Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the urinary system?
What is the function of the urinary system?
- To remove waste from the blood in the form of urine (correct)
- To digest food and convert it into energy
- To regulate the body's temperature
- To transport oxygen-rich blood throughout the body
Where do nephrons, the blood-filtering units, begin in the kidney?
Where do nephrons, the blood-filtering units, begin in the kidney?
- Renal Pyramus
- Renal Cortex (correct)
- Descending Aorta
- Inferior Vena Cava
What is the primary function of the Inferior Vena Cava?
What is the primary function of the Inferior Vena Cava?
- Regulate blood pressure
- Supply blood to the kidneys
- Transport deoxygenated blood from the lower extremities back to the heart (correct)
- Carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body's organs
What is the primary function of renal pyramids in the kidneys?
What is the primary function of renal pyramids in the kidneys?
Which kidney structure acts like a funnel, collecting urine and leading it to the ureter?
Which kidney structure acts like a funnel, collecting urine and leading it to the ureter?
What is the specialized tissue that lines the inside of the urinary tract?
What is the specialized tissue that lines the inside of the urinary tract?
What is the main function of the ureters in the urinary system?
What is the main function of the ureters in the urinary system?
Where does the bladder extend into when it is full?
Where does the bladder extend into when it is full?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
The Urinary System
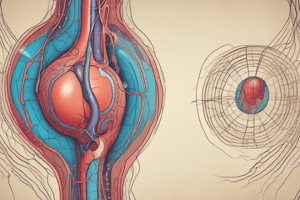
- The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, removes waste from the blood in the form of urine and regulates blood volume, pressure, and electrolyte levels.
- The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Inferior Vena Cava
- The inferior vena cava transports almost all deoxygenated blood from the abdomen and lower extremities back to the right side of the heart for oxygenation.
Descending Aorta
- The descending aorta is the longest part of the aorta, carrying oxygen-rich blood from the heart through the chest and abdomen.
- It branches off into smaller arteries to supply blood to other parts of the body.
Renal Cortex
- The renal cortex is where nephrons (blood-filtering units) begin, with each kidney having approximately 1 million nephrons.
- The filtering unit of the nephron is the glomerulus, which is attached to a tubule that removes wastes and returns needed substances to the body.
Renal Pyramus (Renal Pyramid)
- The renal pyramids are cone-shaped kidney tissues that help with blood filtration and water concentration regulation within the kidneys.
- Humans have seven renal pyramids in each kidney.
Pelvis of the Kidney
- The kidney pelvis collects urine produced in the kidney and leads to the ureter, acting like a funnel.
- The epithelial lining of the kidney pelvis is an urothelium, expanding from a single cell layer to three to six cell layers as it reaches the ureter.
Renal Arteries
- The renal arteries are large blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the kidneys.
- The right renal artery supplies blood to the right kidney, while the left artery sends blood to the left kidney.
Ureter
- The ureters are bilateral thin tubular structures that connect the kidneys to the urinary bladder, transporting urine from the renal pelvis into the bladder.
- The muscular layers of the ureter are responsible for peristaltic activity, moving urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.