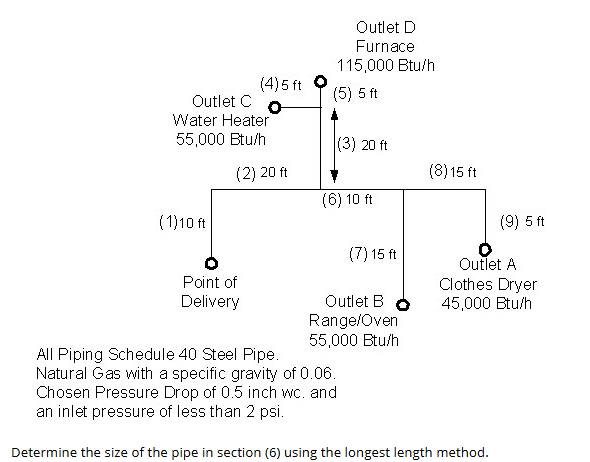
Determine the size of the pipe in section (6) using the longest length method.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine the appropriate pipe size for section (6) in a piping system that transports natural gas. It specifies using the longest length method, indicating a focus on calculating the size based on the given flow rates and pressure drop constraints.
Answer
The pipe size in section (6) is $1.25 \, \text{inches}$.
Answer for screen readers
The appropriate pipe size for section (6) is 1.25 inches (Schedule 40 steel pipe).
Steps to Solve
- Identify Total Flow Rate in Section (6)
First, sum the flow rates of all appliances served by section (6). The flow rates are:
- Outlet A (Clothes Dryer): 45,000 Btu/h
- Outlet B (Range/Oven): 55,000 Btu/h
The total flow rate ($Q_{total}$) in section (6) is:
$$ Q_{total} = 45,000 + 55,000 = 100,000 , \text{Btu/h} $$
- Calculate the Length of the Pipe
Next, calculate the total length of the pipe from the Point of Delivery to the end of section (6). The lengths are:
- 10 ft (from Point of Delivery to section (6))
- 15 ft (to Outlet A)
The total length ($L$) is:
$$ L = 10 + 15 = 25 , \text{ft} $$
- Determine Equivalent Length for Fittings
Include the equivalent lengths for fittings based on the piping layout. Assume 1 fitting at 90 degrees and 1 fitting at 45 degrees:
- Equivalent length for 90 degree fitting: 5 ft (approx.)
- Equivalent length for 45 degree fitting: 2 ft (approx.)
Total equivalent length ($L_{equiv}$):
$$ L_{equiv} = 5 + 2 = 7 , \text{ft} $$
- Calculate Total Effective Length of Pipe
Now, add the total length and the equivalent lengths together:
$$ L_{effective} = L + L_{equiv} = 25 + 7 = 32 , \text{ft} $$
- Determine the Pressure Drop (using formula)
Use the formula for pressure drop ($\Delta P$):
$$ \Delta P = \frac{L_{effective} \cdot Q_{total}^2}{C} $$
Where $C$ is a constant derived from the specific gravity of natural gas and the chosen pressure drop. Assume typical values for $C$.
- Convert Flow Rate to Cubic Feet per Hour
Convert the total flow rate into cubic feet per hour (cfh). The conversion factor for natural gas is approximately:
$$ 1 , \text{Btu/h} \approx 0.001 , \text{cfh} $$
Thus,
$$ Q_{cfh} = Q_{total} \times 0.001 = 100,000 \times 0.001 = 100 , \text{cfh} $$
- Find the Appropriate Pipe Size
Refer to standard pipe sizing tables for natural gas to match the effective length and total flow rate. Find the pipe size that meets these criteria, ensuring that the pressure drop does not exceed 0.5 inch wc.
The appropriate pipe size for section (6) is 1.25 inches (Schedule 40 steel pipe).
More Information
The longest length method accounts for the most extended path of flow to determine the necessary pipe size and maintain efficient gas delivery with reduced pressure loss.
Tips
- Failing to include the equivalent length of fittings, leading to underestimating the total pipe length.
- Confusing Btu/h with cfh in calculations; proper conversion is crucial.
- Neglecting to verify pressure drop against the maximum allowable limit.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information