pathogens (correct)
- Engulfing extracellular fluid
- Removing waste from the cell
Which process is involved in moving large molecules from inside the cell to the outside?
Which process is involved in moving large molecules from inside the cell to the outside?
- Exocytosis (correct)
- Diffusion
- Pinocytosis
- Endocytosis
What is one of the primary functions of the phospholipid bilayer in plant cells?
What is one of the primary functions of the phospholipid bilayer in plant cells?
- Permitting all substances to pass freely
- Facilitating protein synthesis only
- Transporting oxygen exclusively
- Providing structural integrity and barrier function (correct)
How do membrane proteins contribute to cell function?
How do membrane proteins contribute to cell function?
During which process does the plant cell membrane play a vital role in forming new cell walls?
During which process does the plant cell membrane play a vital role in forming new cell walls?
What type of membrane protein creates pores to allow the passage of molecules like ions and water?
What type of membrane protein creates pores to allow the passage of molecules like ions and water?
Which function is NOT attributed to membrane proteins?
Which function is NOT attributed to membrane proteins?
Cell surface identity markers are primarily important for which biological process?
Cell surface identity markers are primarily important for which biological process?
Which of the following proteins is involved in cell-to-cell adhesion?
Which of the following proteins is involved in cell-to-cell adhesion?
Which type of membrane protein binds to hormones and triggers cellular responses?
Which type of membrane protein binds to hormones and triggers cellular responses?
What is the primary role of ATPases in the context of membrane proteins?
What is the primary role of ATPases in the context of membrane proteins?
Which membrane protein allows for the attachment of the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane?
Which membrane protein allows for the attachment of the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane?
Which type of membrane protein is responsible for moving specific molecules across the membrane through processes like facilitated diffusion?
Which type of membrane protein is responsible for moving specific molecules across the membrane through processes like facilitated diffusion?
Which component is not part of cellular membranes?
Which component is not part of cellular membranes?
What characteristic of fatty acids makes them hydrophobic?
What characteristic of fatty acids makes them hydrophobic?
In the fluid mosaic model, what role do transmembrane proteins primarily serve?
In the fluid mosaic model, what role do transmembrane proteins primarily serve?
Which structure is responsible for forming the flexible yet stable barrier of the membrane?
Which structure is responsible for forming the flexible yet stable barrier of the membrane?
What aspect of the phospholipid head enhances its interaction with water?
What aspect of the phospholipid head enhances its interaction with water?
What is the purpose of the porous nature of cell membranes and cell walls?
What is the purpose of the porous nature of cell membranes and cell walls?
What method can be used to separate layers of a membrane to reveal proteins?
What method can be used to separate layers of a membrane to reveal proteins?
What component of plant cells is found outside the cell membrane?
What component of plant cells is found outside the cell membrane?
What distinguishes integral membrane proteins from peripheral membrane proteins?
What distinguishes integral membrane proteins from peripheral membrane proteins?
Which of the following is an example of passive transport?
Which of the following is an example of passive transport?
What type of transport involves molecules moving from a low concentration to a high concentration?
What type of transport involves molecules moving from a low concentration to a high concentration?
Which statement about facilitated diffusion is true?
Which statement about facilitated diffusion is true?
What role do vesicles play in vesicular transport?
What role do vesicles play in vesicular transport?
Which of the following is NOT a type of active transport?
Which of the following is NOT a type of active transport?
How does osmosis differ from diffusion?
How does osmosis differ from diffusion?
In which scenario would primary active transport be utilized?
In which scenario would primary active transport be utilized?
What characterizes a hypertonic solution?
What characterizes a hypertonic solution?
How do plant cells primarily maintain rigidity?
How do plant cells primarily maintain rigidity?
What is the primary function of the sodium-potassium pump?
What is the primary function of the sodium-potassium pump?
Which of the following best describes secondary active transport?
Which of the following best describes secondary active transport?
What is the key mechanism by which paramecia prevent over-expansion?
What is the key mechanism by which paramecia prevent over-expansion?
What is the defining feature of isosmotic regulation in cells?
What is the defining feature of isosmotic regulation in cells?
What is a characteristic of vesicular transport through endocytosis?
What is a characteristic of vesicular transport through endocytosis?
Which function do kidneys perform to maintain blood osmotic balance?
Which function do kidneys perform to maintain blood osmotic balance?
Which type of membrane protein primarily functions by binding to specific molecules to facilitate their movement across the membrane?
Which type of membrane protein primarily functions by binding to specific molecules to facilitate their movement across the membrane?
What role do MHC proteins play in the immune system related to membrane proteins?
What role do MHC proteins play in the immune system related to membrane proteins?
Which membrane proteins are primarily responsible for mediating adhesion between cells?
Which membrane proteins are primarily responsible for mediating adhesion between cells?
How do anchor proteins contribute to cell function in relation to membrane proteins?
How do anchor proteins contribute to cell function in relation to membrane proteins?
Which type of membrane protein functions primarily as an enzyme to facilitate energy transport across the membrane?
Which type of membrane protein functions primarily as an enzyme to facilitate energy transport across the membrane?
What is the primary function of receptor proteins located on the cell surface?
What is the primary function of receptor proteins located on the cell surface?
Which type of membrane protein is crucial for identifying blood types based on surface markers?
Which type of membrane protein is crucial for identifying blood types based on surface markers?
Cell surface proteins that facilitate communication between cells primarily include which of the following?
Cell surface proteins that facilitate communication between cells primarily include which of the following?
Which type of transport specifically requires integral proteins to facilitate the movement of larger or polar molecules?
Which type of transport specifically requires integral proteins to facilitate the movement of larger or polar molecules?
What is true about primary active transport?
What is true about primary active transport?
What distinguishes passive transport from active transport?
What distinguishes passive transport from active transport?
Which of the following statements about osmosis is correct?
Which of the following statements about osmosis is correct?
What best describes vesicular transport?
What best describes vesicular transport?
Which of the following processes is NOT a characteristic of passive transport?
Which of the following processes is NOT a characteristic of passive transport?
In terms of concentration gradients, what defines facilitated diffusion?
In terms of concentration gradients, what defines facilitated diffusion?
Which type of membrane protein is primarily responsible for spanning the entire lipid bilayer?
Which type of membrane protein is primarily responsible for spanning the entire lipid bilayer?
Which process is specifically responsible for a cell taking in extracellular fluid and dissolved substances?
Which process is specifically responsible for a cell taking in extracellular fluid and dissolved substances?
What role do membrane proteins play in signal reception and communication within cells?
What role do membrane proteins play in signal reception and communication within cells?
Which function of the phospholipid bilayer contributes to the structural integrity of plant cells?
Which function of the phospholipid bilayer contributes to the structural integrity of plant cells?
What characterizes the process of exocytosis in cellular function?
What characterizes the process of exocytosis in cellular function?
During which phase of cell activity is the plant cell membrane crucial for forming the new cell wall?
During which phase of cell activity is the plant cell membrane crucial for forming the new cell wall?
How do saltwater fish primarily prevent dehydration?
How do saltwater fish primarily prevent dehydration?
What role do contractile vacuoles play in protists like paramecium?
What role do contractile vacuoles play in protists like paramecium?
Which process directly uses ATP to transport molecules against their concentration gradient?
Which process directly uses ATP to transport molecules against their concentration gradient?
What is the primary mechanism through which glucose is transported into cells in secondary active transport?
What is the primary mechanism through which glucose is transported into cells in secondary active transport?
Which feature distinguishes isosmotic regulation in cells?
Which feature distinguishes isosmotic regulation in cells?
Which is NOT a method used by organisms to maintain osmotic balance?
Which is NOT a method used by organisms to maintain osmotic balance?
What distinguishes a hypotonic solution from isotonic and hypertonic solutions?
What distinguishes a hypotonic solution from isotonic and hypertonic solutions?
What is the primary role of glycerol in the phospholipid structure?
What is the primary role of glycerol in the phospholipid structure?
Which component of the cell membrane is responsible for cell surface identity?
Which component of the cell membrane is responsible for cell surface identity?
How do the heads and tails of phospholipids contribute to membrane structure?
How do the heads and tails of phospholipids contribute to membrane structure?
What characteristic defines the 'fluid' aspect of the fluid mosaic model?
What characteristic defines the 'fluid' aspect of the fluid mosaic model?
Which statement correctly describes the primary difference between ionic and non-ionic diffusion across membranes?
Which statement correctly describes the primary difference between ionic and non-ionic diffusion across membranes?
In microscopy, what does freeze-fracturing techniques primarily reveal?
In microscopy, what does freeze-fracturing techniques primarily reveal?
What property allows phospholipid bilayers to form stable barriers in biological membranes?
What property allows phospholipid bilayers to form stable barriers in biological membranes?
Which type of cells are known to have both a cell membrane and a cell wall?
Which type of cells are known to have both a cell membrane and a cell wall?
Flashcards
Membrane Transporters
Membrane Transporters
Membrane proteins that move materials across the cell membrane.
Membrane Enzymes
Membrane Enzymes
Membrane proteins that catalyze chemical reactions at the membrane surface.
Cell Surface Receptors
Cell Surface Receptors
Membrane proteins that receive signals from outside the cell.
Cell Surface Identity Markers
Cell Surface Identity Markers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell-to-Cell Adhesion Proteins
Cell-to-Cell Adhesion Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Attachment to Cytoskeleton
Attachment to Cytoskeleton
Signup and view all the flashcards
Channel Proteins
Channel Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carrier Proteins
Carrier Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phospholipid Bilayer
Phospholipid Bilayer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrophilic Head
Hydrophilic Head
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrophobic Tail
Hydrophobic Tail
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid Mosaic Model
Fluid Mosaic Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Membrane Proteins
Membrane Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Wall (plants, bacteria, fungi)
Cell Wall (plants, bacteria, fungi)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phospholipid Components
Phospholipid Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are peripheral membrane proteins?
What are peripheral membrane proteins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are integral proteins?
What are integral proteins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Passive transport
Passive transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active transport
Active transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is diffusion?
What is diffusion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is osmosis?
What is osmosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vesicular transport
Vesicular transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypertonic Solution
Hypertonic Solution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypotonic Solution
Hypotonic Solution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Isotonic Solution
Isotonic Solution
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution?
What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution?
What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Active Transport
Primary Active Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Active Transport
Secondary Active Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endocytosis
Endocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Concentration Gradient
Concentration Gradient
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phospholipid Bilayer - Structural Integrity
Phospholipid Bilayer - Structural Integrity
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do transporter proteins do?
What do transporter proteins do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enzymes at the membrane
Enzymes at the membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell-to-Cell Adhesion
Cell-to-Cell Adhesion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why are phospholipids important for cell membranes?
Why are phospholipids important for cell membranes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are membrane proteins?
What are membrane proteins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Wall
Cell Wall
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is freeze-fracturing?
What is freeze-fracturing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is concentration?
What is concentration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a concentration gradient?
What is a concentration gradient?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is exocytosis?
What is exocytosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is the phospholipid bilayer important?
Why is the phospholipid bilayer important?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What role does the phospholipid bilayer play in plant cell division?
What role does the phospholipid bilayer play in plant cell division?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osmosis
Osmosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contractile Vacuole
Contractile Vacuole
Signup and view all the flashcards
Turgor Pressure
Turgor Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Membrane Proteins
Types of Membrane Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does Endocytosis do?
What does Endocytosis do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Phospholipid Bilayer and Membranes
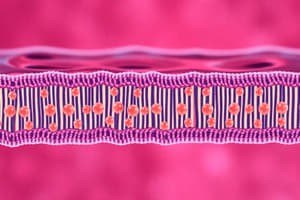
- Phospholipid bilayer is a fundamental structure in biological membranes, including plant cells.
- It's composed of two layers of phospholipids, arranged tail-to-tail, creating a flexible but stable barrier.
- Phospholipid components:
- Heads are polar (hydrophilic).
- Tails are nonpolar (hydrophobic).
Phospholipid Bilayer Structure
- Glycerol, a 3-carbon polyalcohol, forms the backbone of the phospholipid.
- Two fatty acids attach to the glycerol.
- A phosphate group is attached to the glycerol.
- Fatty acid chains are nonpolar, hydrophobic (water-fearing).
- The phosphate group is polar, hydrophilic (water-loving).
Membrane Proteins
- Membrane proteins are embedded within or attached to the phospholipid bilayer.
- They perform various functions:
- Transporters
- Enzymes
- Cell surface receptors
- Cell surface identity markers
- Cell-to-cell adhesion proteins
- Attachments to the cytoskeleton
Types of Membrane Proteins
- Peripheral proteins:
- Loosely associated with the membrane surface, not spanning the lipid bilayer.
- Do not interact with the hydrophobic core.
- Often attached to integral proteins or lipid heads.
- Water-soluble and can be removed with changing salt concentrations or pH.
- Integral proteins:
- Embedded within the lipid bilayer.
- Some span the entire membrane (transmembrane).
- Directly interact with the hydrophobic core.
- Typically insoluble in water, need detergents for extraction.
Membrane Transport
- Passive Transport: Molecules move from high to low concentration.
- Diffusion: Movement of molecules through the lipid bilayer.
- Example: Oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Facilitated Diffusion: Movement of larger/polar molecules through integral proteins.
- Example: Glucose via glucose transporter.
- Osmosis: Specific type of facilitated diffusion for water.
- Aquaporins often facilitate.
- Water moves from dilute to concentrated solutions.
- Diffusion: Movement of molecules through the lipid bilayer.
- Active Transport: Molecules move against their concentration gradient (low to high).
- Primary active transport: Direct use of energy (ATP) for transport.
- Example: Sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+ pump).
- Secondary active transport: Uses energy from ion gradients created by primary active transport.
- Example: Sodium-glucose symporter.
- Primary active transport: Direct use of energy (ATP) for transport.
Vesicular Transport
- Endocytosis: Taking in material from outside the cell by forming a vesicle.
- Phagocytosis: Engulfing large particles (e.g., bacteria)
- Pinocytosis: Engulfing extracellular fluid and dissolved substances.
- Exocytosis: Moving molecules/waste from inside the cell to outside through vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane.
- Example: Secretion of hormones, neurotransmitters.
Terms to Know
- Concentration: Amount of solute in a solution.
- Solute: Dissolved substance.
- Solution: Mixture of two or more substances.
- Concentration gradient: Gradual difference in solute concentration between regions.
Importance of Phospholipid Bilayer and Membranes in Plants
- Structural Integrity and Barrier Function: Forms the basic structure of the cell membrane.
- Selective Permeability: Regulates passage of substances (water, ions, small molecules) in and out of the cell.
- Signal Reception and Communication: Membrane proteins involved in signal transduction.
- Cell-Cell Communication and Interaction: Thylakoid membranes in chloroplasts contain proteins/pigments important for photosynthesis.
- Role in Cell Growth and Division: Essential for new cell wall formation during division.
- Protection Against Pathogens: Acts as first line of defense against pathogens/environmental stress.
How Organisms Deal with Osmotic Pressure
- Bacteria & Plants: Cell walls prevent over-expansion.
- Protists (e.g., Paramecium): Contractile vacuoles remove excess water.
- Saltwater Fish: Specialized gills pump out salt.
- Animal Cells: Kidneys maintain blood isotonic balance.
Osmotic Solutions
- Hypertonic solution: Higher solute concentration than another.
- Hypotonic solution: Lower solute concentration than another.
- Isotonic solution: Same solute concentration as another.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.