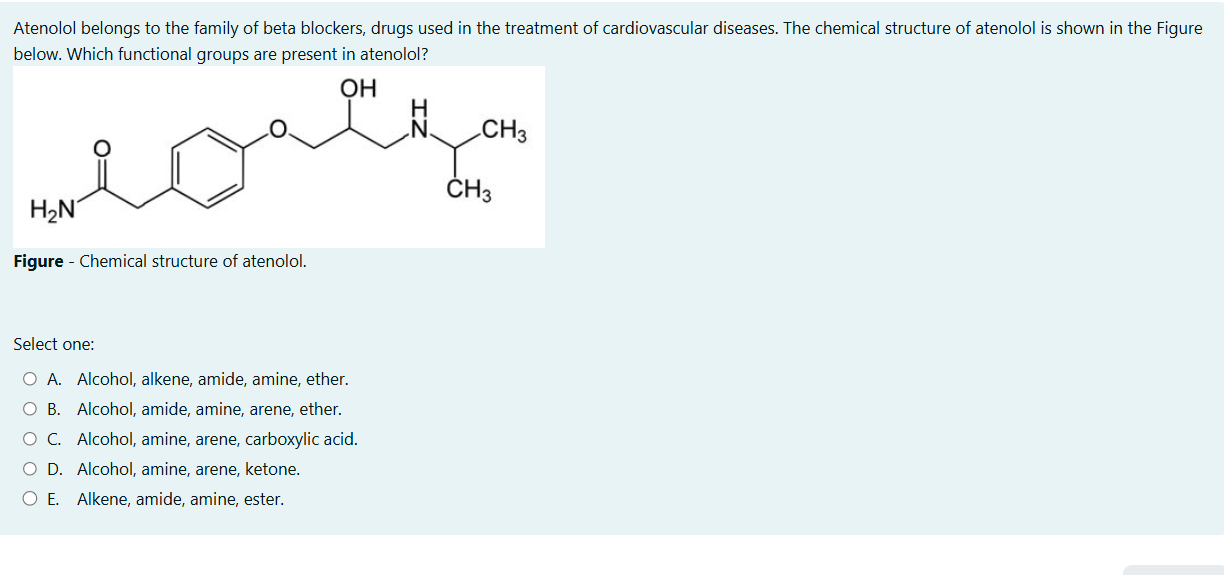
Which functional groups are present in atenolol?
Understand the Problem
The question asks to identify the functional groups present in the chemical structure of atenolol, a beta blocker drug used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Answer
The functional groups present in atenolol are alcohol, amide, amine, arene, and ether.
The correct answer is B. Alcohol, amide, amine, arene, ether.
Answer for screen readers
The correct answer is B. Alcohol, amide, amine, arene, ether.
More Information
Atenolol contains the following functional groups:
- Alcohol (-OH): A hydroxyl group attached to a carbon atom.
- Amide (-C(O)N-): A carbonyl group (C=O) is attached to a nitrogen atom.
- Amine (-N-): A nitrogen atom bonded to one or more alkyl or aryl groups.
- Arene (Benzene ring): A six-carbon ring with alternating double bonds.
- Ether (-O-): An oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups.
Tips
It's important to correctly identify the different functional groups by recognizing their specific atomic arrangements and bonding patterns.
Sources
- Solved Identify all the functional groups on the drugs shown - Chegg - chegg.com
- Which functional groups are present in Atenolol? - YouTube - youtube.com
- Identifying functional groups (video) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information