What are the differences between animal and plant cells?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking about the differences between plant and animal cells, specifically in terms of their structural components. It suggests a comparison using a Venn diagram to illustrate both unique and shared features of these cell types.
Answer
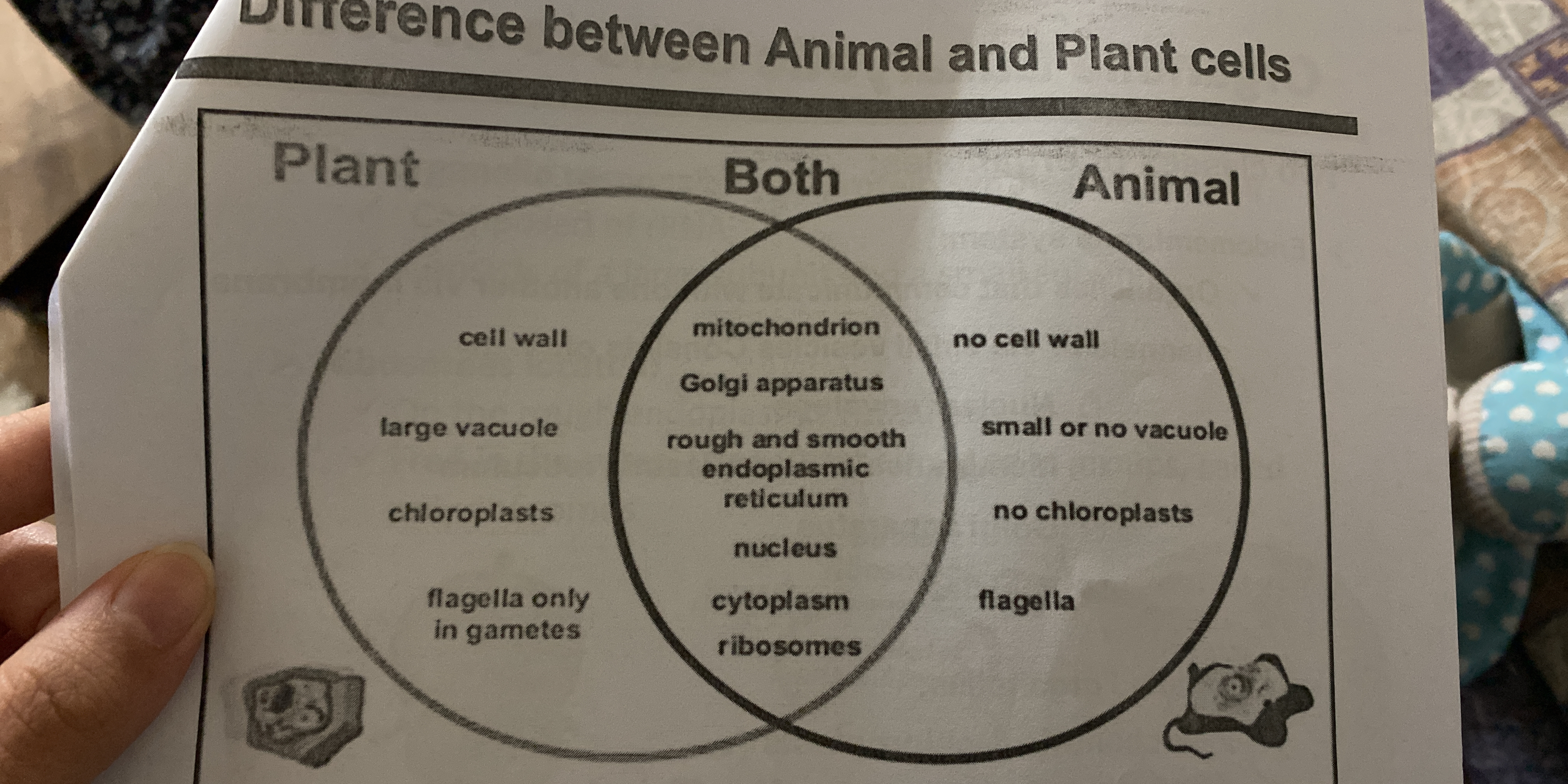
Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts; animal cells do not.
Plant cells have a cell wall, large vacuole, chloroplasts, and plasmodesmata. Animal cells have no cell wall, small or no vacuole, flagella, and centrioles. Both types have mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer for screen readers
Plant cells have a cell wall, large vacuole, chloroplasts, and plasmodesmata. Animal cells have no cell wall, small or no vacuole, flagella, and centrioles. Both types have mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum.
More Information
Plant cells have additional structures, such as chloroplasts for photosynthesis, which animal cells lack. Animal cells contain specialized structures like lysosomes for digestion.
Tips
Avoid confusing the presence of chloroplasts in plant cells with any structures in animal cells.
Sources
- Animal vs. Plant Cells - Open Oregon - openoregon.pressbooks.pub
- Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells - ThoughtCo - thoughtco.com
- Difference Between Plant and Animal Cell - BYJU'S - byjus.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information