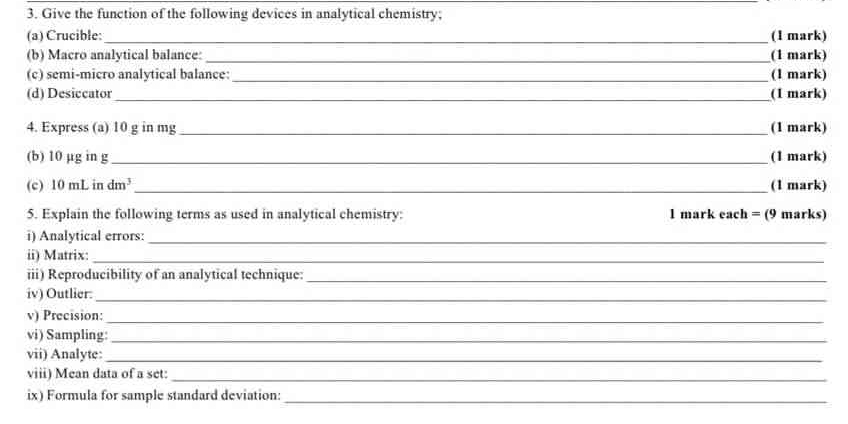
3. Give the function of the following devices in analytical chemistry: (a) Crucible; (b) Macro analytical balance; (c) Semi-micro analytical balance; (d) Desiccator. 4. Express (a)... 3. Give the function of the following devices in analytical chemistry: (a) Crucible; (b) Macro analytical balance; (c) Semi-micro analytical balance; (d) Desiccator. 4. Express (a) 10 g in mg; (b) 10 µg in g; (c) 10 mL in dm³. 5. Explain the following terms as used in analytical chemistry: i) Analytical errors; ii) Matrix; iii) Reproducibility of an analytical technique; iv) Outlier; v) Precision; vi) Sampling; vii) Analyte; viii) Mean data of a set; ix) Formula for sample standard deviation.
Understand the Problem
The question asks for the functions of various devices used in analytical chemistry, conversions between units of measurement, and explanations for specific analytical terms.
Answer
3. (a) Crucible: high-temp heating. (b) Macro balance: large mass measurement. (c) Semi-micro balance: small mass measurement. (d) Desiccator: moisture-free storage. 4. (a) 10,000 mg. (b) 0.00001 g. (c) 0.01 dm³. 5. i) Deviations. ii) Matrix: environment. iii) Reproducibility: repeatability. iv) Outlier: differing value. v) Precision: closeness. vi) Sampling: representative portion. vii) Analyte: substance analyzed. viii) Mean: average. ix) s = √(Σ(xi - x̄)² / (n - 1)).
-
Functions: (a) Crucible is used for heating substances at high temperatures. (b) Macro analytical balance measures large mass amounts with high precision. (c) Semi-micro analytical balance measures smaller mass amounts with higher precision. (d) Desiccator stores samples in a moisture-free environment.
-
Conversions: (a) 10 g in mg = 10,000 mg. (b) 10 µg in g = 0.00001 g. (c) 10 mL in dm³ = 0.01 dm³.
-
Terms: i) Analytical errors are deviations from true value. ii) Matrix is the environment in which analytes exist. iii) Reproducibility is the ability to repeat results under unchanged conditions. iv) Outlier is a value significantly different from others. v) Precision refers to closeness of multiple measurements. vi) Sampling is obtaining a representative portion. vii) Analyte is the substance being analyzed. viii) Mean data is the average of a data set. ix) Sample standard deviation formula: s = √(Σ(xi - x̄)² / (n - 1)).
Answer for screen readers
-
Functions: (a) Crucible is used for heating substances at high temperatures. (b) Macro analytical balance measures large mass amounts with high precision. (c) Semi-micro analytical balance measures smaller mass amounts with higher precision. (d) Desiccator stores samples in a moisture-free environment.
-
Conversions: (a) 10 g in mg = 10,000 mg. (b) 10 µg in g = 0.00001 g. (c) 10 mL in dm³ = 0.01 dm³.
-
Terms: i) Analytical errors are deviations from true value. ii) Matrix is the environment in which analytes exist. iii) Reproducibility is the ability to repeat results under unchanged conditions. iv) Outlier is a value significantly different from others. v) Precision refers to closeness of multiple measurements. vi) Sampling is obtaining a representative portion. vii) Analyte is the substance being analyzed. viii) Mean data is the average of a data set. ix) Sample standard deviation formula: s = √(Σ(xi - x̄)² / (n - 1)).
More Information
Balances and desiccators are crucial in preserving sample integrity. Understanding measurements and conversions ensures accuracy in experiments.
Tips
Common mistakes include confusing precision with accuracy and failing to differentiate between micro and macro balances.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information