Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which muscle type controls movements of the vocal folds?
Which muscle type controls movements of the vocal folds?
- Extrinsic muscles
- Depressors of larynx
- Elevators of larynx
- Intrinsic muscles (correct)
Which of the following muscles cannot be damaged if a patient is unable to move or depress their larynx?
Which of the following muscles cannot be damaged if a patient is unable to move or depress their larynx?
- Elevators of larynx
- Extrinsic muscles
- Depressors of larynx
- Intrinsic muscles (correct)
What is the function of the elevators of the larynx?
What is the function of the elevators of the larynx?
- To move the vocal folds
- To elevate the larynx (correct)
- To depress the larynx
- To control breathing
What type of muscles are responsible for controlling the laryngeal inlet?
What type of muscles are responsible for controlling the laryngeal inlet?
Which muscle type is responsible for moving the larynx?
Which muscle type is responsible for moving the larynx?
What is the function of the depressors of the larynx?
What is the function of the depressors of the larynx?
Which of the following structures is not a part of the quadrangular membrane?
Which of the following structures is not a part of the quadrangular membrane?
What constitutes the vestibular ligament?
What constitutes the vestibular ligament?
What is the function of the conus elasticus?
What is the function of the conus elasticus?
Which of the following structures is not a part of the superior surface of the epiglottis?
Which of the following structures is not a part of the superior surface of the epiglottis?
What is the function of the median glossoepiglottic fold?
What is the function of the median glossoepiglottic fold?
What is the function of the aryepiglottic fold?
What is the function of the aryepiglottic fold?
Which muscle is an abductor of the larynx?
Which muscle is an abductor of the larynx?
Which muscle increases the length of the vocal folds?
Which muscle increases the length of the vocal folds?
Which muscle is a depressor of the larynx?
Which muscle is a depressor of the larynx?
Which muscle closes the glottis?
Which muscle closes the glottis?
Which muscle is responsible for shortening the vocal folds?
Which muscle is responsible for shortening the vocal folds?
Which muscle is an elevator of the larynx?
Which muscle is an elevator of the larynx?
Which muscle adducts the vocal folds?
Which muscle adducts the vocal folds?
Which muscle is responsible for opening the glottis?
Which muscle is responsible for opening the glottis?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
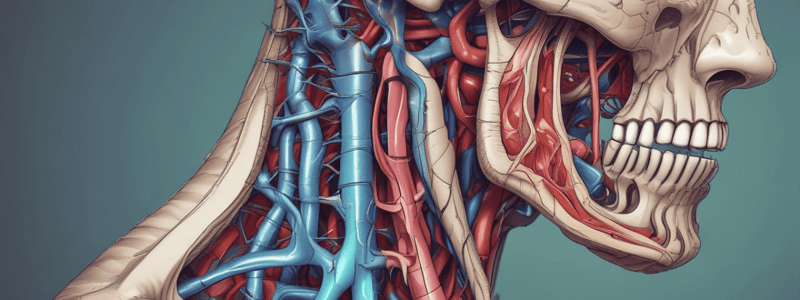
Larynx Anatomy
- Posterior wall of pharynx leads to esophagus
- Epiglottis is located above the larynx
- Pyriform sinus is located lateral to the epiglottis
- Vallecula is a small depression located above the epiglottis
Laryngeal Surface of Epiglottis
- Laryngeal surface of epiglottis faces the larynx
- Ventricle is located below the laryngeal surface of epiglottis
Vocal Cords
- True vocal cords are located in the larynx
- False vocal cords are located above the true vocal cords
- True vocal cords are also known as vocal folds
Hypopharynx
- Posterior wall of hypopharynx leads to esophagus
- Corniculate tubercle is located on the arytenoid cartilage
- Cuneiform tubercle is located on the arytenoid cartilage
Cartilaginous Rings of Trachea
- True vocal cords are located in the trachea
- Cricoid ring is a cartilaginous ring in the trachea
Larynx Muscles
- Extrinsic muscles include:
- Elevators of larynx (e.g. digastric, stylohyoid, mylohyoid, geniohyoid, stylopharyngeus, palatopharyngeus)
- Depressors of larynx (e.g. sternohyoid, sternothyroid, omohyoid)
- Intrinsic muscles include:
- Muscles controlling laryngeal inlet (e.g. oblique arytenoid, thyroepiglottic muscle, aryepiglottic muscle)
- Muscles controlling movements of vocal folds (e.g. cricothyroid, posterior cricoarytenoid, thyroarytenoid, vocalis)
Quadrangular Membrane
- Fibroelastic membrane that extends between the epiglottis, thyroid angle, and arytenoid cartilage
- Its free inferior margin constitutes the vestibular ligament stretching between the thyroid angle and vocal process of arytenoids above the attachment of vocal ligaments
- The upper free border is in the aryepiglottic fold
Conus Elasticus
- Extends between the arch of the cricoid and the vocal process of the arytenoid and the junction of the two thyroid laminae
- The free thickened upper border is the vocal ligament
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.