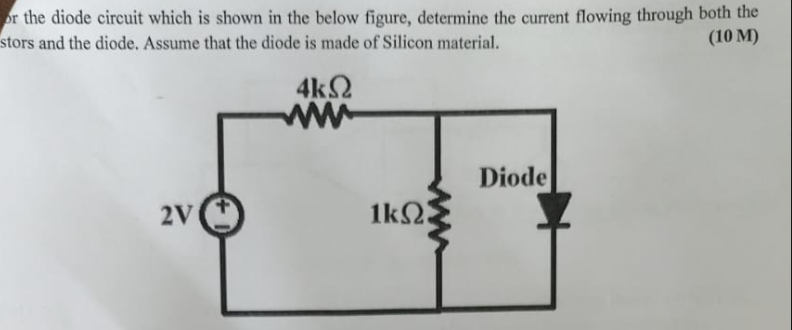
For the diode circuit shown in the figure, determine the current flowing through both the resistors and the diode. Assume that the diode is made of Silicon material.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine the current flowing through both resistors and the diode in a given circuit diagram. The circuit consists of a 2V power supply, a diode made of silicon, and two resistors (4kΩ and 1kΩ) connected in a specific configuration. The answer will require applying Ohm's Law and possibly considering the diode's forward voltage drop.
Answer
The current flowing through both resistors and the diode is \( 260μA \).
Answer for screen readers
The current flowing through both resistors and the diode is ( 260μA ).
Steps to Solve
- Identify the Circuit Configuration
The circuit consists of a 2V power supply connected in series with a 4kΩ resistor, a 1kΩ resistor, and a silicon diode. The silicon diode has a forward voltage drop of approximately 0.7V when it is conducting.
- Calculate the Equivalent Resistance
Since the 4kΩ and 1kΩ resistors are in series, the total resistance ( R_{total} ) can be calculated as follows:
$$ R_{total} = R_1 + R_2 = 4kΩ + 1kΩ = 5kΩ $$
- Determine the Voltage across the Resistors
The voltage across the resistors can be calculated by subtracting the forward voltage drop of the diode from the total supply voltage:
$$ V_{R} = V_{supply} - V_{diode} = 2V - 0.7V = 1.3V $$
- Calculate the Current through the Resistors
Using Ohm's Law, we can calculate the current ( I ) flowing through the series resistors:
$$ I = \frac{V_{R}}{R_{total}} = \frac{1.3V}{5kΩ} = 0.00026A = 260μA $$
- Determine the Current through the Diode
In a series circuit, the current flowing through the resistors is the same as the current flowing through the diode. Therefore, the current through the diode is also:
$$ I_{diode} = 260μA $$
The current flowing through both resistors and the diode is ( 260μA ).
More Information
This circuit analysis demonstrates the application of Ohm's Law and the effect of diode voltage drops in determining current flow in series circuits. Silicon diodes are commonly used in electronic circuits due to their relatively low forward voltage drop.
Tips
- Forgetting to account for the diode's forward voltage drop when calculating the voltage across the resistors.
- Not converting units correctly, such as using milliamps instead of microamps.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information