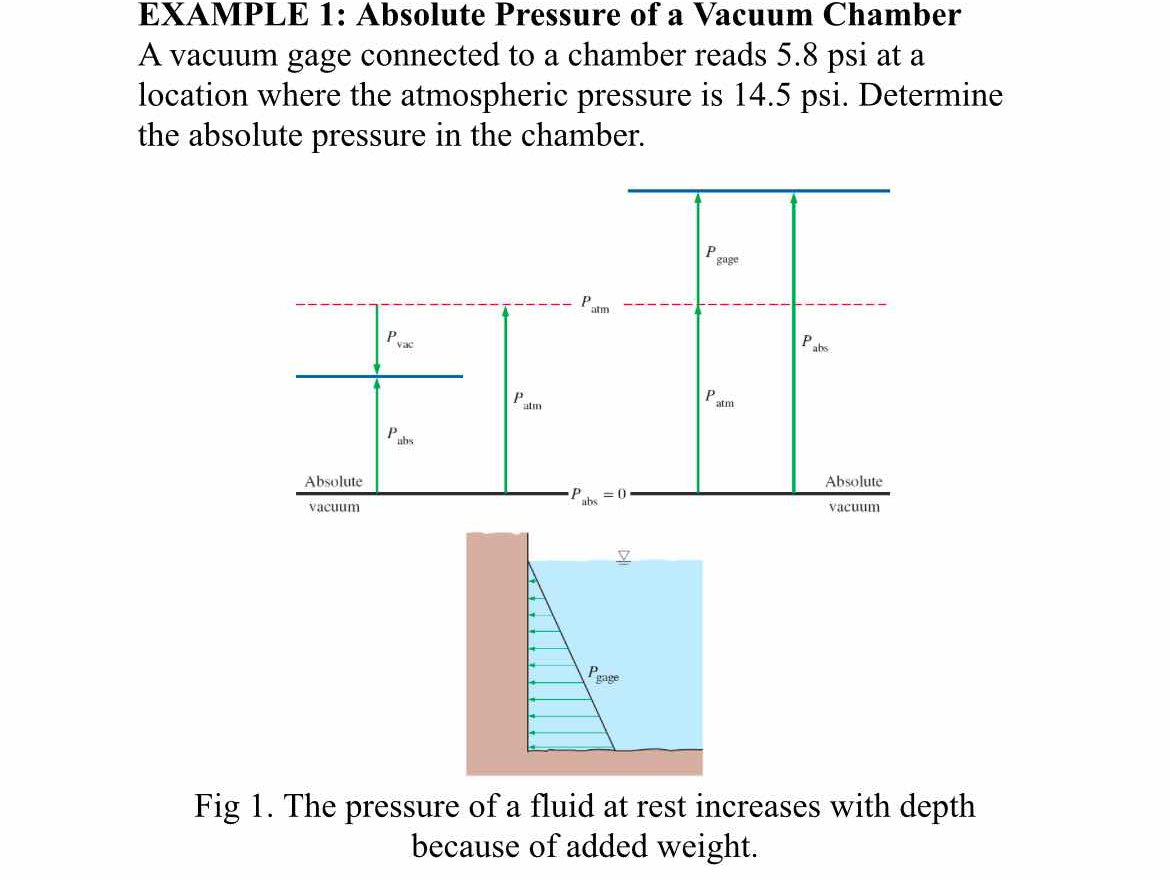
A vacuum gauge connected to a chamber reads 5.8 psi at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 14.5 psi. Determine the absolute pressure in the chamber.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to calculate the absolute pressure in a vacuum chamber using the readings from a vacuum gauge and the atmospheric pressure. The absolute pressure can be determined by adding the gauge pressure to the atmospheric pressure.
Answer
$P_{\text{abs}} = 8.7 \, \text{psi}$
Answer for screen readers
The absolute pressure in the chamber is $8.7 , \text{psi}$.
Steps to Solve
-
Identify Given Values The gauge pressure is given as $P_{\text{gauge}} = 5.8 , \text{psi}$ and the atmospheric pressure as $P_{\text{atm}} = 14.5 , \text{psi}$.
-
Understand Pressure Relationships The absolute pressure in the chamber can be calculated using the formula: $$ P_{\text{abs}} = P_{\text{atm}} - P_{\text{gauge}} $$
-
Substituting Values Now, substitute the given values into the formula: $$ P_{\text{abs}} = 14.5 , \text{psi} - 5.8 , \text{psi} $$
-
Calculate Absolute Pressure Perform the subtraction: $$ P_{\text{abs}} = 14.5 - 5.8 = 8.7 , \text{psi} $$
The absolute pressure in the chamber is $8.7 , \text{psi}$.
More Information
Absolute pressure is the total pressure exerted on a system, including atmospheric pressure. In vacuum applications, it's important to account for both atmospheric pressure and gauge pressure to get accurate measurements.
Tips
- Confusing gauge pressure with absolute pressure; ensure you subtract gauge pressure from atmospheric pressure for absolute values.
- Not properly identifying atmospheric pressure or not converting units if they are not consistent.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information