Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the classification of the Temporomandibular joint, in regards to its structure?
What is the classification of the Temporomandibular joint, in regards to its structure?
- Ball and socket joint
- Simple joint
- Complex joint
- Composite joint (correct)
What is the classification of the Temporomandibular joint, based on its form?
What is the classification of the Temporomandibular joint, based on its form?
- Condylar joint (correct)
- Hinge joint
- Pivot joint
- Plane joint
What is the name of the elastic ligament that extends from the Processus retroarticularis to Collum mandibulae in equids, and ruminants?
What is the name of the elastic ligament that extends from the Processus retroarticularis to Collum mandibulae in equids, and ruminants?
- Lig. dorsale
- Lig. laterale
- Lig. caudale (correct)
- Lig. ventrale
What is the name of the ligament located on the lateral surface of the joint capsule of the Temporomandibular joint?
What is the name of the ligament located on the lateral surface of the joint capsule of the Temporomandibular joint?
What type of joint is the Atlanto-occipital joint?
What type of joint is the Atlanto-occipital joint?
What type of joint is the Atlanto-axial joint?
What type of joint is the Atlanto-axial joint?
Which of the following ligaments connects the Tuberculum dorsale of the atlas to the Processus spinosus of the axis?
Which of the following ligaments connects the Tuberculum dorsale of the atlas to the Processus spinosus of the axis?
Which of the following ligaments connects the Tuberculum ventrale of the atlas to the Crista ventralis of the axis in equids and ruminants?
Which of the following ligaments connects the Tuberculum ventrale of the atlas to the Crista ventralis of the axis in equids and ruminants?
What are the two main types of joints found in the vertebral column?
What are the two main types of joints found in the vertebral column?
What is the name of the ligament that supports much of the weight of the head, relieving the load from the head and neck musculature?
What is the name of the ligament that supports much of the weight of the head, relieving the load from the head and neck musculature?
Which of the following is caused by the rupture or degeneration of a disc in the vertebral column?
Which of the following is caused by the rupture or degeneration of a disc in the vertebral column?
What type of joint is the Costovertebral joint?
What type of joint is the Costovertebral joint?
What does the term "synsarcosis" refer to?
What does the term "synsarcosis" refer to?
What is the classification, based on form, of the Shoulder joint (articulatio humeri)?
What is the classification, based on form, of the Shoulder joint (articulatio humeri)?
What is the classification of the Elbow joint (articulatio cubiti) based on its number of components?
What is the classification of the Elbow joint (articulatio cubiti) based on its number of components?
What type of joint is the Radioulnar articulation in dogs and cats?
What type of joint is the Radioulnar articulation in dogs and cats?
What is the classification of the Carpal joint (articulatio carpi), based on its form?
What is the classification of the Carpal joint (articulatio carpi), based on its form?
Which of the following joints forms the connection between the radius and ulna, and the proximal carpal bones?
Which of the following joints forms the connection between the radius and ulna, and the proximal carpal bones?
Which joint is formed by the articulation between the proximal and distal carpal bones?
Which joint is formed by the articulation between the proximal and distal carpal bones?
Which of the following joints allows the articulation between the individual carpal bones?
Which of the following joints allows the articulation between the individual carpal bones?
Which joint allows the articulation between the distal carpal bones and the metacarpal bones?
Which joint allows the articulation between the distal carpal bones and the metacarpal bones?
What type of joint is the Metacarpophalangeal joint?
What type of joint is the Metacarpophalangeal joint?
What type of joint is the Proximal Interphalangeal joint?
What type of joint is the Proximal Interphalangeal joint?
What type of joint is the Distal Interphalangeal joint?
What type of joint is the Distal Interphalangeal joint?
What are the two elastic cords that extend across the dorsal part of the Distal Interphalangeal joint, responsible for passively keeping the claws retracted?
What are the two elastic cords that extend across the dorsal part of the Distal Interphalangeal joint, responsible for passively keeping the claws retracted?
What is the classification, based on its form, of the Sacroiliac joint?
What is the classification, based on its form, of the Sacroiliac joint?
Which of the following joins are considered tight joints?
Which of the following joins are considered tight joints?
What kind of joint is the Coxofemoral or Hip joint (articulatio coxae)?
What kind of joint is the Coxofemoral or Hip joint (articulatio coxae)?
What is the name of the fibrocatilaginous rim that enlarges the acetabulum of the Hip joint?
What is the name of the fibrocatilaginous rim that enlarges the acetabulum of the Hip joint?
What is the classification, based on form, of the Stifle joint?
What is the classification, based on form, of the Stifle joint?
Which part of the Stifle joint acts as a sledge joint, allowing for gliding movements?
Which part of the Stifle joint acts as a sledge joint, allowing for gliding movements?
What is the classification, based on its number of components, of the Stifle joint?
What is the classification, based on its number of components, of the Stifle joint?
Which type of joint is formed between the tibia and fibula in carnivores?
Which type of joint is formed between the tibia and fibula in carnivores?
Which type of joint is formed between the tibia and fibula in ruminants?
Which type of joint is formed between the tibia and fibula in ruminants?
Which type of joint is formed between the tibia and fibula in horses?
Which type of joint is formed between the tibia and fibula in horses?
What is the classification, based on form, of the Tarsocrural joint?
What is the classification, based on form, of the Tarsocrural joint?
Which joint is responsible for the articulation between the tibia and the tarsal bones?
Which joint is responsible for the articulation between the tibia and the tarsal bones?
Which joint is responsible for the articulation between the proximal tarsal bones?
Which joint is responsible for the articulation between the proximal tarsal bones?
Which joint is responsible for the articulation between the distal tarsal bones?
Which joint is responsible for the articulation between the distal tarsal bones?
Which joint is responsible for the articulation between the tarsal bones and the metatarsal bones?
Which joint is responsible for the articulation between the tarsal bones and the metatarsal bones?
Which of the following joints is NOT found in the hind limb?
Which of the following joints is NOT found in the hind limb?
What is the classification of the avian shoulder joint, based on its structure?
What is the classification of the avian shoulder joint, based on its structure?
What are the two components of the avian hip joint?
What are the two components of the avian hip joint?
The avian shoulder joint is similar to the mammalian shoulder joint in its structure.
The avian shoulder joint is similar to the mammalian shoulder joint in its structure.
The avian hip joint is composed of a single articulation.
The avian hip joint is composed of a single articulation.
Flashcards
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
A complex joint that allows for opening and closing of the mouth, along with limited side-to-side and forward/backward movement of the jaw.
Composite Joint
Composite Joint
A joint formed by more than two bony surfaces.
Condylar Joint
Condylar Joint
A type of joint characterized by an ovoid condyle of one bone fitting into an elliptical cavity of another; permitting movement in two planes.
Nuchal Ligament
Nuchal Ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atlanto-occipital Joint
Atlanto-occipital Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atlanto-axial Joint
Atlanto-axial Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pivot Joint
Pivot Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ellipsoidal Joint
Ellipsoidal Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intervertebral Articulations
Intervertebral Articulations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Long Ligaments
Long Ligaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Short Ligaments
Short Ligaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Costovertebral Joint
Costovertebral Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shoulder Joint
Shoulder Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synsarcosis
Synsarcosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elbow Joint
Elbow Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radioulnar Articulation
Radioulnar Articulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carpal Joint
Carpal Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phalangeal Joints
Phalangeal Joints
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Joint
Hip Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stifle Joint
Stifle Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sacroiliac Joint
Sacroiliac Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Axial Skeleton Joints
- Skull Joints:
- Sutures (sutural joints)
- Temporohyoid joint (articulatio temporohyoidea)
- Intermandibular joint (articulatio intermandibularis)
- Temporomandibular joint (articulatio temporomandibularis)
Temporomandibular Joint
- Composition: A composite joint, involving more than two surfaces.
- Shape: Condylar joint.
- Movement: Up and down (opening and closing the mouth), limited side-to-side (lateral grinding), and forward/backward mandible movement.
- Ligaments: One ligament in smaller animals, two in larger animals. Ligamentum caudale and Ligamentum laterale are mentioned.
Vertebral Column, Thorax, and Skull Joints
- Atlantooccipital Joint: (articulatio atlantooccipitalis) Between the skull and the first cervical vertebra.
- Atlantoaxial Joint: (articulatio atlantoaxialis) Between the first and second cervical vertebrae.
- Intervertebral Articulations: (symphysis intervertebralis), articulations between adjacent vertebrae.
- Thoracic Vertebrae and Ribs: (articulationes costovertebrales), articulations between thoracic vertebrae and ribs.
- Sternum and Costal Cartilages: (articulationes sternocostales), articulations between the sternum and costal cartilages.
- Ribs and Costal Cartilages: (articulationes costochondrales), articulations between ribs and costal cartilages.
- Interchondral Articulations: (articulationes intrachondrales), articulations between costal cartilages.
- Sternal Articulations: (synchondroses sternales), articulations between individual sternebrae in the sternum.
Nuchal Ligament
- Components: Funiculus nuchae (connecting occipital protuberance and spinous processes along the vertebral column). Lamina nuchae (connecting spinous processes along the vertebral column to the funiculus nuchae).
- Function: Supports the head's weight, reducing the load on the neck muscles.
Atlanto-occipital and Atlanto-axial Joints (details)
- Atlanto-occipital Joint (1):
- Form: Ellipsoidal
- Number: Simple (one joint)
- Mobility: Biaxial (movement in two planes)
- Atlanto-axial Joint (2):
- Form: Pivot
- Number: Simple (one joint)
- Mobility: Uniaxial (movement in one plane)
Cervical and other Intervertebral Joints (more detail)
- Intervertebral Articulations:
- Cartilaginous joints between vertebral bodies
- Synovial joints between articular processes
Costovertebral Joint
- Explanation: The joint between the ribs and the thoracic vertebrae is implicated in pressure on nerves and spinal cord if damaged.
- Causes of Damage: Aging, obesity, mechanical stress, other health issues.
- Effects of Damage: Rupture or degeneration of discs causes the pulpy nucleus to bulge.
- Typical Location of Problem: Thoracolumbar junction or neck region
Thoracic Limb Joints
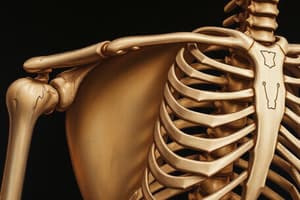
- Shoulder Joint: (articulatio humeri)
- Form: Spheroidal.
- Number: Simple.
- Mobility: Multiaxial (movement in three planes).
- Elbow Joint: (articulatio cubiti)
- Form: Hinge.
- Number: Composite (two joints).
- Mobility: Uniaxial (movement in one plane).
Radioulnar Articulation:
- Description: A pivot joint.
- Structure: Proximal and distal radioulnar articulations.
- Type: Pivot (dogs).
- Number: Simple.
- Mobility: Uniaxial (in one plane).
Carpal Joint
- Description: Multiple joints combining to make the carpal joint.
- Type: Hinge.
- Number: Composite
- Mobility: Uniaxial.
Phalangeal Joints
- Description: Three articulations within each digit.
- Type: Hinge (metacarpophalangeal), saddle (proximal and distal interphalangeal).
- Number: Composite (metacarpophalangeal and distal interphalangeal), simple (proximal interphalangeal).
- Mobility: Uniaxial.
Hind Limb Joints
- Sacroiliac Joint:
- Form: Plane.
- Number: Simple.
- Mobility: Tight (limited movement).
- Hip Joint: (articulatio coxae)
- Form: Spheroidal.
- Number: Simple (two joints – coxocapital and coxotrochanteric).
- Mobility: Multiaxial.
- Stifle Joint: (articulatio genus)
- Form: Hinge (overall), sledge (femoropatellar), condylar (femorotibial).
- Number: Composite.
- Mobility: Uniaxial.
- Tarsal Joint: (articulatio tarsi)
- Form: Hinge.
- Number: Composite.
- Mobility: Uniaxial.
Bird Joints
- Shoulder Joint: (articulatio omalis) Different from mammals, the humerus articulates with the scapula and coracoid.
- Hip Joint: (articulatio coxae) Composed of coxocapital and coxotrochanteric articulations.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.