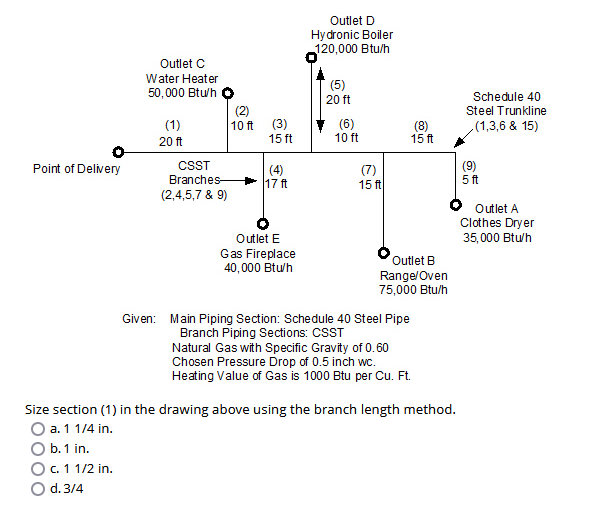
Size section (1) in the drawing above using the branch length method.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine the appropriate pipe section size for a gas piping system using the branch length method from the provided diagram and data. It includes the flow rates for various outlets and specifications about the materials used.
Answer
The appropriate pipe section size is \(1 \frac{1}{2} \text{ in}\).
Answer for screen readers
The appropriate pipe section size is (1 \frac{1}{2} \text{ in}).
Steps to Solve
- Calculate Total Flow Rate
To find the total flow rate, add the flow rates for all outlets.
[ \text{Total Flow Rate} = Q_C + Q_D + Q_E + Q_B + Q_A ]
Where:
- (Q_C = 50,000 \text{ Btu/h})
- (Q_D = 120,000 \text{ Btu/h})
- (Q_E = 40,000 \text{ Btu/h})
- (Q_B = 75,000 \text{ Btu/h})
- (Q_A = 35,000 \text{ Btu/h})
Calculating,
[ \text{Total Flow Rate} = 50,000 + 120,000 + 40,000 + 75,000 + 35,000 = 320,000 \text{ Btu/h} ]
- Determine Equivalent Lengths for Branches
Next, calculate the equivalent lengths for each outlet based on their distances and any fittings or valves.
- Using the branch length method, assume each fitting adds an equivalent length of piping:
- ( (2) ) and ( (3) ) = 10 ft each
- ( (5) ) = 20 ft
- ( (4) ) = 17 ft
- ( (6) ) = 10 ft
- ( (7) ) = 15 ft
- ( (9) ) = 5 ft
Calculate the total equivalent length.
- Calculate Pressure Drop Using Formula
Use the formula for pressure drop in the gas pipeline, which incorporates the equivalent length and flow rate:
[ \Delta P = K \times \frac{Q^2}{D^5} ]
Where (K) is a constant based on gas type and system configuration. Determine a suitable diameter (D) based on pressure drop constraints.
- Select Appropriate Pipe Size
Consult the gas pipe sizing chart using the calculated total flow rate and the allowable pressure drop of 0.5 inches of water column.
Cross-reference the calculated values with the pipe options available: 1 1/4 in, 1 in, 1 1/2 in, and 3/4 in.
Choose the size that meets the requirements.
The appropriate pipe section size is (1 \frac{1}{2} \text{ in}).
More Information
This problem involves gas piping, where proper sizing ensures safe and efficient gas flow. It's crucial to consider flow rates, lengths, and pressure drops to select the right pipe diameter.
Tips
- Ignoring Equivalent Lengths: Not accounting for fittings can lead to underestimating the total length and resultant pressure drop.
- Misreading Flow Rates: Ensure the flow rates for each outlet are correctly totaled.
- Confusing Units: Make sure to remain consistent with units when calculating flow rates and lengths.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information