What are the differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Understand the Problem
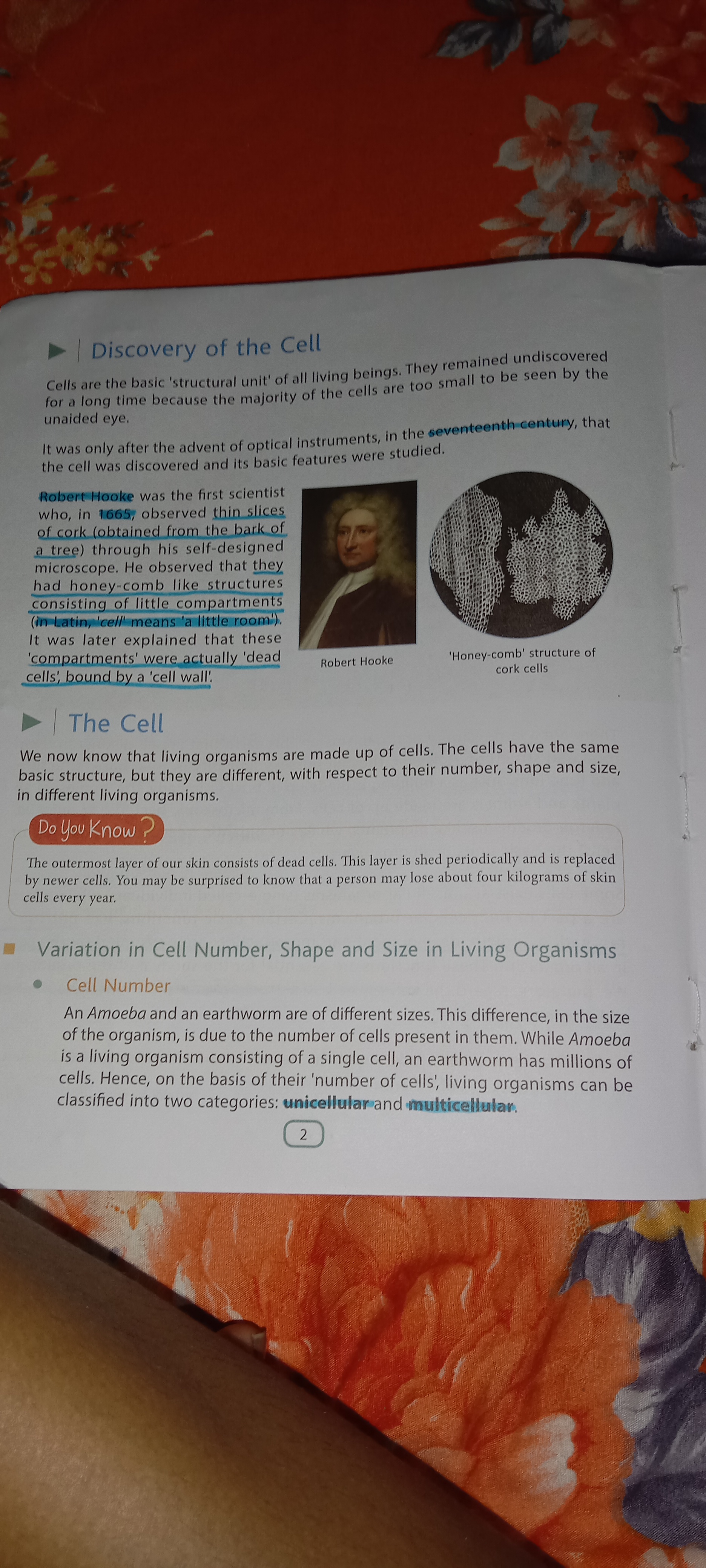
The text provides information about the discovery of cells and their classification based on number, shape, and size in living organisms, specifically mentioning Robert Hooke and differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Answer
Unicellular: one cell; Multicellular: many specialized cells.
Unicellular organisms consist of a single cell that performs all necessary functions, while multicellular organisms are made up of multiple cells with specialized functions. Multicellular organisms are always eukaryotic, whereas unicellular organisms can be either prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
Answer for screen readers
Unicellular organisms consist of a single cell that performs all necessary functions, while multicellular organisms are made up of multiple cells with specialized functions. Multicellular organisms are always eukaryotic, whereas unicellular organisms can be either prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
More Information
Unicellular organisms can offer insights into primitive life forms, while multicellular organisms demonstrate evolved cellular specialization.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing the cell functions in unicellular organisms with specialized cells in multicellular ones.
Sources
- Education National Geographic - Unicellular vs Multicellular - education.nationalgeographic.org
- Difference Between Unicellular And Multicellular Organisms - BYJU'S - byjus.com
- Difference Between Unicellular And Multicellular Organisms - GeeksforGeeks - geeksforgeeks.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information