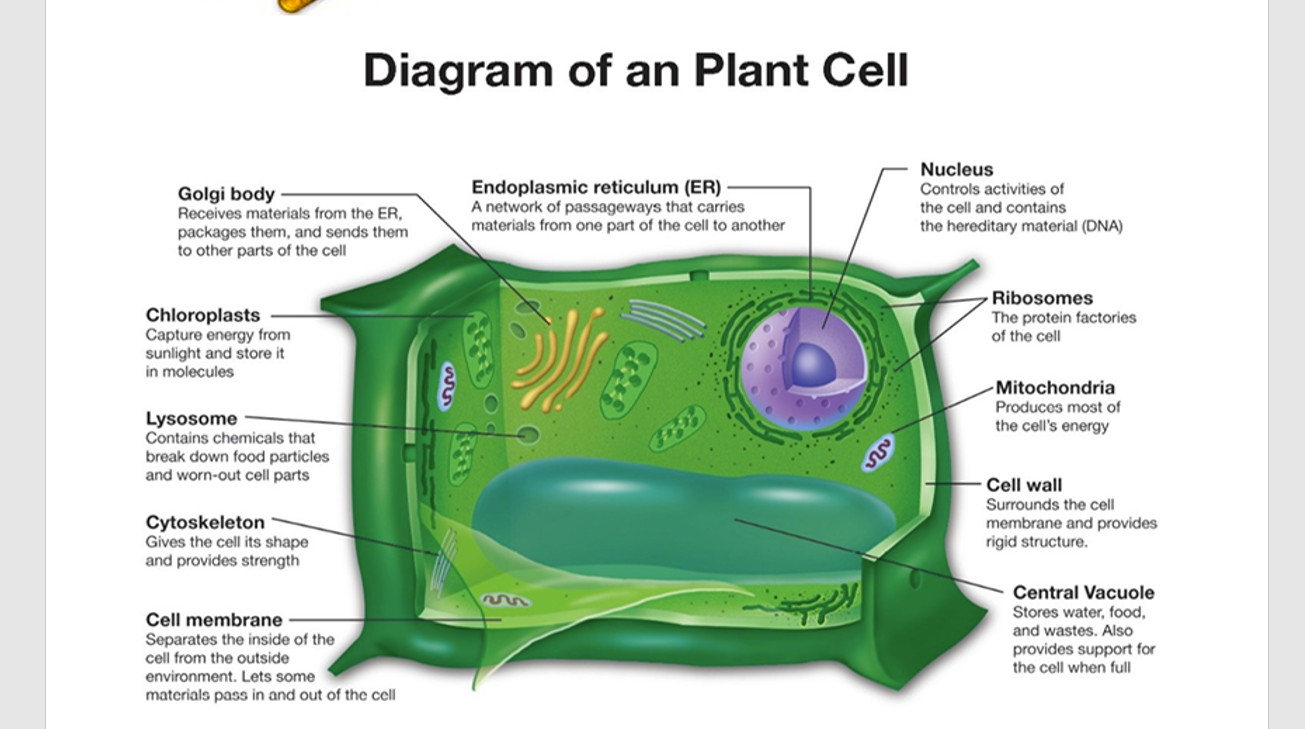
What are the functions of the various parts of a plant cell shown in the diagram?
Understand the Problem
The image is a diagram of a plant cell, highlighting various components and their functions. The question likely relates to understanding the roles of these parts.
Answer
Plant cell parts: Cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, Golgi body, ER, ribosomes, lysosome, cytoskeleton, central vacuole.
The plant cell parts include:
- Cell Wall: Provides structure and protection.
- Cell Membrane: Controls material movement in and out.
- Nucleus: Contains DNA, controls the cell.
- Chloroplasts: Perform photosynthesis.
- Mitochondria: Produce energy (ATP).
- Golgi Body: Packages and transports proteins.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Synthesizes proteins and lipids.
- Ribosomes: Protein synthesis.
- Lysosome: Digestion and waste removal.
- Cytoskeleton: Maintains cell shape.
- Central Vacuole: Stores nutrients and waste, maintains pressure.
Answer for screen readers
The plant cell parts include:
- Cell Wall: Provides structure and protection.
- Cell Membrane: Controls material movement in and out.
- Nucleus: Contains DNA, controls the cell.
- Chloroplasts: Perform photosynthesis.
- Mitochondria: Produce energy (ATP).
- Golgi Body: Packages and transports proteins.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Synthesizes proteins and lipids.
- Ribosomes: Protein synthesis.
- Lysosome: Digestion and waste removal.
- Cytoskeleton: Maintains cell shape.
- Central Vacuole: Stores nutrients and waste, maintains pressure.
More Information
Plant cells are complex structures that include many organelles, each with specialized functions essential for plant growth, energy conversion, and homeostasis.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing the roles of chloroplasts (photosynthesis) and mitochondria (energy production).
Sources
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information