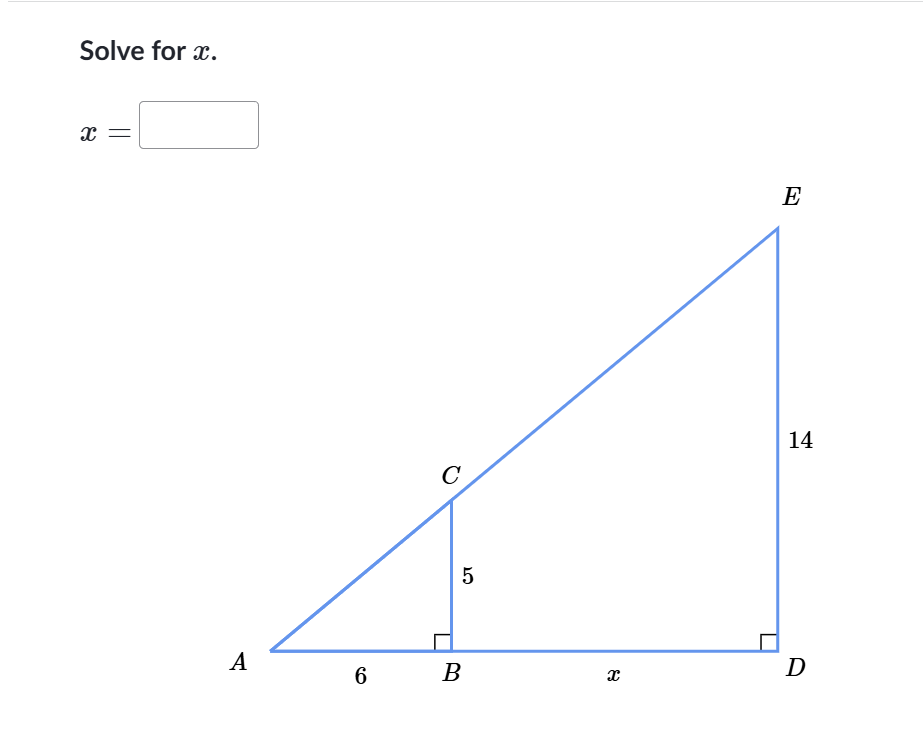
Solve for x.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking us to solve for the length of side x in a right triangle where AB is a horizontal segment measuring 6, BC is a vertical segment measuring 5, and ED is a vertical segment measuring 14. We may need to apply the Pythagorean theorem to find the value of x.
Answer
The length of side \( x \) is \( \sqrt{61} \).
Answer for screen readers
The length of side ( x ) is:
$$ x = \sqrt{61} $$
Steps to Solve
- Identify the right triangle segments
In this right triangle, segment AB is horizontal and measures 6 units, segment BC is vertical and measures 5 units. Segment ED is vertical and measures 14 units.
- Set up the Pythagorean theorem
For right triangles, the Pythagorean theorem states that:
$$ a^2 + b^2 = c^2 $$
where ( a ) and ( b ) are the legs and ( c ) is the hypotenuse.
- Assign the triangle sides to the formula
In this case, the legs are ( AB = 6 ) and ( BC = 5 ), while the hypotenuse ( AD ) must include both BC and ED. We find that ( AD ) can be represented as ( 5 + 14 = 19 ).
- Input the values into the Pythagorean theorem
Substituting the values into the theorem:
$$ 6^2 + 5^2 = x^2 $$
where ( x ) represents the length of side ( AD ).
- Calculate the squares
Compute ( 6^2 ) and ( 5^2 ):
$$ 36 + 25 = x^2 $$
- Solve for ( x^2 )
Combine the squares:
$$ x^2 = 36 + 25 = 61 $$
- Find ( x )
Take the square root of both sides to find ( x ):
$$ x = \sqrt{61} $$
The length of side ( x ) is:
$$ x = \sqrt{61} $$
More Information
The result ( \sqrt{61} ) is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Its approximate value is about 7.81.
Tips
- Confusing the sides of the triangle can lead to incorrect assignments in the Pythagorean theorem.
- Forgetting to add both vertical segments ( BC ) and ( ED ) when calculating the hypotenuse can result in errors.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information