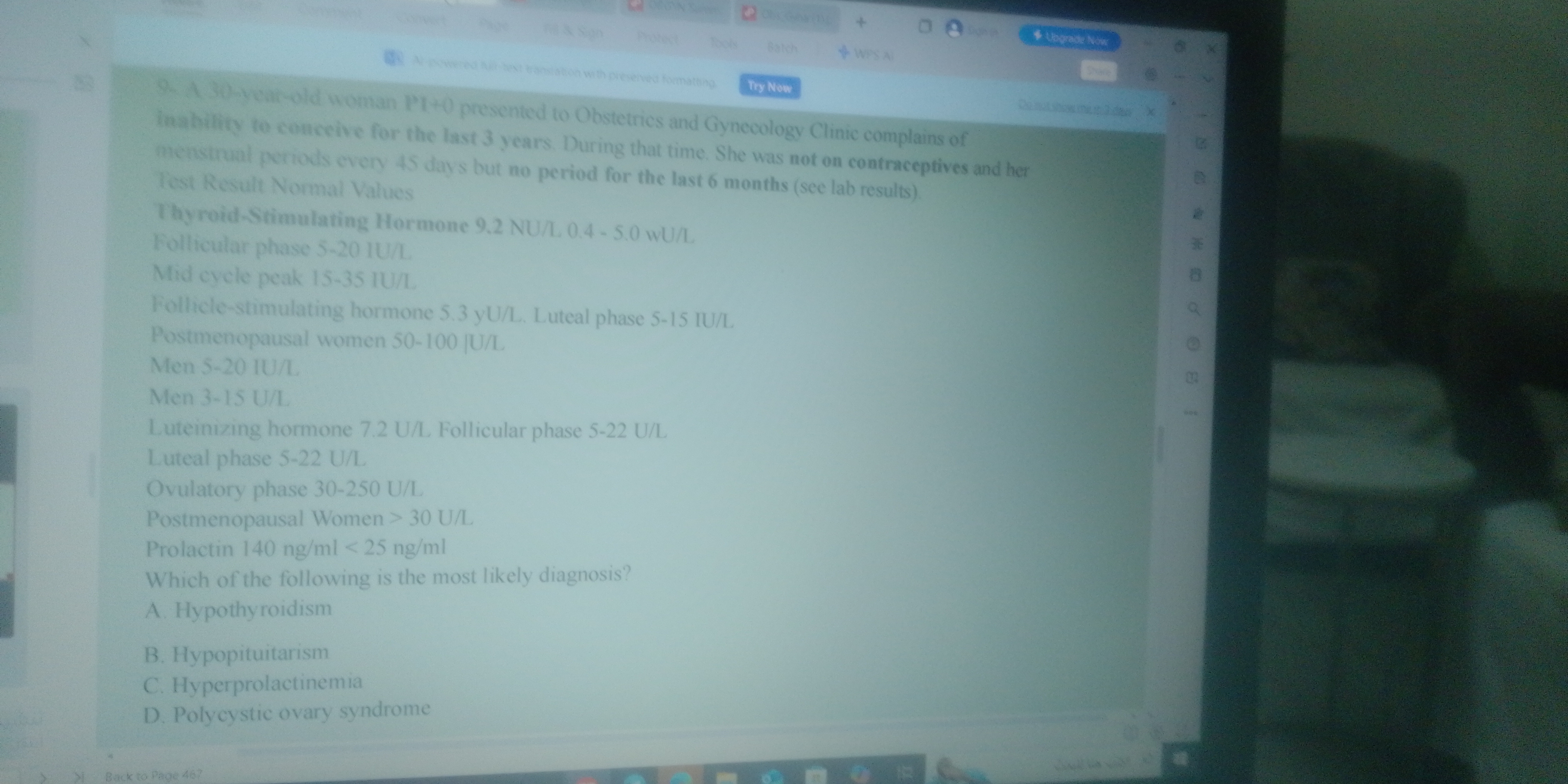
A 30-year-old woman presents with infertility, irregular periods, and the following lab results: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone: 9.2 NU/L (Normal: 0.4-5.0 uU/L) Follicle-Stimulating... A 30-year-old woman presents with infertility, irregular periods, and the following lab results: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone: 9.2 NU/L (Normal: 0.4-5.0 uU/L) Follicle-Stimulating Hormone: 5.3 yU/L (Luteal phase: 5-15 IU/L) Luteinizing Hormone: 7.2 U/L (Follicular phase: 5-22 U/L) Prolactin: 140 ng/ml (Normal: < 25 ng/ml) Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? A. Hypothyroidism B. Hypopituitarism C. Hyperprolactinemia D. Polycystic ovary syndrome
Understand the Problem
The question describes a 30-year-old woman experiencing infertility and irregular menstrual cycles, along with provided lab results for thyroid-stimulating hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, and prolactin. The task is to determine the most likely diagnosis of her symptoms based on the provided information.
Answer
The most likely diagnosis is Hyperprolactinemia, since the Prolactin level is high.
The most likely diagnosis is C. Hyperprolactinemia. The patient's prolactin level is significantly elevated (140 ng/mL) above the normal range (<25 ng/mL), which is indicative of hyperprolactinemia. This condition can cause irregular periods and infertility.
Answer for screen readers
The most likely diagnosis is C. Hyperprolactinemia. The patient's prolactin level is significantly elevated (140 ng/mL) above the normal range (<25 ng/mL), which is indicative of hyperprolactinemia. This condition can cause irregular periods and infertility.
More Information
Hyperprolactinemia can be caused by various factors, including pituitary tumors (prolactinomas), certain medications, and other medical conditions. It can lead to infertility by interfering with the normal hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle.
Tips
When evaluating lab results, always compare the patient's values to the provided normal ranges and consider how each abnormal result correlates with the patient's symptoms.
Sources
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) blood test Information | Mount Sinai - mountsinai.org
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Levels Test - MedlinePlus - medlineplus.gov
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information