Podcast
Questions and Answers
What aspect of cell membranes is emphasized in Cooper's text?
What aspect of cell membranes is emphasized in Cooper's text?
- Membrane transport proteins
- Cell membrane dynamics (correct)
- Membrane lipid composition
- Membrane associated diseases
Which textbook extensively discusses the pathophysiology of myocardial infarction?
Which textbook extensively discusses the pathophysiology of myocardial infarction?
- The Cell: A Molecular Approach
- Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease
- Braunwald's Heart Disease (correct)
- Molecular Biology of the Cell
In which publication can one find an overview of inflammatory processes in muscle injury?
In which publication can one find an overview of inflammatory processes in muscle injury?
- Skeletal Muscle Structure, Function, and Plasticity
- Molecular Biology of the Cell
- The Cell: A Molecular Approach
- Inflammatory processes in muscle injury and repair (correct)
What key process is highlighted in Kumar, Abbas, and Aster's textbook?
What key process is highlighted in Kumar, Abbas, and Aster's textbook?
Which book primarily focuses on skeletal muscle physiology and trauma responses?
Which book primarily focuses on skeletal muscle physiology and trauma responses?
What is the primary role of phospholipids in cell membranes?
What is the primary role of phospholipids in cell membranes?
What is a consequence of direct trauma to membrane proteins?
What is a consequence of direct trauma to membrane proteins?
Which of the following best describes the interaction between the cell membrane and cytoskeleton?
Which of the following best describes the interaction between the cell membrane and cytoskeleton?
In the context of mitochondrial dynamics, what happens during ischemia and reperfusion?
In the context of mitochondrial dynamics, what happens during ischemia and reperfusion?
How does the immune system respond to cellular injury?
How does the immune system respond to cellular injury?
What is a potential complication of persistent inflammation and ineffective repair?
What is a potential complication of persistent inflammation and ineffective repair?
What is a key pathophysiological mechanism involved in myocardial infarction?
What is a key pathophysiological mechanism involved in myocardial infarction?
Which of the following describes the excitation-contraction coupling mechanism in skeletal muscle?
Which of the following describes the excitation-contraction coupling mechanism in skeletal muscle?
What is the primary composition of the cell membrane?
What is the primary composition of the cell membrane?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the cell membrane?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the cell membrane?
How does the cytoskeleton contribute to the cell membrane?
How does the cytoskeleton contribute to the cell membrane?
What effect can physical trauma have on the cell membrane?
What effect can physical trauma have on the cell membrane?
Which downstream effect can result from membrane damage?
Which downstream effect can result from membrane damage?
Why is membrane integrity critical for cellular homeostasis?
Why is membrane integrity critical for cellular homeostasis?
What type of structure is the phospholipid bilayer considered?
What type of structure is the phospholipid bilayer considered?
What role do membrane proteins play in the cell membrane?
What role do membrane proteins play in the cell membrane?
Which of the following best describes the cell membrane's function in energy production?
Which of the following best describes the cell membrane's function in energy production?
What is a consequence of disrupted membrane integrity?
What is a consequence of disrupted membrane integrity?
What is a potential complication of prolonged medication use related to liver function?
What is a potential complication of prolonged medication use related to liver function?
What role does IGF/FGF play in muscle regeneration?
What role does IGF/FGF play in muscle regeneration?
What consequence results from excessive TNFα/IL-1β levels in muscular injury?
What consequence results from excessive TNFα/IL-1β levels in muscular injury?
What event triggers action potentials in cardiomyocytes?
What event triggers action potentials in cardiomyocytes?
What is a significant outcome following myocardial infarction due to arterial blockage?
What is a significant outcome following myocardial infarction due to arterial blockage?
What mechanism describes the primary method of cardiac repair post-myocardial infarction?
What mechanism describes the primary method of cardiac repair post-myocardial infarction?
What consequence does poorly maintained collagen turnover during myocardial repair have?
What consequence does poorly maintained collagen turnover during myocardial repair have?
What is the consequence of prolonged elevated intracellular calcium in muscle cells?
What is the consequence of prolonged elevated intracellular calcium in muscle cells?
What is a common result of ischemia-induced remodelling in cardiac tissue?
What is a common result of ischemia-induced remodelling in cardiac tissue?
What symptom was exhibited by the patient with exertional rhabdomyolysis following their long run?
What symptom was exhibited by the patient with exertional rhabdomyolysis following their long run?
What primarily causes localized openings or defects in the plasma membrane following direct trauma?
What primarily causes localized openings or defects in the plasma membrane following direct trauma?
Which of the following best describes how direct trauma affects integral proteins in the plasma membrane?
Which of the following best describes how direct trauma affects integral proteins in the plasma membrane?
What is a consequence of calcium overload during ischemia?
What is a consequence of calcium overload during ischemia?
How do anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a affect vascular permeability?
How do anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a affect vascular permeability?
What triggers the release of cytochrome c during mitochondrial permeability transition?
What triggers the release of cytochrome c during mitochondrial permeability transition?
During muscle tear pathophysiology, what effect does eccentric contraction have on the sarcomere structure?
During muscle tear pathophysiology, what effect does eccentric contraction have on the sarcomere structure?
What is the primary role of integrins in focal adhesions?
What is the primary role of integrins in focal adhesions?
Which of the following describes the function of choline/phosphate head groups in membrane lipids?
Which of the following describes the function of choline/phosphate head groups in membrane lipids?
What initiates the apoptotic cascade following loss of mitochondrial integrity?
What initiates the apoptotic cascade following loss of mitochondrial integrity?
What is the impact of shear and compression forces on membrane lipid organization?
What is the impact of shear and compression forces on membrane lipid organization?
Flashcards
Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane
The outer boundary of a cell, composed primarily of a phospholipid bilayer, which controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Cell Membrane Disruption
Cell Membrane Disruption
The process of injury or damage to the cell membrane, disrupting its structural integrity and compromising its selective permeability.
Signaling Cascade in Muscle Injury
Signaling Cascade in Muscle Injury
A series of interconnected events triggered by cell membrane disruption, involving signaling molecules and pathways that ultimately lead to cellular responses.
Skeletal Muscle Injury
Skeletal Muscle Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Muscle Injury
Cardiac Muscle Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apoptosis
Apoptosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tissue Repair
Tissue Repair
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrosis
Fibrosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Membrane Function
Cell Membrane Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial Infarction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Injury and Repair
Muscle Injury and Repair
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellular Injury
Cellular Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflammation
Inflammation
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the plasma membrane?
What is the plasma membrane?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does direct trauma affect membrane lipids?
How does direct trauma affect membrane lipids?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explain how trauma affects integral proteins.
Explain how trauma affects integral proteins.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are focal adhesions?
What are focal adhesions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does lateral pressure affect membrane integrity?
How does lateral pressure affect membrane integrity?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are mitochondria?
What are mitochondria?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does ischemia affect ATP production?
How does ischemia affect ATP production?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does ischemia cause calcium overload?
How does ischemia cause calcium overload?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)?
What are Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the mitochondrial permeability transition?
What is the mitochondrial permeability transition?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid bilayer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Membrane proteins
Membrane proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid mosaic model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cytoskeleton's role in membrane structure
Cytoskeleton's role in membrane structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physical trauma and membrane disruption
Physical trauma and membrane disruption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Effect of membrane damage on mitochondria
Effect of membrane damage on mitochondria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflammation response to membrane damage
Inflammation response to membrane damage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tissue repair mechanisms
Tissue repair mechanisms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of membrane integrity
Importance of membrane integrity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Regeneration
Muscle Regeneration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrosis in Muscle Injury
Fibrosis in Muscle Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcium Toxicity in Muscle Cells
Calcium Toxicity in Muscle Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiomyocyte Structure and Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Cardiomyocyte Structure and Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology
Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Repair After Myocardial Infarction
Cardiac Repair After Myocardial Infarction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction
Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Membrane: Interface of Cellular Integrity and Injury
Cell Membrane: Interface of Cellular Integrity and Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflammation and Cell Death Pathways in Muscle Injury
Inflammation and Cell Death Pathways in Muscle Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Injury: Molecular Insights
Muscle Injury: Molecular Insights
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
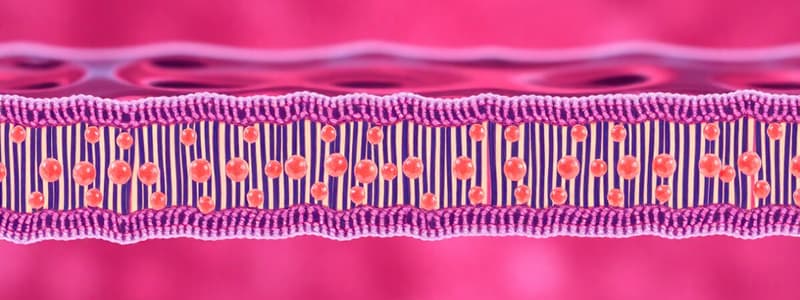
Cell Membrane Structure and Function
- The cell membrane is a dynamic and complex structure, critical for cell life.
- It acts as a boundary between the cell's internal and external environments.
- Primarily composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
- Controls the passage of substances into and out of the cell.
- Maintains cellular homeostasis, signaling, and energy production.
- The cell membrane's integrity is vital.
Learning Outcomes
- Gain a comprehensive understanding of cell membrane composition and architecture, including the role of phospholipids.
- Analyze the effects of physical trauma on the membrane's integrity and permeability.
- Understand the interplay between the cell membrane and cytoskeleton during stress.
- Learn about membrane protein functions and direct trauma consequences.
- Investigate cellular responses to trauma including inflammation and apoptosis.
- Understand the structural organization and importance of mitochondria in cellular metabolism.
- Analyze clinical cases related to muscle and myocardial injury.
- Discuss implications of ischemia and reperfusion on mitochondrial function and reactive oxygen species generation.
Membrane Composition and Structure
- The membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails inward.
- Proteins are embedded in the membrane, having diverse functions including transport, signaling, and cell recognition.
- Specialized proteins like glycoproteins and glycolipids function in cell communication and recognition.
- Cholesterol contributes to membrane fluidity and stability.
Overview
- Introduction to the molecular mechanisms involved in cell membrane disruption.
- Detailing the signaling cascade during muscle injury.
- Covering skeletal and cardiac muscle injury.
- Clinical case presentations highlighting injury mechanisms.
Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Membrane Disruption
- Chemical disruption through lipid peroxidation and enzymatic cleavage alters membrane fluidity.
- Physical breaches such as nanoruptures and membrane tears disrupt the phospholipid bilayer, causing cytosol leaks.
- Pore formation creates gaps in the membrane due to physical trauma.
Effects on Membrane Lipid Organisation
- Direct trauma (shear/compression) disrupts lipid tail packing.
- Physical forces break non-covalent interactions between neighboring lipid tails.
- Lipid separation leads to membrane openings where cytosol leaks and selective permeability is lost.
Effects on Membrane Integral Proteins
- Transmembrane domains embedded in the phospholipid bilayer anchor proteins in place.
- Hydrophobic interactions maintain protein tertiary structure within the membrane.
- Direct impact and shearing forces distort protein conformations, displacing transmembrane helices.
- Peripheral domains detach from the membrane, affecting protein function (transport, signaling).
Effects on Membrane-Cytoskeleton Interactions
- Focal adhesions contain integrin heterodimers that interact with actin fibers.
- Integrin cytoplasmic domains attach to actin via adapter proteins.
- Forces parallel to the membrane strain these integrin complexes, leading to cytoskeleton detachment.
Increased Lateral Pressure on Membrane
- Actin transmits force across membrane integrins putting strain on the cell membrane.
- Lipids are stretched beyond tolerable thinning pressure, causing them to separate and no longer pack tightly.
Detachment of Cytoskeleton from Membrane
- Strong perpendicular strain overcomes integrin-actin binding strength.
- Detaches entire cytoskeletal scaffold from focal adhesions.
- Alteration of lipid fluidity from removed constraints.
- Changes in membrane curvature and cellular mechanotransduction.
Mitochondrial Structure and Function
- Inner and outer mitochondrial membranes enclose cristae and matrix.
- Cristae contain the electron transport chain complexes.
- Glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation occur within mitochondria.
- Essential for ATP production via oxidative phosphorylation.
Ischemia Halts ATP Production
- Loss of blood flow cuts off oxygen (O2), the final electron acceptor.
- Inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, halting electron transport.
- Stops ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation.
Calcium Overload During Ischemia
- Lack of ATP inhibits Na+/K+ and Ca2+ ATPases.
- Intracellular and mitochondrial Ca2+ concentrations rise sharply, causing damage.
Reactive Oxygen Species Burst
- Reperfusion reintroduces oxygen, leading to xanthine oxidase pathway activation.
- Damaged electron carriers in the electron transport chain leak electrons to oxygen, producing superoxide radicals (O2-) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
- These reactive oxygen species cause damage to the cell.
Mitochondrial Permeability Transition
- High Ca2+ triggers the opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pores.
- Collapses the proton gradient and membrane potential.
- Facilitates the release of molecules damaging the cell.
Cytochrome C Release
- Loss of inner membrane integrity releases cytochrome c.
- Triggers caspase cascade, leading to apoptosis.
Activation of Complement System & Increased Vascular Permeability
- Cell membrane damage exposes cellular antigens and phospholipids.
- Activates complement system.
- Anaphylatoxins bind to endothelial cells (C3a and C5a)
- Stimulates actin cytoskeleton contraction and junction widening.
Neutrophil Recruitment & Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Release
- Chemokines and cytokines induce selectins and integrins.
- Resulting in neutrophil tethering, rolling, adhesion, and transmigration.
- Neutrophils and macrophages secrete inflammatory mediators (TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) to amplify response.
Skeletal Muscle Structure, Excitation-Contraction Coupling & Muscle Tear Pathophysiology
- Striated muscle cells with basal lamina and connective tissue sheath.
- Multinucleated fibers formed by myoblast fusion.
- Neuromuscular junction depolarization triggers inward calcium current.
- Calcium binds troponin C, exposing binding sites on actin for myosin cross-bridges.
- Direct blunt force or eccentric contraction leads to sarcomere stretching beyond limits.
- Ruptures Z-disks, pulling apart actin-myosin filaments.
Mechanisms of Rhabdomyolysis
- Prolonged ischemia exhausts energy stores and Na+/K+ ATPase function.
- Sarcoplasmic calcium accumulation triggers proteolysis of contractile proteins.
Clinical Case of Quadriceps Tear
- 28M presents with acute thigh pain after a rugby tackle.
- Unable to fully extend knee, crepitus present.
- MRI shows a partial distal quadriceps tendon tear.
- A 23-year-old male presents with left thigh pain following a soccer injury.
- Examination reveals a swollen thigh and inability to fully extend the knee.
- Compartment syndrome is suspected as a likely diagnosis.
Clinical Case of Medication Complication
- Female taking medication following a heart attack.
- Increased fatigue and swelling of legs observed.
- Hepatotoxicity from the medication is a potential complication.
Inflammation and Membrane Repair, Satellite Cell Activation & Regeneration of Myofibers
- Damaged membranes activate kinin-kallikrein and complement pathways.
- Neutrophils clear debris and release TGFβ/IGF for regeneration.
- IGF/FGF stimulates quiescent satellite cells adjacent to basal lamina.
- Satellite cells proliferate, fuse, and differentiate into new myofibers.
- Myotubes align, fuse nuclei, and reform motor endplates.
Persistent Inflammation Complications & Clinical Case of Exertional Rhabdomyolysis
- Excessive TNFα/IL-1β causes fibrosis instead of regeneration.
- Transforming growth factor beta promotes collagen deposition.
- A 42-year-old female collapsing after a long run, with tea-colored urine, and elevated CK (100,000 U/L).
- Demonstrates acute kidney injury.
Membrane Disruption in Ca2+ Toxicity & Proteolytic Degradation of Muscle
- High intracellular Ca2+ activates phospholipases and proteases.
- Leads to phospholipid hydrolysis and membrane protein denaturation.
- Calpains and cathepsins cleave cytoskeletal and contractile proteins.
- Triggers oncosis and myoglobin/protein release into the bloodstream.
Cardiomyocyte Structure & Excitation-Contraction Coupling
- Branched, striated cardiomyocytes connected via intercalated discs.
- Higher mitochondria content for aerobic metabolism.
- SA node pacemaker potential activates action potentials.
- Voltage gated L-type Ca2+ channels open, allowing calcium to enter the cytoplasm.
Pathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction & Clinical Case of STEMI
- Coronary artery plaque rupture causes thrombosis and vessel occlusion.
- Ischemia and calcium/ROS mediate membrane damage downstream.
- 62M presents with crushing chest pain radiating to the left arm.
- EKG shows ST elevations in lateral leads, elevated troponin.
- Cardiac resynchronisation therapy is the appropriate management strategy.
Physiological Repair After MI, Limitations of Cardiomyocyte Regeneration & Arrhythmias After MI
- Inflammation clears necrotic myocytes.
- Fibroblasts deposit collagen scar tissue in infarcted areas.
- Post-mitotic cardiomyocytes have limited proliferation after early neonatal period.
- Repair by surviving cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.
- Ischemia-induced connexin remodeling causes non-uniform repolarization.
- Substrate for reentry circuits leads to lethal ventricular arrhythmias.
Heart Failure After MI & Molecular Basis of Cardiac Rupture
- Loss of contractile tissue leads to compensated dilation and hypertrophy.
- Eventually leads to dilated cardiomyopathy if the defect is substantial.
- Imbalance in collagen turnover during repair weakens the infarct zone.
- Scar tissue might rupture due to inability to withstand wall stress during contraction.
Summary
- Cell membrane serves as an interface for cellular integrity and injury.
- Traumatic impacts and ischemic repercussions have significant consequences.
- Inflammatory response and cell death pathways in muscle injury are outlined.
- Clinical cases illustrate muscle injury from molecular insights.
- Cardiac muscles have specific responses to injury.
- Comparative molecular insights to injury are explored.
- Concluding thoughts on the presented material.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.