What are the differences between organic farming and natural farming in terms of external inputs, microbial action, regulation, and cost?
Understand the Problem
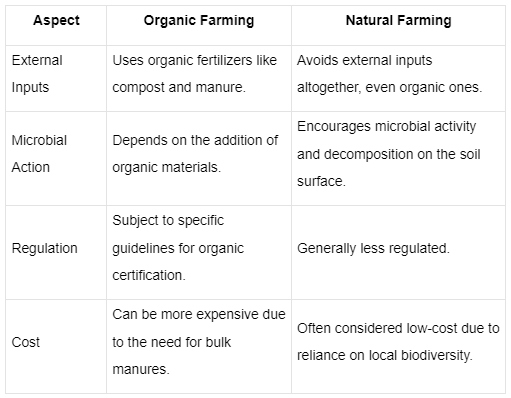
The image provides a comparison of organic farming and natural farming across four aspects: external inputs, microbial action, regulation, and cost. Each aspect details the differences between the two farming methods.
Answer
Organic farming needs organic inputs; it's costly and regulated. Natural farming avoids inputs, is less regulated, and cost-effective.
Organic farming requires organic inputs and is tightly regulated, often costly due to input needs. Natural farming avoids external inputs, promotes microbial soil activity, is less regulated, and is typically lower in cost.
Answer for screen readers
Organic farming requires organic inputs and is tightly regulated, often costly due to input needs. Natural farming avoids external inputs, promotes microbial soil activity, is less regulated, and is typically lower in cost.
More Information
Organic farming often includes specific certifications which can add to its costs. Natural farming, on the other hand, tends to focus on building ecosystem resilience.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing natural processes with lack of management; both farming types require specific management strategies.
Sources
- What is the difference between organic farming and natural farming? - researchgate.net
- Differences Between Organic And Natural Farming - Nature's Box - naturesbox.in
- Natural vs organic farming: What you need to know - gfm.akshayakalpa.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information