Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of neural circuits in the Jeffress model?
What is the primary function of neural circuits in the Jeffress model?
What did the delayed sound arrival to the right ear create in Jeffress's example?
What did the delayed sound arrival to the right ear create in Jeffress's example?
How is a time delay produced in the Jeffress model?
How is a time delay produced in the Jeffress model?
What arrangement of neurons is suggested in the Jeffress model to detect sound direction?
What arrangement of neurons is suggested in the Jeffress model to detect sound direction?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens when a sound source is located directly in front of the animal in the Jeffress model?
What happens when a sound source is located directly in front of the animal in the Jeffress model?
Signup and view all the answers
In the context of the Jeffress model, what does the term 'place code' refer to?
In the context of the Jeffress model, what does the term 'place code' refer to?
Signup and view all the answers
Why is it essential for sound signals from both ears to coincide at the detector?
Why is it essential for sound signals from both ears to coincide at the detector?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do the neurons in the Jeffress model play in sound localization?
What role do the neurons in the Jeffress model play in sound localization?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of outer hair cells in the cochlea?
What is the primary function of outer hair cells in the cochlea?
Signup and view all the answers
What causes fluid movements in the cochlea?
What causes fluid movements in the cochlea?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do tip links play in hair cell activity?
What role do tip links play in hair cell activity?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the ionic basis of depolarization in hair cells?
What is the ionic basis of depolarization in hair cells?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the tonotopic organization of the basilar membrane aid in sound perception?
How does the tonotopic organization of the basilar membrane aid in sound perception?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the outcome of shear force acting on hair cells?
What is the outcome of shear force acting on hair cells?
Signup and view all the answers
What is labelled line coding in relation to auditory processing?
What is labelled line coding in relation to auditory processing?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the outer hair cells when they undergo depolarization?
What happens to the outer hair cells when they undergo depolarization?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure is responsible for the generation of electrical activity in response to sound waves?
Which structure is responsible for the generation of electrical activity in response to sound waves?
Signup and view all the answers
What characterizes the inner hair cells in the auditory system?
What characterizes the inner hair cells in the auditory system?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the outer ear?
What is the primary function of the outer ear?
Signup and view all the answers
Which part of the ear is primarily responsible for amplifying sound waves?
Which part of the ear is primarily responsible for amplifying sound waves?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Auditory System Overview
- The auditory system is involved in hearing, including the anatomy of the ear, molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying hearing, and integration and encoding of auditory information by the brainstem.
- Learning outcomes include describing specialized sense organs involved in hearing at a molecular and cellular level, and describing the circuitry that processes this type of sensory information in the central nervous system (CNS).
Sound Properties
- Sound is characterized by pitch (tone) and intensity (loudness).
- Pitch is related to frequency, with humans typically hearing 20-20,000Hz, and bats having a higher range (20-200kHz).
- Loudness is related to amplitude of the sound wave.
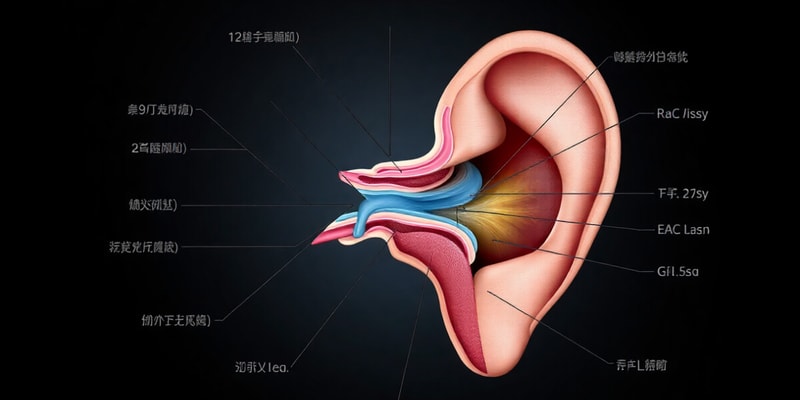
The Human Ear
- The ear has three regions: outer, middle, and inner.
- The outer ear amplifies sound pressure for frequencies between 2-5kHz, and localizes sound sources (elevation).
- The middle ear is crucial for amplifying the sound wave.
- The inner ear contains specialized sensory cells (hair cells) for auditory sensation.
Signal Amplification
- Sound waves travel from low-impedance air to high-impedance fluids in the inner ear.
- The middle ear amplifies sound by concentrating force from the large tympanic membrane onto the smaller oval window.
- This lever action also involves the malleus and incus bones.
Inner Ear Structure
- The inner ear contains the cochlea, consisting of the scala vestibuli, scala tympani, and scala media (cochlear duct).
- The cochlea contains 16,000 inner and 12,000 outer hair cells.
- The basilar membrane is a tapered structure, gradually increasing in width from the base to the apex.
- The tonotopic organization of the basilar membrane allows distinguishing between different frequencies.
Hair Cell Activation
- Vibrations in the basilar membrane cause mechanical movement of specialized sensory cells, hair cells.
- Movement of stereocilia results in the opening of mechanically gated cation channels.
- This leads to depolarization and hyperpolarization, which creates a graded response (generator potential).
Hair Cell Types
- Outer hair cells (OHCs) have efferent inputs, amplifying the motion of the basilar membrane and enhancing the responsiveness of inner hair cells.
- Inner hair cells (IHCs) receive signals (afferent), sending signals to the CNS.
Hair Cell Tip Links
- Stereocilia are connected by tip links, which connect to mechanically gated channels.
- Mechanical deformation of stereocilia opens or closes these channels, triggering electrical signals.
Ionic Basis of Hair Cell Activity
- Endolymph (high K+) bathes stereocilia, while perilymph (low K+) bathes the base.
- The distortion of stereocilia opens ion channels and creates a graded potential.
Encoding Properties
- Patterns of electrical activity (firing rates and patterns) encode information about sound properties.
- Tonotopic organization and labelled-line coding mean that different frequencies and locations are encoded by different neurons.
Sound Localization
- Neural circuits in the brainstem detect interaural time differences and intensity differences for localization.
- The medial superior olive (MSO) helps process these differences.
Summary of Hearing
- The human ear has outer, middle, and inner sections.
- Specialized hair cells in the inner ear transduce mechanical vibrations into electrical signals.
- Different firing patterns encode sound properties.
- Mechanisms for sound localization in the auditory pathways involve detecting time and intensity differences.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the intricacies of the auditory system, including the anatomy of the ear and the molecular mechanisms that allow us to hear. This quiz covers sound properties, the structure of the human ear, and how sensory information is processed in the central nervous system. Gain a deeper understanding of the specialized organs and circuitry involved in hearing.