Solve the inequality 5(x+1) > 2x+3 and sketch your solutions.
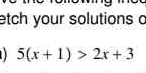
Understand the Problem
The question asks us to solve the inequality 5(x+1) > 2x+3 and sketch the solution. This involves algebraic manipulation to isolate 'x' and then representing the solution on a number line.
Answer
$x > -\frac{2}{3}$
Answer for screen readers
$x > -\frac{2}{3}$
Steps to Solve
- Distribute the 5 on the left side
Apply the distributive property to remove the parentheses:
$5(x+1) = 5x + 5$
The inequality becomes:
$5x+5 > 2x+3$
- Subtract $2x$ from both sides
Subtract $2x$ from both sides to get the $x$ terms on one side:
$5x - 2x + 5 > 2x - 2x + 3$
$3x + 5 > 3$
- Subtract 5 from both sides
Subtract 5 from both sides to isolate the term with $x$:
$3x + 5 - 5 > 3 - 5$
$3x > -2$
- Divide both sides by 3
Divide both sides by 3 to solve for $x$:
$\frac{3x}{3} > \frac{-2}{3}$
$x > -\frac{2}{3}$
- Sketching the solution
Draw a number line. Place an open circle at $-\frac{2}{3}$ to indicate that it is not included in the solution. Shade the region to the right of $-\frac{2}{3}$, indicating that all values greater than $-\frac{2}{3}$ are solutions.
$x > -\frac{2}{3}$
More Information
The solution to the inequality $5(x+1) > 2x+3$ is all real numbers greater than $-\frac{2}{3}$. On a number line, this is represented by an open circle at $-\frac{2}{3}$ and the line shaded to the right, extending to positive infinity.
Tips
A common mistake is forgetting to distribute the 5 correctly in the first step, which would lead to an incorrect inequality. Another mistake might be flipping the inequality sign when dividing by a negative number, but in this case, we divided by a positive number (3), so the inequality sign remains the same. Lastly, some students may include $-\frac{2}{3}$ in the solution set; however the problem stated that $x > -\frac{2}{3}$, not greater than or equal to.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information