Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which muscle is not part of the thenar muscles?
Which muscle is not part of the thenar muscles?
- Opponens Pollicis
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis
- Adductor Pollicis (correct)
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis
What is the primary result of carpal tunnel syndrome on the thenar muscles?
What is the primary result of carpal tunnel syndrome on the thenar muscles?
- Weakness or atrophy of the muscles (correct)
- Increased thumb flexibility
- Enhanced grip strength
- Improved dexterity in fine motor skills
Which functions are primarily associated with the thenar muscles?
Which functions are primarily associated with the thenar muscles?
- Wrist flexion and extension
- Thumb extension and rotation
- Grasping and pinching (correct)
- Elbow flexion and extension
Which nerve primarily innervates the thenar muscles?
Which nerve primarily innervates the thenar muscles?
What can thenar atrophy indicate?
What can thenar atrophy indicate?
Which muscle has two heads and is involved in thumb flexion?
Which muscle has two heads and is involved in thumb flexion?
What role do the thenar muscles play in fine motor skills?
What role do the thenar muscles play in fine motor skills?
Which of the following describes the relationship between the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis and nerves?
Which of the following describes the relationship between the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis and nerves?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Muscle Anatomy
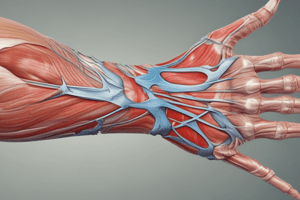
- The thenar muscles are a group of three intrinsic muscles located at the base of the thumb.
- Major muscles include:
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Abducts the thumb.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Flexes the thumb; has two heads (superficial and deep).
- Opponens Pollicis: Allows opposition of the thumb, enabling grasping and pinching.
- All thenar muscles originate from the tubercle of the scaphoid and trapezium bones and the flexor retinaculum.
Innervation
- Medial Nerve: Primarily innervates the thenar muscles.
- Ulnar Nerve: Supplies the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis and the adductor pollicis.
Functions Of Thenar Muscles
- Grasping and Pinching: Essential for thumb opposition and manipulation of objects.
- Thumb Abduction and Flexion: Facilitates various hand functions, including precision grip.
- Fine Motor Skills: Critical in tasks requiring dexterity, such as writing or buttoning clothing.
Clinical Significance
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the median nerve can lead to weakness or atrophy of thenar muscles.
- Thenar Atrophy: Indicates median nerve damage; presents as a flattening of the thenar eminence.
- Functional Impairments: Difficulty in gripping or pinching can affect daily activities, impacting quality of life.
Muscle Anatomy
- Thenar muscles are three intrinsic muscles found at the base of the thumb, crucial for thumb movement.
- Key Muscles:
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Responsible for abducting the thumb away from the hand.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Flexes the thumb and has two heads—superficial and deep.
- Opponens Pollicis: Facilitates thumb opposition, vital for grasping and pinching.
- All thenar muscles originate from the tubercle of the scaphoid and trapezium bones as well as from the flexor retinaculum.
Innervation
- Median Nerve: The primary nerve supplying all thenar muscles, enabling their movement.
- Ulnar Nerve: Provides innervation specifically to the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis and the adductor pollicis.
Functions Of Thenar Muscles
- Essential for grasping and pinching actions due to their role in thumb opposition.
- Enable thumb abduction and flexion, allowing for various hand functions, such as precision gripping.
- Key in fine motor skills that require dexterity, including activities like writing or buttoning clothes.
Clinical Significance
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Results from median nerve compression, potentially leading to weakness or atrophy in the thenar muscles.
- Thenar Atrophy: A sign of median nerve damage, which can be identified by the flattening of the thenar eminence.
- Functional Impairments: Difficulty in gripping or pinching affects daily activities, diminishing quality of life.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.