(9 + x) - (1 - x)² - 2(3 - x)
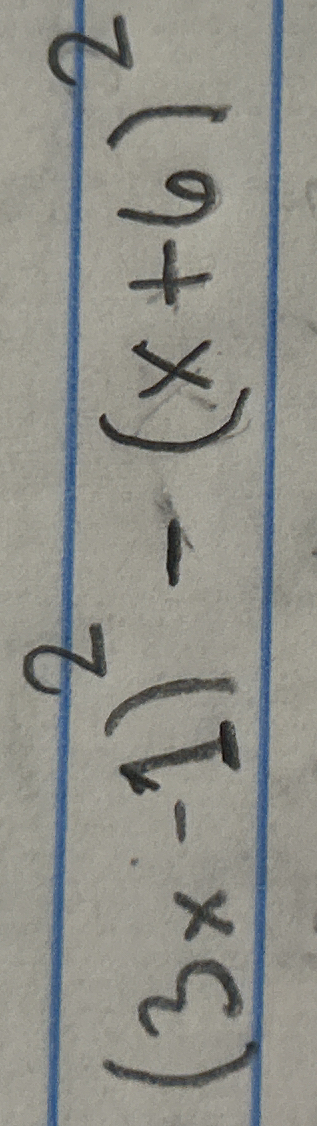
Understand the Problem
The question presents a mathematical expression that appears to involve algebraic operations. It likely requires simplification or solving for a variable.
Answer
The simplified expression is $-x^2 + 5x + 2$.
Answer for screen readers
The simplified expression is $-x^2 + 5x + 2$.
Steps to Solve
-
Expand the expression First, we need to expand the terms in the expression: $$(9 + x) - (1 - x)^2 - 2(3 - x)$$
-
Expand $(1 - x)^2$ Using the formula $(a - b)^2 = a^2 - 2ab + b^2$, we have: $$(1 - x)^2 = 1^2 - 2 \cdot 1 \cdot x + x^2 = 1 - 2x + x^2$$
-
Distribute $-2$ over $(3 - x)$ Next, we distribute $-2$: $$-2(3 - x) = -6 + 2x$$
-
Combine all expanded terms Now combine all the terms: $$(9 + x) - (1 - 2x + x^2) - 6 + 2x$$
-
Simplify the expression Combine like terms:
- The constant terms: $9 - 1 - 6 = 2$.
- The $x$ terms: $x + 2x + 2x = 5x$.
- The $x^2$ term remains as is.
So we have: $$2 + 5x - x^2$$
- Rearrange the expression Finally, to write it in standard form, we rearrange it: $$-x^2 + 5x + 2$$
The simplified expression is $-x^2 + 5x + 2$.
More Information
This expression represents a quadratic function in standard form. Quadratic functions can have interesting properties such as vertex and roots, which can be explored further.
Tips
- Forgetting to distribute the negative sign when expanding the square.
- Not combining like terms accurately at the end.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information