What is a Nash equilibrium and how does it apply to the example of Anne and Bob selling food at a market?
Understand the Problem
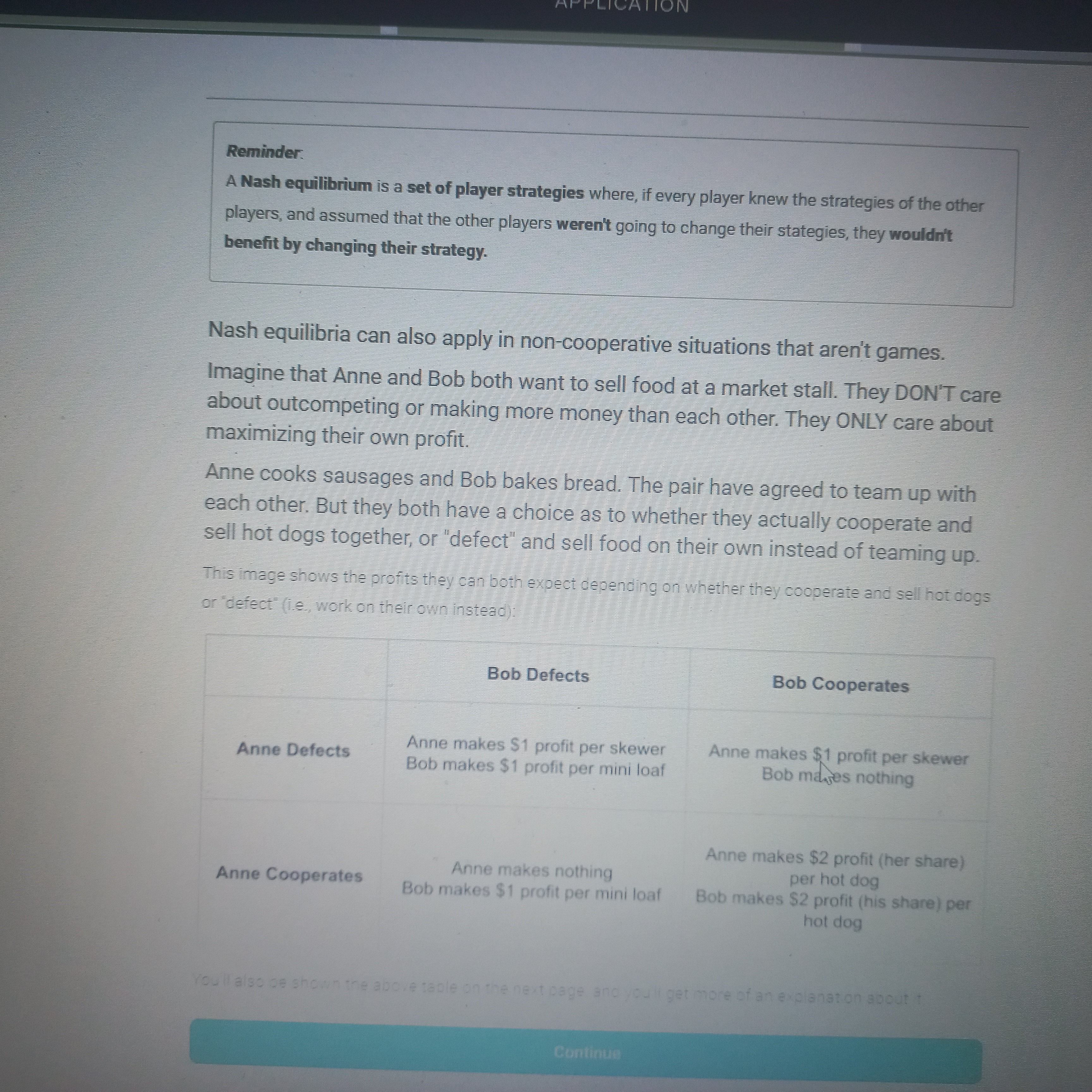
The question is discussing Nash equilibria in the context of Anne and Bob's decision-making regarding food selling at a market. It presents a scenario where each has options to cooperate or defect, focusing on their potential profits based on these choices.
Answer
Anne and Bob defect, each earning $1 profit (Nash equilibrium).
The final answer is that the Nash equilibrium occurs when both Anne and Bob defect, each earning $1 profit per item. Deviating unilaterally would not increase their profit.
Answer for screen readers
The final answer is that the Nash equilibrium occurs when both Anne and Bob defect, each earning $1 profit per item. Deviating unilaterally would not increase their profit.
More Information
In this market scenario, Anne and Bob focus on maximizing their own profits without cooperation. The Nash equilibrium highlights their best individual strategies given the other's choice.
Tips
A common mistake is assuming cooperative strategies always lead to higher profits; in non-cooperative games, individual maximization prevails.
Sources
- Nash Equilibrium - Investopedia - investopedia.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information