Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary inorganic component of the bone matrix?
What is the primary inorganic component of the bone matrix?
- Amorphous Calcium Phosphate
- Magnesium
- Type 1 collagen
- Calcium hydroxypatite (correct)
Which component is predominantly found in the organic matter of the bone matrix?
Which component is predominantly found in the organic matter of the bone matrix?
- Calcium-binding proteins
- Amorphous Calcium Phosphate
- Proteoglycans (correct)
- Hydroxyapatite
What role do glycoproteins like osteonectin play in the bone matrix?
What role do glycoproteins like osteonectin play in the bone matrix?
- Promote osteoblast differentiation
- Regulate collagen synthesis
- Facilitate mineralization (correct)
- Enhance osteoclast activity
Which of the following statements about bone cells is correct?
Which of the following statements about bone cells is correct?
Which of the following elements is NOT a major component of the inorganic matter in the bone matrix?
Which of the following elements is NOT a major component of the inorganic matter in the bone matrix?
What is the primary function of bone as described in the content?
What is the primary function of bone as described in the content?
Which statement about primary bone tumors is correct?
Which statement about primary bone tumors is correct?
What role do bone cells play in the context of osteosarcoma?
What role do bone cells play in the context of osteosarcoma?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the composition of bone?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the composition of bone?
What is a key characteristic of metastatic bone tumors?
What is a key characteristic of metastatic bone tumors?
What specifies the levers in the skeletal system?
What specifies the levers in the skeletal system?
What happens when cancer cells spread to bones from other malignancies?
What happens when cancer cells spread to bones from other malignancies?
What vital roles does bone serve in ion storage?
What vital roles does bone serve in ion storage?
What structural characteristic of osteoclasts facilitates their function in bone resorption?
What structural characteristic of osteoclasts facilitates their function in bone resorption?
What is the primary defect in osteopetrosis that impacts bone health?
What is the primary defect in osteopetrosis that impacts bone health?
Which type of bone structure contains osteoclasts responsible for matrix resorption?
Which type of bone structure contains osteoclasts responsible for matrix resorption?
Osteopetrosis is characterized by which of the following conditions?
Osteopetrosis is characterized by which of the following conditions?
What is the role of the cytoplasmic zone surrounding the osteoclasts during the resorption process?
What is the role of the cytoplasmic zone surrounding the osteoclasts during the resorption process?
What might result from the obliteration of marrow cavities due to osteopetrosis?
What might result from the obliteration of marrow cavities due to osteopetrosis?
What is one of the primary functions of osteoclasts in bone remodeling?
What is one of the primary functions of osteoclasts in bone remodeling?
How does the ruffled border of osteoclasts change during bone resorption?
How does the ruffled border of osteoclasts change during bone resorption?
What percentage of total bone mass does compact (cortical) bone constitute?
What percentage of total bone mass does compact (cortical) bone constitute?
Which type of bone is characterized by a random disposition of collagen fibers?
Which type of bone is characterized by a random disposition of collagen fibers?
Which type of bone is primarily found in adults and is organized into layers?
Which type of bone is primarily found in adults and is organized into layers?
What unique feature do osteons possess that allows communication between them?
What unique feature do osteons possess that allows communication between them?
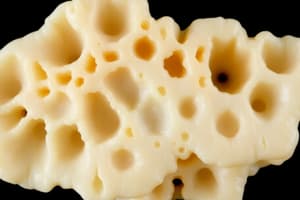
Where is cancellous bone primarily located within long bones?
Where is cancellous bone primarily located within long bones?
Which bone development process involves the differentiation of osteoblasts?
Which bone development process involves the differentiation of osteoblasts?
What characteristic of woven bone contributes to its lower strength compared to lamellar bone?
What characteristic of woven bone contributes to its lower strength compared to lamellar bone?
Which of the following statements is true about the relationship between trabecular bone and endosteum?
Which of the following statements is true about the relationship between trabecular bone and endosteum?
What role do osteocytes play in response to mechanical loads on bone?
What role do osteocytes play in response to mechanical loads on bone?
What characterizes the cellular structure of osteoclasts?
What characterizes the cellular structure of osteoclasts?
In which population is osteoporosis most frequently found?
In which population is osteoporosis most frequently found?
What is the primary result of the imbalance between resorption and bone formation in osteoporosis?
What is the primary result of the imbalance between resorption and bone formation in osteoporosis?
What is the function of the lacunar-canalicular network in osteocytes?
What is the function of the lacunar-canalicular network in osteocytes?
What is the primary function of mechanostat regarding bone health?
What is the primary function of mechanostat regarding bone health?
Which statement is true regarding the relationship between exercise and bone density?
Which statement is true regarding the relationship between exercise and bone density?
What is a consequence of immobilization on bone health?
What is a consequence of immobilization on bone health?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Overview of Bone
- Bone forms the skeletal system, serving as specialized connective tissue consisting of bone matrix and bone cells.
- Provides structural support, protects vital organs, and acts as a reservoir for calcium, phosphate, and other ions.
- Functions as levers that amplify forces during muscular contraction, enabling bodily movements.
- Primary bone tumors, such as osteosarcoma, originate from osteoprogenitor cells, but most bone tumors are metastatic.
Bone Matrix
- Composed of calcified extracellular materials, including inorganic (50%) and organic components.
- Inorganic matter includes calcium hydroxypatite, magnesium, potassium, sodium, and amorphous calcium phosphate.
- Organic matter consists of type 1 collagen, proteoglycans, glycoproteins, osteonectin, osteocalcin, and matrix vesicles promoting calcification.
- Resorption of calcified bone is essential during growth and remodeling, facilitated by osteoclasts residing in resorption cavities.
Osteocytes
- Enclosed within lacunae, osteocytes extend dendritic processes, forming a lacunar-canalicular network and enabling mechanotransduction.
- Act as sensors for mechanical loads, helping adjust the bone matrix based on stress and microdamage (mechanostat).
- Most abundant cell type in bone, crucial for maintaining bone health and density.
Osteoclasts
- Multinucleated giant cells that remove calcified bone matrix and remodel bone tissue.
- Integral to the bone resorption process, helping regulate bone density and health.
Types of Bone
- Compact Bone: Constitutes 80% of total bone mass; dense and located near the surface beneath the periosteum.
- Cancellous Bone (Spongy Bone): Makes up 20% of total bone mass; features numerous interconnecting cavities adjacent to marrow.
- Lamellar Bone: Predominant in adults; structured in layers (lamellae) around a central canal (osteon or Haversian canal).
- Woven Bone: Nonlamellar form with random collagen disposition; first to appear during embryonic development and fracture repair; replaced by lamellar bone in adults except in calvaria.
Bone Structure
- Epiphyses: Bulbous ends of long bones composed of spongy bone covered by a thin layer of compact bone.
Osteogenesis
- Refers to bone development processes, particularly involving the differentiation of osteoblasts during intramembranous ossification.
Bone-Related Conditions
- Osteopetrosis: Genetic disorder characterized by dense, marbled bones due to defective osteoclast function.
- Osteoporosis: Common in immobilized patients and postmenopausal women; involves bone resorption exceeding formation, resulting in decreased bone mineral density and calcium loss.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.