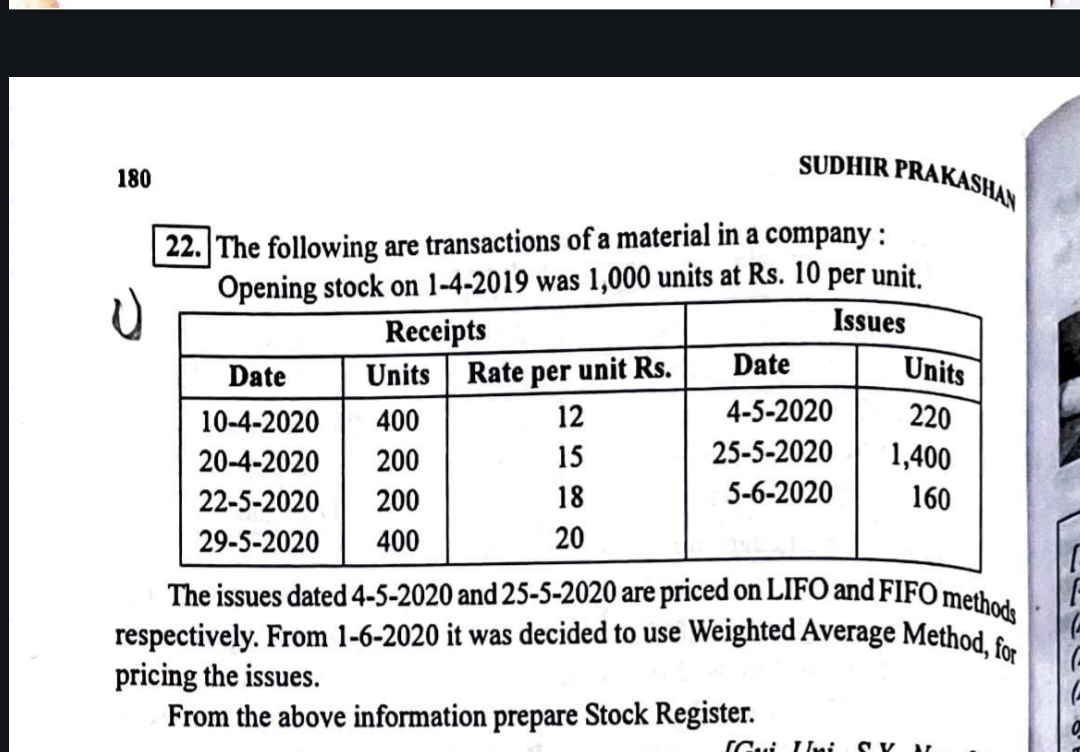
The following are transactions of a material in a company: Opening stock on 1-4-2019 was 1,000 units at Rs. 10 per unit. The issues dated 4-5-2020 and 25-5-2020 are priced on LIFO... The following are transactions of a material in a company: Opening stock on 1-4-2019 was 1,000 units at Rs. 10 per unit. The issues dated 4-5-2020 and 25-5-2020 are priced on LIFO and FIFO methods respectively. From 1-6-2020 it was decided to use Weighted Average Method for pricing the issues. From the above information prepare Stock Register.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to prepare a Stock Register based on the provided transactions of material in a company, including details of receipts and issues along with their respective pricing methods (LIFO, FIFO, and Weighted Average).
Answer
420 units remaining after all transactions.
Answer for screen readers
The final answer displays the completed stock register after applying LIFO, FIFO, and Weighted Average methods.
- Total Units after all transactions = 1,000 (Opening) + 1,200 (Receipts) - 220 (LIFO) - 1,400 (FIFO) - 160 (Weighted Average) = 420 units remaining.
Steps to Solve
- List Opening Stock
The opening stock as of 1-4-2019 consists of 1,000 units at Rs. 10 per unit.
- Record Receipts
Record the receipts in the stock register as follows:
- 10-4-2020: 400 units at Rs. 12
- 20-4-2020: 200 units at Rs. 15
- 22-5-2020: 200 units at Rs. 18
- 29-5-2020: 400 units at Rs. 20
- Calculate Total Available Stock
Calculate the total quantity of material available before any issues:
[ \text{Total Units} = \text{Opening Stock} + \text{Total Receipts} ]
Where,
- Total Receipts = 400 + 200 + 200 + 400 = 1,200 units
So,
[ \text{Total Units} = 1000 + 1200 = 2200 \text{ units} ]
- Record Issues (LIFO and FIFO)
-
4-5-2020 Issue (LIFO): For 220 units, use the latest received inventory.
- Use 220 units from 10-4-2020 (400 units at Rs. 12):
[ 220 \text{ units} \times 12 = 2640 \text{ Rs.} ]
-
25-5-2020 Issue (FIFO): For 1,400 units:
- Use units through first purchased stock.
- First, use all from 20-4-2020 (200 units at Rs. 15):
[ 200 \text{ units} \times 15 = 3000 \text{ Rs.} ]
- Next, use remaining 1,200 units from 22-5-2020 (200 units at Rs. 18):
[ 200 \text{ units} \times 18 = 3600 \text{ Rs.} ]
- Finally, use from 29-5-2020 (total leftover):
[ 800 \text{ units at 20 Rs.} = 16000 \text{ Rs.} ]
- Record Further Issues Using Weighted Average
- 5-6-2020 Issue: For 160 units, use the weighted average method.
Calculate the Weighted Average:
[ \text{Total Cost} = 1200 \times 20 = 24000 ]
Total units after issues: [ 1,200 + 1,400 + 220 = 2,820 \text{ units} ]
Average Cost = [ \frac{24000 \text{ Rs.}}{2820 \text{ units}} \approx 8.51 \text{ Rs. per unit} ]
So the cost for 160 units:
[ 160 \times 8.51 \approx 1361.6 \text{ Rs.} ]
- Complete Stock Register
Prepare the final stock register showing details of all transactions including opening stock, receipts, issues, balance, and their costs.
The final answer displays the completed stock register after applying LIFO, FIFO, and Weighted Average methods.
- Total Units after all transactions = 1,000 (Opening) + 1,200 (Receipts) - 220 (LIFO) - 1,400 (FIFO) - 160 (Weighted Average) = 420 units remaining.
More Information
The methods employed in this problem for inventory costing significantly impact profit calculations, financial reports, and tax liabilities. Understanding LIFO, FIFO, and Weighted Average aids in accurate stock valuation.
Tips
- Not applying the LIFO, FIFO, or weighted average correctly can lead to inaccurate inventory valuation.
- Failure to keep track of how many units remain after issues can result in overstating or understating stock.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information