Podcast
Questions and Answers
What primary motion is expected at the talocrural joint?
What primary motion is expected at the talocrural joint?
- Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion (correct)
- Inversion and eversion
- Supination and pronation
- Abduction and adduction
Which combination of motions describes pronation in a non-weightbearing foot?
Which combination of motions describes pronation in a non-weightbearing foot?
- Plantarflexion, inversion, adduction
- Dorsiflexion, inversion, adduction
- Dorsiflexion, eversion, abduction (correct)
- Plantarflexion, eversion, abduction
Which tarsal bone articulates with the distal tibia and fibula to form the talocrural joint?
Which tarsal bone articulates with the distal tibia and fibula to form the talocrural joint?
- Cuboid
- Navicular
- Calcaneus
- Talus (correct)
Which statement best describes the axis of the talocrural joint in a neutral position?
Which statement best describes the axis of the talocrural joint in a neutral position?
What effect does weight-bearing dorsiflexion have on the tibia and fibula?
What effect does weight-bearing dorsiflexion have on the tibia and fibula?
Which ligament primarily resists eversion at the talocrural, subtalar, and talonavicular joints?
Which ligament primarily resists eversion at the talocrural, subtalar, and talonavicular joints?
Which ligament restricts combined plantarflexion with inversion or adduction of the ankle?
Which ligament restricts combined plantarflexion with inversion or adduction of the ankle?
Which statement is true regarding lateral tibial torsion?
Which statement is true regarding lateral tibial torsion?
What is the most common configuration of articular surfaces in the proximal tibiofibular joint?
What is the most common configuration of articular surfaces in the proximal tibiofibular joint?
What best describes the primary function of the fibula's mobility in the ankle?
What best describes the primary function of the fibula's mobility in the ankle?
Which statement accurately describes the articulations of the subtalar joint?
Which statement accurately describes the articulations of the subtalar joint?
Which ligament is considered the strongest and most important for subtalar joint stability?
Which ligament is considered the strongest and most important for subtalar joint stability?
What occurs during weight-bearing supination at the subtalar joint?
What occurs during weight-bearing supination at the subtalar joint?
During weight-bearing, what effect does medial rotation of the leg have on the subtalar joint?
During weight-bearing, what effect does medial rotation of the leg have on the subtalar joint?
What two joints form the transverse tarsal joint?
What two joints form the transverse tarsal joint?
Which ligament primarily reinforces the talonavicular joint inferiorly and is a major stabilizer of the medial longitudinal arch?
Which ligament primarily reinforces the talonavicular joint inferiorly and is a major stabilizer of the medial longitudinal arch?
What is the primary function of the tarsometatarsal joints during weight-bearing?
What is the primary function of the tarsometatarsal joints during weight-bearing?
What combination of motions occurs when extreme pronation at the subtalar joint leads to a supination twist?
What combination of motions occurs when extreme pronation at the subtalar joint leads to a supination twist?
During open chain talocrural joint arthrokinematics, what occurs during dorsiflexion?
During open chain talocrural joint arthrokinematics, what occurs during dorsiflexion?
During open chain subtalar joint arthrokinematics, what movements occur during supination with inversion?
During open chain subtalar joint arthrokinematics, what movements occur during supination with inversion?
What is the consequence of forefoot varus, identified during non-weightbearing assessment?
What is the consequence of forefoot varus, identified during non-weightbearing assessment?
What statement accurately describes the arches of the foot?
What statement accurately describes the arches of the foot?
Which bone acts as the keystone of the medial longitudinal arch (MLA)?
Which bone acts as the keystone of the medial longitudinal arch (MLA)?
What key function is provided by the plantar arches of the foot?
What key function is provided by the plantar arches of the foot?
What function does the long plantar ligament provide to the transverse tarsal joint?
What function does the long plantar ligament provide to the transverse tarsal joint?
Of the intrinsic muscles that support the arch, what action do lumbricals perform at the great toe and lesser toes?
Of the intrinsic muscles that support the arch, what action do lumbricals perform at the great toe and lesser toes?
Which statement accurately describes the effect of tension in the plantar aponeurosis when the toes are extended at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints?
Which statement accurately describes the effect of tension in the plantar aponeurosis when the toes are extended at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints?
According to the windlass mechanism, what occurs with tension increases in the plantar aponeurosis?
According to the windlass mechanism, what occurs with tension increases in the plantar aponeurosis?
How does supination of a weight-bearing foot influence the plantar aponeurosis?
How does supination of a weight-bearing foot influence the plantar aponeurosis?
Which statement about the distribution of body weight through the foot is MOST accurate?
Which statement about the distribution of body weight through the foot is MOST accurate?
Considering the position of muscles relative to joint axes, what action does a muscle anterior to the talocrural joint axis produce?
Considering the position of muscles relative to joint axes, what action does a muscle anterior to the talocrural joint axis produce?
How do the tibialis anterior muscle act at both the ankle and subtalar joints simultaneously?
How do the tibialis anterior muscle act at both the ankle and subtalar joints simultaneously?
Which group of muscles is primarily responsible for pronation (eversion) at the subtalar joint?
Which group of muscles is primarily responsible for pronation (eversion) at the subtalar joint?
What contribution do the fibularis longus and brevis muscles make at the subtalar joint?
What contribution do the fibularis longus and brevis muscles make at the subtalar joint?
Which action is characteristic of both the extensor digitorum longus and fibularis tertius?
Which action is characteristic of both the extensor digitorum longus and fibularis tertius?
What is a potential foot deformity as a result of weakness in the anterior tibialis muscle?
What is a potential foot deformity as a result of weakness in the anterior tibialis muscle?
What is the primary mechanical effect of weakness in the fibularis brevis muscle?
What is the primary mechanical effect of weakness in the fibularis brevis muscle?
In the context of the foot's musculature, what is typically observed?
In the context of the foot's musculature, what is typically observed?
Which tendons pass through the tarsal tunnel?
Which tendons pass through the tarsal tunnel?
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the talus and the ankle mortise?
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the talus and the ankle mortise?
How does the oblique axis of the talocrural joint affect its motion?
How does the oblique axis of the talocrural joint affect its motion?
What is the functional consequence of the lateral malleolus being more distal and posterior compared to its tibial counterpart?
What is the functional consequence of the lateral malleolus being more distal and posterior compared to its tibial counterpart?
During closed chain dorsiflexion, what compensatory motion occurs in the lower leg to maintain stability?
During closed chain dorsiflexion, what compensatory motion occurs in the lower leg to maintain stability?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the deltoid ligament's role in ankle stability?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the deltoid ligament's role in ankle stability?
How does the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) primarily contribute to ankle joint stability?
How does the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) primarily contribute to ankle joint stability?
Which statement most accurately explains the clinical relevance of accounting for normal lateral tibial torsion?
Which statement most accurately explains the clinical relevance of accounting for normal lateral tibial torsion?
Which statement best integrates the function of the tibiofibular joints with talocrural joint mechanics?
Which statement best integrates the function of the tibiofibular joints with talocrural joint mechanics?
Why is the mobility of the fibula crucial for optimal talocrural joint function?
Why is the mobility of the fibula crucial for optimal talocrural joint function?
Inversion of the calcaneus during non-weight bearing subtalar joint motion is coupled with which movements?
Inversion of the calcaneus during non-weight bearing subtalar joint motion is coupled with which movements?
During weight-bearing, what set of coupled movements occur with calcaneal eversion at the subtalar joint?
During weight-bearing, what set of coupled movements occur with calcaneal eversion at the subtalar joint?
A patient presents with limited subtalar joint mobility following a calcaneal fracture. Which ligament would MOST likely be implicated in restricting motion following immobilization?
A patient presents with limited subtalar joint mobility following a calcaneal fracture. Which ligament would MOST likely be implicated in restricting motion following immobilization?
What is the combined arthrokinematic effect of the alternating convex-concave facets of the subtalar joint?
What is the combined arthrokinematic effect of the alternating convex-concave facets of the subtalar joint?
Medial rotation of the tibia during weight-bearing activities has what effect on the subtalar joint?
Medial rotation of the tibia during weight-bearing activities has what effect on the subtalar joint?
How does the transverse tarsal joint assist in adapting to uneven terrain?
How does the transverse tarsal joint assist in adapting to uneven terrain?
To isolate motion at the midfoot during a pronation assessment, what action should be taken?
To isolate motion at the midfoot during a pronation assessment, what action should be taken?
Which statement best describes the role of the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (spring ligament) in supporting the talonavicular joint?
Which statement best describes the role of the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (spring ligament) in supporting the talonavicular joint?
What structural feature provides reinforcement to the calcaneocuboid joint?
What structural feature provides reinforcement to the calcaneocuboid joint?
What occurs at the tarsometatarsal (TMT) joints when hindfoot position is at its end range of motion and the transverse tarsal joint is unable to compensate?
What occurs at the tarsometatarsal (TMT) joints when hindfoot position is at its end range of motion and the transverse tarsal joint is unable to compensate?
During extreme pronation at the subtalar joint, what position does the talus assume that initiates a supination twist? Choose the single best answer.
During extreme pronation at the subtalar joint, what position does the talus assume that initiates a supination twist? Choose the single best answer.
How do the tarsometatarsal joints compensate for extreme subtalar supination in a pronation twist?
How do the tarsometatarsal joints compensate for extreme subtalar supination in a pronation twist?
What arthrokinematic motions occur at the talocrural joint during open-chain plantarflexion?
What arthrokinematic motions occur at the talocrural joint during open-chain plantarflexion?
During open chain supination with inversion at the subtalar joint, what arthrokinematic motion occurs between the calcaneus and talus?
During open chain supination with inversion at the subtalar joint, what arthrokinematic motion occurs between the calcaneus and talus?
During transverse tarsal joint plantarflexion, which arthrokinematic motions occur?
During transverse tarsal joint plantarflexion, which arthrokinematic motions occur?
How is forefoot varus best identified during a biomechanical assessment?
How is forefoot varus best identified during a biomechanical assessment?
What is the effect of calcaneovalgus on the medial angle formed between the calcaneus and the posterior leg?
What is the effect of calcaneovalgus on the medial angle formed between the calcaneus and the posterior leg?
What bony landmark serves as the keystone of the transverse arch of the foot?
What bony landmark serves as the keystone of the transverse arch of the foot?
Which statement describes the function of the plantar arches in relation to weight distribution?
Which statement describes the function of the plantar arches in relation to weight distribution?
What is the consequence on plantar aponeurosis when the foot supinates during weight-bearing?
What is the consequence on plantar aponeurosis when the foot supinates during weight-bearing?
What percentage of body weight is transmitted through the posterior subtalar joint (articulation between the talus and calcaneus)?
What percentage of body weight is transmitted through the posterior subtalar joint (articulation between the talus and calcaneus)?
Considering muscle positioning relative to joint axes, what is the expected action of a muscle located medially to the subtalar joint axis?
Considering muscle positioning relative to joint axes, what is the expected action of a muscle located medially to the subtalar joint axis?
How does the tibialis posterior muscle contribute to the stability of the medial longitudinal arch (MLA)?
How does the tibialis posterior muscle contribute to the stability of the medial longitudinal arch (MLA)?
What is the collective action of the fibularis longus and brevis muscles at the subtalar joint?
What is the collective action of the fibularis longus and brevis muscles at the subtalar joint?
What mechanical effect results from weakness of the anterior tibialis muscle?
What mechanical effect results from weakness of the anterior tibialis muscle?
What mechanical advantage is gained from the fibularis longus muscle due to weakness of the anterior tibialis muscle?
What mechanical advantage is gained from the fibularis longus muscle due to weakness of the anterior tibialis muscle?
How would weakness in the fibularis brevis muscle alter foot biomechanics?
How would weakness in the fibularis brevis muscle alter foot biomechanics?
What synergistic action supports the foot's arches?
What synergistic action supports the foot's arches?
What represents the sequence of structures found within the tarsal tunnel from anterior to posterior?
What represents the sequence of structures found within the tarsal tunnel from anterior to posterior?
Considering its ligamentous attachments, what functional consequence would result from damage to the deltoid ligament?
Considering its ligamentous attachments, what functional consequence would result from damage to the deltoid ligament?
What is the functional significance of the distal fibula's greater movement on the lateral facet of the talus during ankle motion?
What is the functional significance of the distal fibula's greater movement on the lateral facet of the talus during ankle motion?
How does the alternating convex-concave arrangement of the subtalar joint's articular facets influence joint motion?
How does the alternating convex-concave arrangement of the subtalar joint's articular facets influence joint motion?
What role does the transverse tarsal joint play in relation to subtalar joint motion during gait?
What role does the transverse tarsal joint play in relation to subtalar joint motion during gait?
How do the tarsometatarsal joints contribute to foot function when transverse tarsal joint motion is inadequate?
How do the tarsometatarsal joints contribute to foot function when transverse tarsal joint motion is inadequate?
Why is considering normal lateral tibial torsion crucial in clinical lower extremity assessments?
Why is considering normal lateral tibial torsion crucial in clinical lower extremity assessments?
Considering the Windlass Mechanism's effect, how is tension in the plantar aponeurosis influenced by the foot's position during gait?
Considering the Windlass Mechanism's effect, how is tension in the plantar aponeurosis influenced by the foot's position during gait?
How does the talonavicular joint's structure contribute to supporting the medial longitudinal arch?
How does the talonavicular joint's structure contribute to supporting the medial longitudinal arch?
How does the interaction between the tibialis posterior and fibularis longus muscles contribute to maintaining the foot's arches?
How does the interaction between the tibialis posterior and fibularis longus muscles contribute to maintaining the foot's arches?
In open chain plantarflexion arthrokinematics at the talocrural joint, what occurs?
In open chain plantarflexion arthrokinematics at the talocrural joint, what occurs?
During weight-bearing, how does medial rotation of the tibia affect the subtalar joint?
During weight-bearing, how does medial rotation of the tibia affect the subtalar joint?
What is the primary function of the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments of the distal tibiofibular joint?
What is the primary function of the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments of the distal tibiofibular joint?
Which statement accurately explains the weight distribution through the foot, initiated by the talus bone?
Which statement accurately explains the weight distribution through the foot, initiated by the talus bone?
During open chain, what arthrokinematic motions occur at the transverse tarsal joint during dorsiflexion?
During open chain, what arthrokinematic motions occur at the transverse tarsal joint during dorsiflexion?
How does the position of the lateral malleolus, being more distal and posterior compared to the medial malleolus, affect ankle joint biomechanics?
How does the position of the lateral malleolus, being more distal and posterior compared to the medial malleolus, affect ankle joint biomechanics?
What is the typical compensation that arises from weakness of the anterior tibialis muscle?
What is the typical compensation that arises from weakness of the anterior tibialis muscle?
What changes occur in the tibia and fibula during weight-bearing dorsiflexion?
What changes occur in the tibia and fibula during weight-bearing dorsiflexion?
In assessing forefoot alignment, what reference position is required to accurately identify forefoot varus or valgus?
In assessing forefoot alignment, what reference position is required to accurately identify forefoot varus or valgus?
What happens to the plantar aponeurosis when the weight-bearing foot supinates?
What happens to the plantar aponeurosis when the weight-bearing foot supinates?
Flashcards
What is the talocrural joint?
What is the talocrural joint?
The articulation of the talus & ankle mortise (distal tibia & fibula). It is a synovial, hinge joint with 1 degree of freedom.
What are the articular surfaces of the talus?
What are the articular surfaces of the talus?
Lateral (fibular), medial (tibial), and trochlear (superior) surfaces.
What is the axis of the talocrural joint?
What is the axis of the talocrural joint?
Axis runs through lateral malleolus, body of talus & medial malleolus Creates oblique axis
What actions occur during weight bearing dorsiflexion at the talocrural joint?
What actions occur during weight bearing dorsiflexion at the talocrural joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the deltoid ligament?
What is the function of the deltoid ligament?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the lateral ligaments of the ankle?
What are the lateral ligaments of the ankle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is tibial torsion?
What is tibial torsion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the tibiofibular joints?
What are the tibiofibular joints?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of tibiofibular joints (TFJ)?
What is the role of tibiofibular joints (TFJ)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the subtalar joint?
What is the subtalar joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the ligamentous functions at the subtalar joint?
What are the ligamentous functions at the subtalar joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What motions occur at the Subtalar Joint during weight-bearing pronation?
What motions occur at the Subtalar Joint during weight-bearing pronation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What motions occur at the Subtalar Joint during weight-bearing supination?
What motions occur at the Subtalar Joint during weight-bearing supination?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to the lower leg during Subtalar supination?
What happens to the lower leg during Subtalar supination?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the transverse tarsal joint?
What is the transverse tarsal joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Talonavicular Joint?
What is the Talonavicular Joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Calcaneocuboid Joint?
What is the Calcaneocuboid Joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Tarsometatarsal Joint Function?
What is the Tarsometatarsal Joint Function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
If extreme pronation at subtalar joint causes ADD & PF of talus, EV of calcaneus, what will the MTJ do?
If extreme pronation at subtalar joint causes ADD & PF of talus, EV of calcaneus, what will the MTJ do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a metatarsal break?
What is a metatarsal break?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the talocrural arthrokinematics open chain?
What is the talocrural arthrokinematics open chain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the open chain arthokinematics of the subtalar Joint?
What is the open chain arthokinematics of the subtalar Joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Calcaneovalgus?
What is Calcaneovalgus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Calcaneovarus?
What is Calcaneovarus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Calcaneovalgus?
What is Calcaneovalgus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Calcaneovarus?
What is Calcaneovarus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you identify Forefoot Varus and Valgus?
How do you identify Forefoot Varus and Valgus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do longitudinal arches provide support for the foot?
How do longitudinal arches provide support for the foot?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are mobility functions of plantar arches?
What are mobility functions of plantar arches?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are stability functions of plantar arches?
What are stability functions of plantar arches?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does spring ligament provide?
What does spring ligament provide?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of plantar aponeurosis?
What is the function of plantar aponeurosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Windlass Mechanism?
What is the Windlass Mechanism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What dictates the muscle function?
What dictates the muscle function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Name some intrinsic muscles of the foot.
Name some intrinsic muscles of the foot.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Objectives
- Describe the structure and function of the joints within the ankle and foot complex.
- Describe weightbearing versus non-weightbearing kinematics of the ankle/foot.
- Discuss ligamentous structures of the ankle/foot.
- Identify normal and abnormal joint alignment and force distribution through the foot.
- Describe the plantar arches and their function in the foot.
- Describe the Windlass mechanism and function of the plantar aponeurosis.
- Review the muscles acting at the foot/ankle and their integrated function.
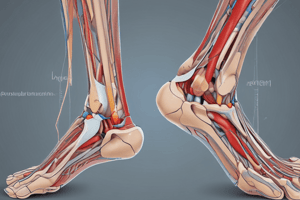
Joints of the Foot & Ankle
- Tibiofibular
- Talocrural
- Subtalar (talocalcaneal)
- Talonavicular
- Calcaneocuboid
- Transverse tarsal
- Intertarsal
- Metatarsophalangeal
- Interphalangeal
Regions of the Foot
- The hindfoot (rearfoot) includes the calcaneus and talus.
- The midfoot includes the navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms.
- The forefoot includes the 5 metatarsals and phalanges.
Motions of the Ankle/Foot
- Movements include dorsiflexion/plantarflexion and inversion/eversion.
- Inversion involves the plantar surface moving toward the midline.
- Eversion involves the plantar surface moving away from the midline.
- Abduction and adduction are also ankle/foot motions.
- Abduction: the distal aspect of the segment moves away from the midline.
- Adduction: the distal aspect of the segment moves toward the midline.
Supination & Pronation
- Supination and pronation are composite motions in NWBing.
- Supination is coupled with plantarflexion, inversion, and adduction.
- Pronation is coupled with dorsiflexion, eversion, and abduction.
Talocrural Joint
- The talocrural joint is an articulation of the talus and ankle mortise, which is the distal tibia and fibula.
- It is a synovial, hinge joint with 1 degree of freedom.
- Its function depends on the stability of the tibiofibular mortise.
- The talus has 3 articular surfaces: lateral (fibular) facet, medial (tibial) facet, trochlear (superior) surface.
- In neutral position, the axis passes through the lateral malleolus, body of talus, and medial malleolus.
- Lateral malleolus and fibular facet of the talus are more distal and posterior than their tibial counterparts, creating an oblique axis and sitting more posteriorly due to normal tibial torsion.
- The ankle axis is rotated ~23° from the frontal plane and has a ~14° inclination from the transverse plane.
- The motion of the talus happens in more than 1 plane.
- Talar rotation, talar tilt, and transverse and frontal plane motions all happen.
- Talar rotation and talar tilts help maintain optimal joint congruency.
Talocrural Joint functions
- Open chain DF: The foot moves upward and slightly lateral to the lower leg, appearing to turn longitudinally away from midline.
- Open chain PF: The foot moves down and slightly medial to the lower leg appearing to turn longitudinally toward the midline.
- WBing DF: Tibia and fibula move toward and medial to foot, with the lower leg rotating medially in the transverse plane.
- WBing PF: Tibia and fibula move away from, and lateral to, the foot, with the lower leg rotating laterally in the transverse plane.
Ligaments of the Ankle
- The Deltoid ligament's proximal attachment is the medial malleolus.
- The Deltoid ligament's distal attachments include the anterior medial talus (anterior tibiotalar ligament), sustentaculum tali of calcaneus (tibiocalcaneal ligament), navicular (tibionavicular), and posterior medial talus (posterior tibiotalar ligament).
- The Deltoid ligament resists eversion at the talocrural, subtalar, and talonavicular joints.
- Lateral ligaments include the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL), calcaneofibular ligament (CFL), and posterior talofibular ligament (PTFL).
Ligaments of the Ankle (functions)
- Anterior Talofibular Ligament: Runs between the lateral malleolus and the neck of the talus, restricts combined motion of plantarflexion with inversion or adduction.
- Calcaneofibular Ligament: Runs between the tip of the lateral malleolus and the lateral aspect of the calcaneus, restricts inversion or varus stress of the talocrural and subtalar joints.
- Posterior Talofibular Ligament: Runs between the lateral malleolar fossa on the posteromedial lateral malleolus and the lateral tubercle of the talus, providing stability to the talus within the joint and restricting abduction during dorsiflexion.
Tibial Torsion
- Tibial torsion accounts for the "normal" toe-out position of the foot in standing.
- It is similar to that of the femur but is typically in the opposite direction.
- Lateral tibial torsion increases from birth until 10 years.
- Ankle joint axis becomes positioned more laterally as torsion increases.
- The normative value is ~ 20° of lateral torsion for adults.
Tibiofibular Joints
- Tibiofibular joints include proximal and distal joints.
- They are anatomically separate from the talocrural joint, but functionally linked and contributing to the total ankle ROM.
- The proximal tibiofibular joint is a plane, synovial joint with variability of joint surfaces that are most commonly a convex tibial facet and a concave fibular facet.
- The proximal tibiofibular joint reinforced by anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments.
- The distal tibiofibular joint: Syndesmosis between concave facet of the tibia and convex facet of the fibula.
- The tibia and fibula are separated by fibroadipose tissue.
- The anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments and interosseous membrane provide support.
- Mobility of the fibula at the TFJs is essential for normal ankle ROM.
- The lateral (fibular) facet is larger than the medial (tibial) facet.
- During ankle motion, the distal fibula moves on the lateral facet of the talus, undergoing more movement than the medial malleolus and resulting in motion of the fibula.
- Mobility of the fibula is required at both proximal and distal TFJs.
Subtalar Joint
- The subtalar joint is formed by the calcaneus and talus, involving 3 articulations.
- It features anterior and middle articulations enclosed in one joint capsule with concave calcaneal facets and a posterior articulation with a separate capsule, where the calcaneus forms the convex surface.
- The subtalar joint is a stable joint, rarely dislocated, due to its strong ligamentous support and congruent osseous anatomy.
- Ligamentous support includes the calcaneofibular, tibiocalcaneal fibers of the deltoid ligament, cervical ligament (strongest talocalcaneal ligament joining the neck of the talus to the neck of the calcaneus), and interosseous talocalcaneal ligaments.
- Portions of the inferior extensor retinaculum also provide support.
Ligaments and Function at Subtalar Joint
- Calcaneofibular ligament limits excessive inversion.
- Tibiocalcaneal fibers of the deltoid ligament limits excessive eversion.
- Interosseous (talocalcaneal) ligament bind talus with calcaneus, limiting extremes of all motions (especially inversion).
- Cervical ligament binds talus with calcaneus, limiting extremes of all motions (especially inversion).
- There are 3 articulations with alternating convex-concave facets which limits joint mobility.
- Triplanar motion is created around the oblique joint axis, resulting in complex twisting or screwlike motion including pronation/supination.
Coupled Movements of Subtalar Pronation/Supination
- Non-weightbearing supination: calcaneal inversion (calcaneal varus), calcaneal adduction, calcaneal plantarflexion
- Non-weightbearing pronation: Calcaneal eversion (calcaneal valgus), calcaneal abduction, calcaneal dorsiflexion.
- Weight-bearing supination: calcaneal inversion (or varus), talar abduction (or lateral rotation), talar dorsiflexion, tibiofibular lateral rotation.
- Weight-bearing pronation: Calcaneal eversion (or valgus), talar adduction (or medial rotation), talar plantarflexion, tibiofibular medial rotation.
- In the subtalar joint, supination is coupled inversion, plantarflexion, and adduction of the calcaneus, while pronation is coupled eversion, dorsiflexion, and abduction of the calcaneus.
- Dorsiflexion and abduction of the talus are observed in elevation of the medial longitudinal arch, while plantar flexion and adduction of the talus are observed in the lowering of medial longitudinal arch.
Subtalar Joint in WBing
- In weightbearing, subtalar supination causes talar abduction, which carries the mortise laterally, producing external rotation of the lower leg.
- In weightbearing, subtalar pronation causes talar adduction, with the body of the talus rotating medially, which brings the lower leg into internal rotation.
- Rotation of the lower leg will impact the subtalar joint when WBing.
Transverse Tarsal Joint
- The transverse tarsal joint is also known as the midtarsal joint.
- It is a compound joint that lies between the rearfoot and midfoot.
- Involves the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints.
- Involved in pronation and supination.
- Plays a major role in compensatory motions to adjust to variations in ground surface.
- It is anatomically and functionally related to the subtalar joint.
Talonavicular Joint
- The talonavicular joint shares a capsule with the anterior and medial subtalar joint articulations,
- Capsular reinforcements include:
- Inferiorly: plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (spring ligament) that spans the gap between the calcaneus and navicular, immediately below the talar head.
- Medially: deltoid ligament.
- Laterally: bifurcate ligaments.
- The spring ligament supports the head of the talus and talonavicular joint, and is a major passive stabilizer of the medial longitudinal arch.
Calcaneocuboid Joint
- Articulation between anterior calcaneus and posterior cuboid.
- Has its own capsule, reinforced by several ligaments.
- Laterally: lateral band of bifurcate ligament (calcaneocuboid ligament).
- Dorsally: dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament.
- Inferiorly: plantar calcaneocuboid (short plantar) & long plantar ligaments.
- Extrinsic muscles of foot provide support for the transverse tarsal joint.
Long Plantar Ligament
- Spans calcaneus and cuboid.
- Extends distally to bases of 2nd, 3rd, & 4th metatarsals.
- Supports transverse tarsal joint and lateral longitudinal arch.
Tarsometatarsal Joint Function
- Contributes to hollowing & flattening of the plantar surface of the foot.
- Augments the function of the transverse tarsal joint in weightbearing.
- Regulates the position of the forefoot in relation to the weightbearing surface.
- Significant tarsometatarsal joint motion is not needed if the transverse tarsal joint's motion is adequate to compensate for hindfoot position.
- The tarsometatarsal joints may rotate to provide further adjustment of the forefoot if the hindfoot position is at the end of ROM or the transverse tarsal joint is unable to fully compensate.
- This may result in a pronation or supination twist.
Supination Twist
- Extreme pronation at the subtalar joint results in adduction and plantarflexion of the talus, eversion of the calcaneus, and pronation at the transverse tarsal joint (due to the navicular being forced down by the talus).
- Tarsometatarsal joints must have a counteracting supination twist to keep the forefoot on the ground.
Pronation Twist
- Extreme supination at the subtalar joint causes abduction and dorsiflexion of the talus, inversion of the calcaneus and supination of the transverse tarsal joint.
- Therefore, the tarsometatarsal joints need a counteracting pronation twist to keep forefoot on ground.
Metatarsal Break
- The metatarsal break describes the occurrence of a hinge or break at the Metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints as the heel rises, during which metatarsal heads and toes remain weightbearing and rising up on your toes.
- Occurs as MTP extension around single oblique running through metatarsal heads.
- It is area of higher stress during gait
Talocrural Arthrokinematics (Open Chain)
- Motion of the talus occurs.
- In dorsiflexion, the talus rolls anteriorly and slides posteriorly.
- In plantarflexion, the talus rolls posteriorly and slides anteriorly.
Arthokinematics: Open Chain
- Subtalar joint: motion of the calcaneus on talus (posterior articulation).
- Supination with inversion: motion medially and slides laterally.
- Pronation with eversion: rolls laterally and slides medially.
- Motion of the phalanges occurs in the Metatarsophalangeal and Interphalangeal joints.
- Flexion: rolls and slides in the plantar direction.
- Extension: rolls and slides dorsally.
Abnormal Foot Postures
- Calcaneovalgus: increase in medial angle between calcaneus and posterior leg.
- Calcaneovarus: decrease in medial angle between calcaneus and posterior leg.
- Calcaneovalgus equals rearfoot valgus, which is the same as hindfoot valgus, and calcaneovarus equals rearfoot varus, which is the same as hindfoot varus.
- These may all lead to problems due to abnormal stresses placed through the bones, tendons, and ligaments of the foot/ankle.
Pes Cavus and Pes Planus
- Pes cavus- Supinated foot with a high arch.
- Pes planus- Flat or hyperpronated foot with a low arch.
- In non-weightbearing position, calcaneus should be in subtalar neutral position when the forefoot varus or valgus is examined with the forefoot deviated in frontal plane from a line bisecting the calcaneus.
Arches of the Foot
- Enhance dynamic function of the foot.
- Includes a Medial longitudinal arch (MLA), lateral longitudinal arch (LLA), and transverse arch.
- Longitudinal arches are anchored posteriorly at the calcaneus and anteriorly at the metatarsal head.
- In longitudinal arches, the talus is equal to the keystone of the medial longitudinal arch and the cuboid is equal to the keystone of the lateral longitudinal arch.
- All weight is transferred from the body to the heel and the forefoot must pass through the talus.
- Transverse arches are most easily visualized in the midfoot at the level of the tarsometatarsal joints with the middle cuneiform equal to the keystone of the arch.
- Shape & arrangement of bones partially contributes to stability of arches.
- Wedge-shape of midtarsal bones provides inherent stability to transverse arch.
- Inclination of calcaneus & 1st metatarsal contribute to stability of MLA, especially when standing.
- Would collapse w/o additional support from ligaments & muscles.
- 2 functions: mobility and stability.
Main Functions of Arches of The Foot
- Plantar arches must be flexible enough to allow the foot to: absorb the impact of weight-bearing forces, reduce/dampen superimposed rotational motions and adapt to changes in the supporting surface.
- Arches must allow: Distribution of weight through the foot for proper weight bearing and conversion of a flexible foot to a rigid lever
Arches Key supports
- Key passive supports to medial longitudinal arch: Spring ligament (most important static stabilizer), interosseous talocalcaneal ligament, and deltoid ligament.
- Key passive supports to lateral longitudinal arch: Long and short plantar ligaments.
- Muscles playing a role in dynamic arch support:
- Tibialis posterior: Major role in the MLA support .
- Tibialis anterior.
- Fibularis longus: Supports the transverse and LLA.
- Flexor digitorum longus. -Fibularis tertius. -Plantar intrinsic muscles: Provide support to the arch in static standing and walking.
Plantar Aponeurosis
- Tension in the aponeurosis increases when the toes are extended at the Metatarsophalangeal joints.
- The metatarsal heads act as pulleys as the plantar aponeurosis is pulled tighter, occurring in both open and closed chains.
- As the plantar aponeurosis wraps around metatarsal heads & tension increases, the heel & Metatarsophalangeal joints are drawn toward each other which raises the arch, contributing to supination of foot.
Function of the Foot
- Supination of the weightbearing foot via ER of lower leg or calcaneal varus: Releases tension in plantar aponeurosis.
- Pronation of the weightbearing foot via IR of lower leg or calcaneal valgus: Increases tension in plantar aponeurosis and can limit MTP joint extension.
Distribution of Body Weight
- Distribution of body weight through foot depends on the shape of the arch and location of the LOG at any given moment, beginning at the talus.
- The body of the talus receives all the weight passing through the leg of which 50% or more is received by the talus passing through the articulation with the calcaneus.
- About 50% or less passes anteriorly through the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints with roughly 2x as much weight passing through the talonavicular joint due to the more medial position of head of the talus.
Muscles and Function around the Foot and Ankle
- Muscle position with respect to joint axis will dictate function.
- Anterior to talocrural joint results in dorsiflexion
- Posterior to talocrural joint results in plantarflexion
- Medial to subtalar joint results in supination and inversion
- Lateral to subtalar to subtalar joint pronation and eversion
Prime movers of the ankle (examples)
- Dorsiflexors: Tibialis anterior, Extensor digitorum longus, Extensor hallucis longus, Fibularis tertius
- Plantarflexors: Gastrocnemius Soleus, Plantaris, Tibialis posterior, Flexor hallucis longus, Flexor digitorum longusFibularis longus,Fibularis brevis
- Invertors: Tibialis anterior, Tibialis posterior, Flexor digitorum longus, Flexor hallucis longus
- Evertors:Fibularis longus, Fibularis brevis, Fibularis tertius, Extensor digitorum longus
- **Important points regarding function
- The position of the muscle and it’s relationship to the axis of rotation dictates function
- Muscles can act at the ankle and subtalar joints simultaneously. Anterior tibialis creates combined DF with supination and inversion
- Extrinsic Muscles of the Leg: Tibialis posterior, FHL, FDL, & plantaris, MA for PF is small, provide only 5% of the total plantarflexor force. The Tibialis posterior largest extrinsic PF after the triceps surae, relatively large MA for both subtalar and transverse tarsal joint supination , important dynamic contributor to the MLA support and important controlling the foot during gait
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.