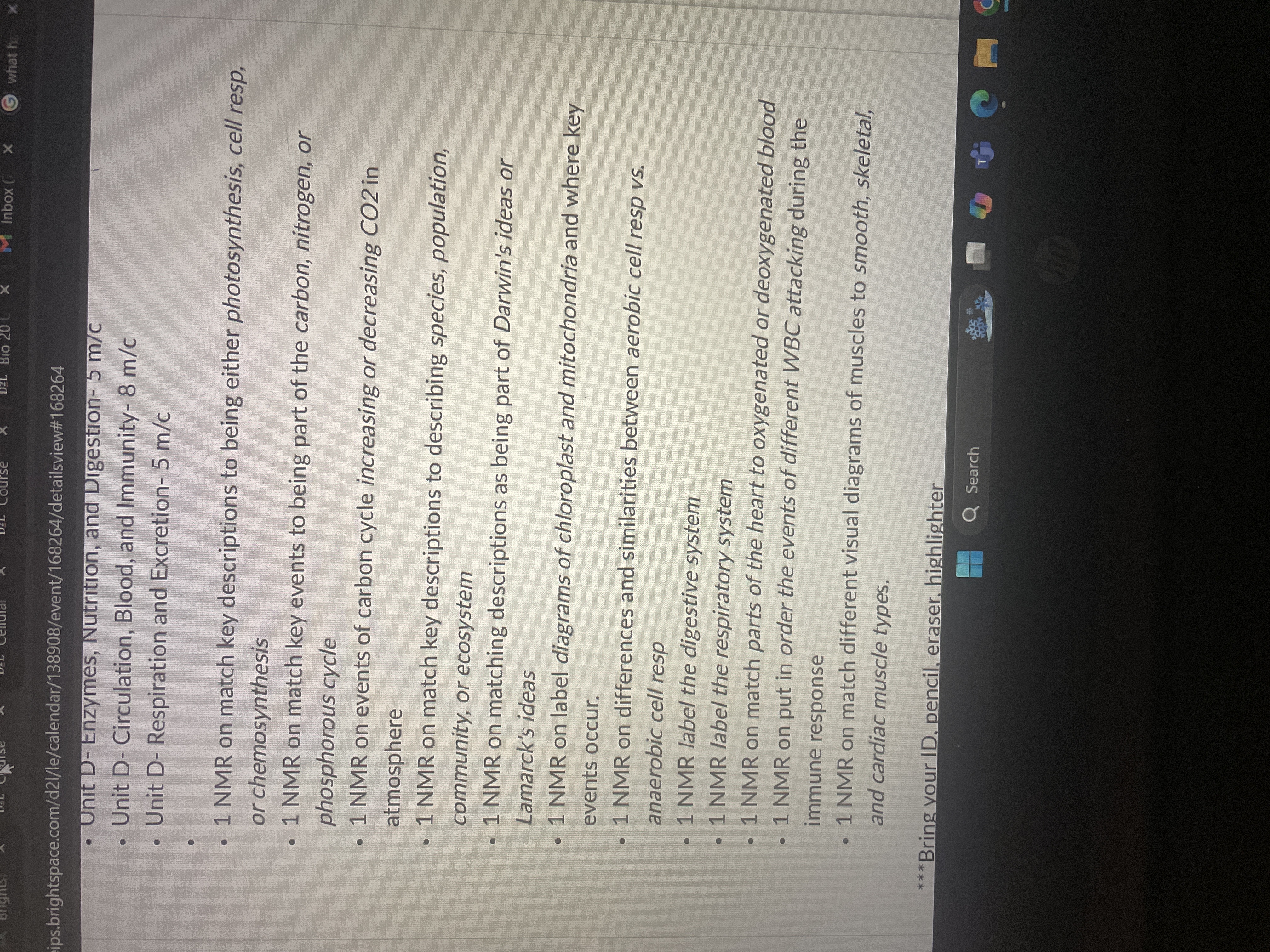
List key descriptions for photosynthesis, cellular respiration, chemosynthesis, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, phosphorus cycle, and match descriptions related to species, populatio... List key descriptions for photosynthesis, cellular respiration, chemosynthesis, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, phosphorus cycle, and match descriptions related to species, population, ecosystem, Darwin's ideas, and label diagrams of chloroplast and mitochondria.
Understand the Problem
The question lists various biological and physiological topics that need to be matched to their key descriptions or diagrams. It implies preparing for a test or review focused on systems and cycles in biology.
Answer
Key descriptions include processes like photosynthesis, cellular respiration, cycles such as carbon and nitrogen, and concepts like species, populations, and ecosystems. Diagrams include chloroplasts and mitochondria.
- Photosynthesis: Converts light energy into chemical energy (glucose) using sunlight.
- Cellular respiration: Converts glucose into ATP with oxygen, releasing carbon dioxide.
- Chemosynthesis: Utilizes chemical reactions, often in the absence of sunlight, for energy production.
- Carbon cycle: Circulation of carbon through the atmosphere, organisms, and earth, balancing CO2 levels.
- Nitrogen cycle: Movement of nitrogen in its various forms between the atmosphere, soil, and organisms.
- Phosphorus cycle: Movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere, crucial for DNA and ATP.
- Species: Groups of organisms capable of interbreeding.
- Population: Individuals of the same species in a specific area.
- Ecosystem: Interaction of living organisms with their environment.
- Darwin’s ideas: Natural selection and evolution.
- Chloroplast diagram: Site of photosynthesis in plant cells, containing thylakoids.
- Mitochondria diagram: Powerhouse of the cell, site of cellular respiration.
Answer for screen readers
- Photosynthesis: Converts light energy into chemical energy (glucose) using sunlight.
- Cellular respiration: Converts glucose into ATP with oxygen, releasing carbon dioxide.
- Chemosynthesis: Utilizes chemical reactions, often in the absence of sunlight, for energy production.
- Carbon cycle: Circulation of carbon through the atmosphere, organisms, and earth, balancing CO2 levels.
- Nitrogen cycle: Movement of nitrogen in its various forms between the atmosphere, soil, and organisms.
- Phosphorus cycle: Movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere, crucial for DNA and ATP.
- Species: Groups of organisms capable of interbreeding.
- Population: Individuals of the same species in a specific area.
- Ecosystem: Interaction of living organisms with their environment.
- Darwin’s ideas: Natural selection and evolution.
- Chloroplast diagram: Site of photosynthesis in plant cells, containing thylakoids.
- Mitochondria diagram: Powerhouse of the cell, site of cellular respiration.
More Information
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interlinked, balancing energy capture and energy release. Biogeochemical cycles like carbon and nitrogen cycles are crucial for maintaining life on Earth.
Tips
Common mistakes include confusing the processes of photosynthesis and respiration, and mixing up the cycles' specific pathways and elements.
Sources
- Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis | CK-12 Foundation - flexbooks.ck12.org
- Intro to photosynthesis (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information