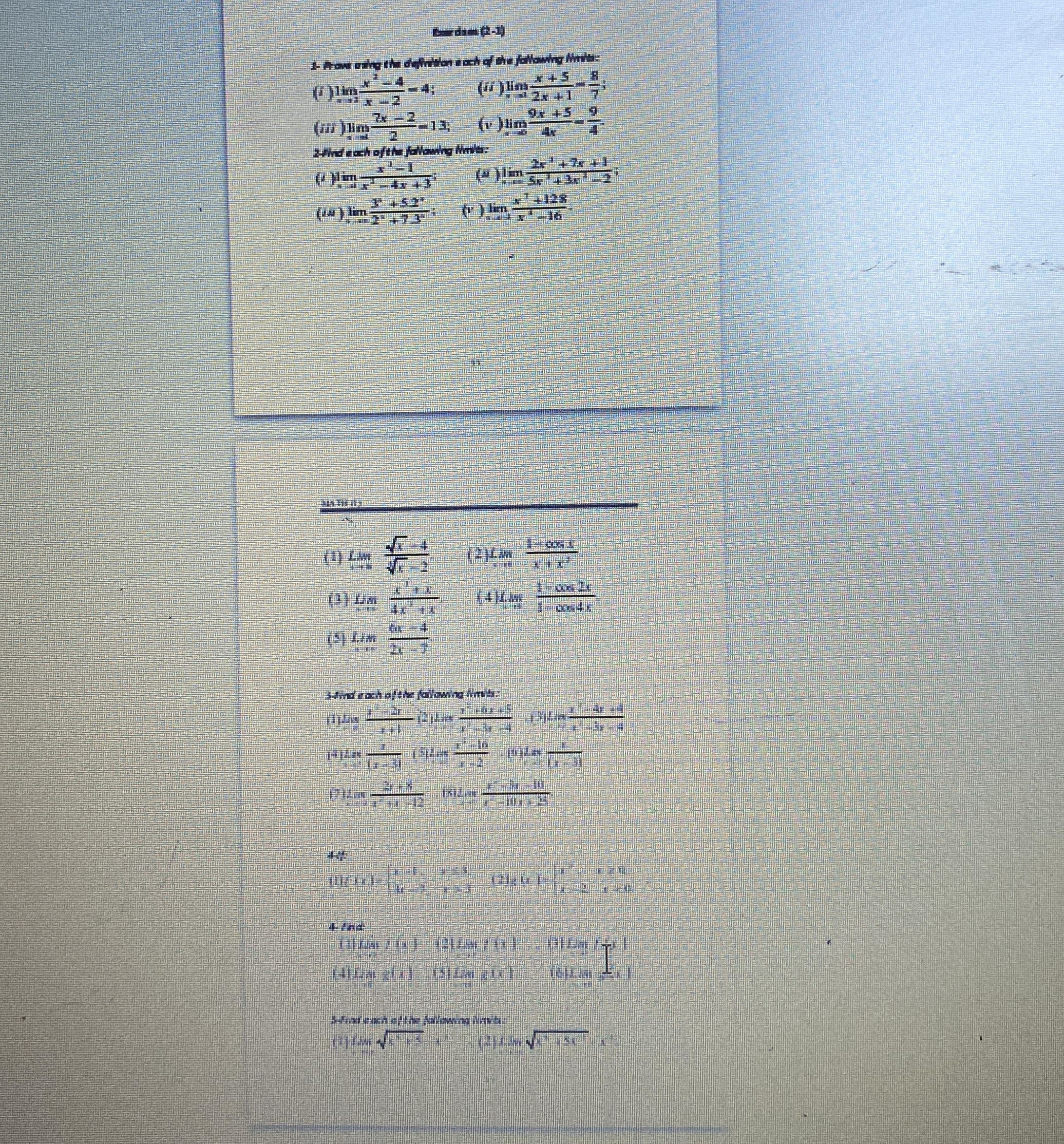
Find each of the following limits: (1) lim x→2 of (sqrt(x) - 2) / (x - 2); (2) lim x→0 of (sin x) / x; (3) lim x→3 of (x^2 - 9) / (x - 3); (4) lim x→π of (cos x); (5) lim x→4 of (x... Find each of the following limits: (1) lim x→2 of (sqrt(x) - 2) / (x - 2); (2) lim x→0 of (sin x) / x; (3) lim x→3 of (x^2 - 9) / (x - 3); (4) lim x→π of (cos x); (5) lim x→4 of (x^2 - 16) / (x - 4).
Understand the Problem
The question involves finding the limits of various functions, which requires applying limit laws and potentially evaluating limits as they approach specific values.
Answer
1. $0$ 2. $14$ 3. $6$ 4. $\frac{1}{4}$ 5. $1$ 6. $2$ 7. $0$ 8. $\frac{1}{2\sqrt{3}}$
Answer for screen readers
- $0$
- $14$
- $6$
- $\frac{1}{4}$
- $1$
- $2$
- $0$
- $\frac{1}{2\sqrt{3}}$
Steps to Solve
-
Evaluate the first limit: $\lim_{x \to 2} (x^2 - 4)$
Substitute $x$ with $2$ in the expression:
$$ \lim_{x \to 2} (x^2 - 4) = 2^2 - 4 = 4 - 4 = 0 $$ -
Evaluate the second limit: $\lim_{x \to 7} \frac{x^2 - 49}{x - 7}$
This expression is of the form $\frac{0}{0}$. Factor the numerator:
$$ \lim_{x \to 7} \frac{(x - 7)(x + 7)}{x - 7} = \lim_{x \to 7} (x + 7) = 7 + 7 = 14 $$ -
Evaluate the third limit: $\lim_{x \to 3} \frac{x^2 - 9}{x - 3}$
This is also of the form $\frac{0}{0}$. Factor the numerator:
$$ \lim_{x \to 3} \frac{(x - 3)(x + 3)}{x - 3} = \lim_{x \to 3} (x + 3) = 3 + 3 = 6 $$ -
Evaluate the fourth limit: $\lim_{x \to 4} \frac{\sqrt{x} - 2}{x - 4}$
This limit also results in $\frac{0}{0}$. Multiply by the conjugate:
$$ \lim_{x \to 4} \frac{(\sqrt{x} - 2)(\sqrt{x} + 2)}{(x - 4)(\sqrt{x} + 2)} = \lim_{x \to 4} \frac{x - 4}{(x - 4)(\sqrt{x} + 2)} = \lim_{x \to 4} \frac{1}{\sqrt{x} + 2} = \frac{1}{2 + 2} = \frac{1}{4} $$ -
Evaluate the fifth limit: $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin x}{x}$
A well-known limit:
$$ \lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin x}{x} = 1 $$ -
Evaluate the sixth limit: $\lim_{x \to 0^+} \frac{1 - \cos x}{x^2}$
Using the limit property:
$$ \lim_{x \to 0} \frac{1 - \cos x}{x^2} = \lim_{x \to 0} \frac{0}{0} = \lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin^2(x/2)}{(x^2/4)} = \lim_{x \to 0} \frac{4 \sin^2(x/2)}{x^2} = 2 $$ -
Evaluate the seventh limit: $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{x}{\sqrt{x^2 + 1}}$
Substituting $x$ gives:
$$ \lim_{x \to 0} \frac{0}{\sqrt{0^2 + 1}} = 0 $$ -
Evaluate the eighth limit: $\lim_{x \to 3} \frac{\sqrt{x} - \sqrt{3}}{x - 3}$
Using the conjugate:
$$ \lim_{x \to 3} \frac{(\sqrt{x} - \sqrt{3})(\sqrt{x} + \sqrt{3})}{(x - 3)(\sqrt{x} + \sqrt{3})} = \lim_{x \to 3} \frac{x - 3}{(x - 3)(\sqrt{x} + \sqrt{3})} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{3} + \sqrt{3}} = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{3}} $$
- $0$
- $14$
- $6$
- $\frac{1}{4}$
- $1$
- $2$
- $0$
- $\frac{1}{2\sqrt{3}}$
More Information
These calculations show how to evaluate limits using direct substitution, factoring, and other algebraic techniques. Understanding these limit laws is essential for calculus.
Tips
- Not recognizing forms like $\frac{0}{0}$ and attempting to substitute directly.
- Forgetting to simplify expressions before evaluating limits.
- Misapplying trigonometric limit properties.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information