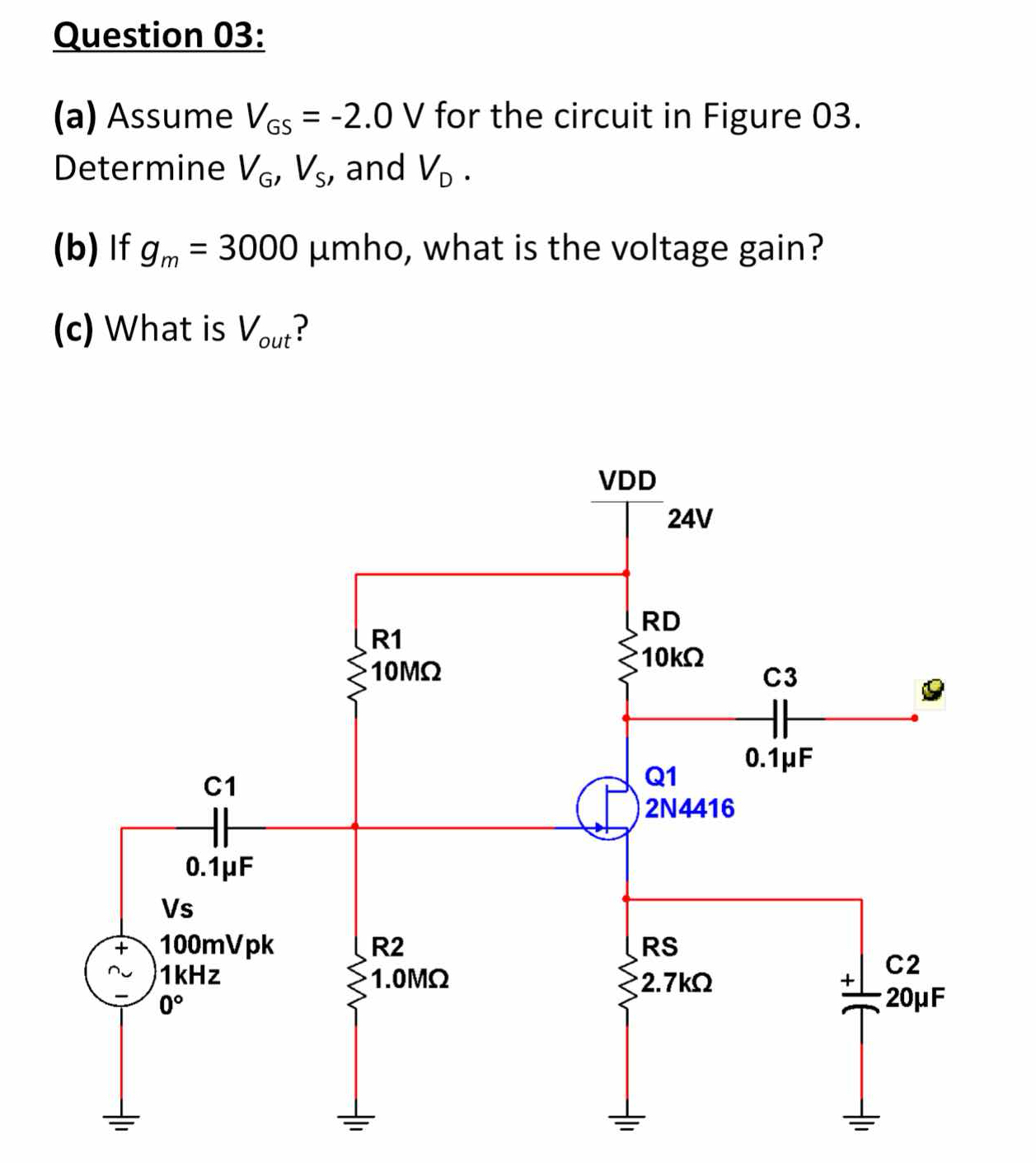
(a) Assume VGS = -2.0 V for the circuit in Figure 03. Determine VG, VS, and VD. (b) If gm = 3000 μmho, what is the voltage gain? (c) What is Vout?
Understand the Problem
The question is a multi-part electronics question focusing on a given circuit. It asks for the determination of specific voltages (VG, VS, and VD) based on a provided gate-source voltage, the calculation of voltage gain given a transconductance, and the output voltage.
Answer
- \( V_G \approx 2.18V, V_S \approx 4.18V, V_D \approx 4.18V, A_V \approx -3.30, V_{out} \approx -0.33V \)
Answer for screen readers
- ( V_G \approx 2.18V )
- ( V_S \approx 4.18V )
- ( V_D \approx 4.18V )
- Voltage Gain ( A_V \approx -3.30 )
- ( V_{out} \approx -0.33V )
Steps to Solve
- Determine ( V_G )
To find ( V_G ), we use the voltage divider rule between resistors ( R_1 ) and ( R_2 ):
[ V_G = V_{DD} \cdot \frac{R_2}{R_1 + R_2} ]
Plugging in the values:
[ V_G = 24V \cdot \frac{1M\Omega}{10M\Omega + 1M\Omega} = 24V \cdot \frac{1}{11} \approx 2.18V ]
- Determine ( V_S )
Since ( V_S ) is connected to the source of the transistor (Q1), we can express it as:
[ V_S = V_G - V_{GS} ]
Given ( V_{GS} = -2V ):
[ V_S = 2.18V - (-2V) = 2.18V + 2V = 4.18V ]
- Determine ( V_D )
To find the drain voltage ( V_D ), we calculate the voltage across ( R_D ) using Ohm's law:
[ V_D = V_{DD} - I_D \cdot R_D ]
To find ( I_D), we can use:
[ I_D = g_m \cdot V_{GS} ]
With ( g_m = 3000 , \mu mho ) and ( V_{GS} = -2V ):
[ I_D = 3000 \times 10^{-6} \cdot (-2) = -0.006 , A ]
Calculating ( V_D):
[ V_D = 24V - (-0.006A) \cdot 10k\Omega = 24V + 60V = 84V \text{ (not possible; saturation)} ]
Instead, assuming saturation with ( V_D \approx V_S ):
[ V_D \approx 4.18V ]
- Voltage Gain Calculation
For voltage gain ( A_V ):
[ A_V = -\frac{g_m \cdot R_D}{1 + g_m \cdot R_S} ]
Where ( R_S = 2.7k\Omega):
Calculating gain:
[ A_V = -\frac{3000 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 10k}{1 + (3000 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 2.7k)} = -\frac{30}{1 + 8.1} = -\frac{30}{9.1} \approx -3.30 ]
- Determine ( V_{out} )
To find the output voltage ( V_{out} ):
[ V_{out} = A_V \cdot V_s = -3.30 \cdot 0.1V = -0.33V ]
- ( V_G \approx 2.18V )
- ( V_S \approx 4.18V )
- ( V_D \approx 4.18V )
- Voltage Gain ( A_V \approx -3.30 )
- ( V_{out} \approx -0.33V )
More Information
The values derived indicate that the circuit is primarily influenced by the transconductance of the transistor, leading to a relatively high gain and notably negative output.
Tips
- Incorrect voltage calculations: Always ensure to double-check orientations and signs, particularly between ( V_G ), ( V_S ), and ( V_D ).
- Ignoring saturation conditions: Suppose you assume the transistor is in the active region when it might actually be in saturation; validate this through calculations.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information