Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the epaxial muscle systems?
What is the primary function of the epaxial muscle systems?
- To rotate the vertebral column
- To extend the vertebral column (correct)
- To flex the vertebral column
- To stabilize the vertebral column
Which of the following vertebral groups can be distinguished by its unique characteristics?
Which of the following vertebral groups can be distinguished by its unique characteristics?
- Cranial thoracic, caudal thoracic, and sacral
- Cervical, lumbar, and cranial thoracic
- Lumbar, sacral, and caudal thoracic
- Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar (correct)
What is the primary function of the hypaxial muscles?
What is the primary function of the hypaxial muscles?
- To flex the vertebral column (correct)
- To extend the vertebral column
- To move the limbs
- To rotate the vertebral column
What is the name of the joint that connects the atlas (C1) to the occipital bone?
What is the name of the joint that connects the atlas (C1) to the occipital bone?
Which of the following vertebrae has a unique characteristic?
Which of the following vertebrae has a unique characteristic?
What is the name of the space that contains the cervical viscera?
What is the name of the space that contains the cervical viscera?
What is the function of the ligaments that support the vertebral column?
What is the function of the ligaments that support the vertebral column?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the epaxial muscles?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the epaxial muscles?
What is the name of the bone that connects the thoracic vertebrae to the ribs?
What is the name of the bone that connects the thoracic vertebrae to the ribs?
What is the characteristic of the thirteenth rib?
What is the characteristic of the thirteenth rib?
What is the term for the junction between the bony and cartilaginous parts of a rib?
What is the term for the junction between the bony and cartilaginous parts of a rib?
How many pairs of ribs do horses have?
How many pairs of ribs do horses have?
What is the part of the sternum that is an easily palpable landmark?
What is the part of the sternum that is an easily palpable landmark?
What is the joint responsible for 'Yes' head movement?
What is the joint responsible for 'Yes' head movement?
What is the term for the spaces between the ribs?
What is the term for the spaces between the ribs?
What is the characteristic of the first nine pairs of ribs?
What is the characteristic of the first nine pairs of ribs?
What is the name of the bony prominence on the axis?
What is the name of the bony prominence on the axis?
What is the sternebra that forms the upper part of the sternum?
What is the sternebra that forms the upper part of the sternum?
What is the primary function of the transverse ligament of the atlas?
What is the primary function of the transverse ligament of the atlas?
What is the outer part of the intervertebral disc composed of?
What is the outer part of the intervertebral disc composed of?
What type of joints are formed between the articular processes of the vertebrae?
What type of joints are formed between the articular processes of the vertebrae?
Which ligament connects the apices of all spinous processes?
Which ligament connects the apices of all spinous processes?
What is the cranial continuation of the supraspinous ligament?
What is the cranial continuation of the supraspinous ligament?
What is the inner part of the intervertebral disc composed of?
What is the inner part of the intervertebral disc composed of?
What is the function of the apical and alar ligaments of the dens?
What is the function of the apical and alar ligaments of the dens?
Where does the nuchal ligament extend to in the large animal?
Where does the nuchal ligament extend to in the large animal?
What is the location of the transverse ligament of the atlas?
What is the location of the transverse ligament of the atlas?
What is the plural term for 'vertebra'?
What is the plural term for 'vertebra'?
Which of the following bones are NOT part of the axial skeleton?
Which of the following bones are NOT part of the axial skeleton?
What is the vertebral formula for the dog and cat?
What is the vertebral formula for the dog and cat?
What is the function of the vertebral arch?
What is the function of the vertebral arch?
What is the cranial articular surface of a vertebral body?
What is the cranial articular surface of a vertebral body?
What forms the floor of the vertebral foramen?
What forms the floor of the vertebral foramen?
What is the term for the resultant alignment of the vertebral foramina when the vertebrae are articulated?
What is the term for the resultant alignment of the vertebral foramina when the vertebrae are articulated?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the vertebral arch?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the vertebral arch?
What is the vertebral formula for the horse?
What is the vertebral formula for the horse?
Match the correct vertebral formula to the correct species
Match the correct vertebral formula to the correct species
Adjacent vertebral bodies, with the exception of ___ and ____, are connected via intervertebral discs
Adjacent vertebral bodies, with the exception of ___ and ____, are connected via intervertebral discs
The caudal articular surface of the vertebral body is convex
The caudal articular surface of the vertebral body is convex
The vertebral arch consists of right and left _________. Select all that apply.
The vertebral arch consists of right and left _________. Select all that apply.
Which cervical vertebra does NOT have a spinous process, but does posses a dorsal tubercle?
Which cervical vertebra does NOT have a spinous process, but does posses a dorsal tubercle?
Choose the correct statement.
Choose the correct statement.
Where do sympathetic pre-ganglionic axons originate from?
Where do sympathetic pre-ganglionic axons originate from?
What is the route of sympathetic pre-ganglionic axons to the sympathetic ganglia?
What is the route of sympathetic pre-ganglionic axons to the sympathetic ganglia?
What is the function of the post-ganglionic fiber/axon?
What is the function of the post-ganglionic fiber/axon?
Where can sympathetic pre-ganglionic axons synapse?
Where can sympathetic pre-ganglionic axons synapse?
What is the location of the neuron cell bodies that give rise to sympathetic pre-ganglionic axons?
What is the location of the neuron cell bodies that give rise to sympathetic pre-ganglionic axons?
Where are the pre-ganglionic neuron cell bodies located in the parasympathetic nervous system? (Select all that apply)
Where are the pre-ganglionic neuron cell bodies located in the parasympathetic nervous system? (Select all that apply)
What is the route of pre-ganglionic fibers exiting the brain in the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is the route of pre-ganglionic fibers exiting the brain in the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is the destination of the dorsal vagal trunk in the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is the destination of the dorsal vagal trunk in the parasympathetic nervous system?
Where are the parasympathetic ganglia and post-ganglionic nerves located in relation to the target organ?
Where are the parasympathetic ganglia and post-ganglionic nerves located in relation to the target organ?
What is the fate of pre-ganglionic fibers exiting the sacral spinal cord in the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is the fate of pre-ganglionic fibers exiting the sacral spinal cord in the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is the function of the celiac branch of the dorsal vagal trunk in the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is the function of the celiac branch of the dorsal vagal trunk in the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is the characteristic of the parasympathetic ganglia and post-ganglionic nerves in terms of visibility?
What is the characteristic of the parasympathetic ganglia and post-ganglionic nerves in terms of visibility?
The cervicothoracic ganglion connects with the ____________- ___________ chain of ganglia
The cervicothoracic ganglion connects with the ____________- ___________ chain of ganglia
Which of the following is FALSE in regards to the ansa subclavia?
Which of the following is FALSE in regards to the ansa subclavia?
All autonomic ganglia observed in lab are going to be sympathetic.
All autonomic ganglia observed in lab are going to be sympathetic.
Ryan Gosling walks into the room and your heart starts racing.. what nerve is responsible for the antagonistic response to this?
Ryan Gosling walks into the room and your heart starts racing.. what nerve is responsible for the antagonistic response to this?
The R & L phrenic nerve will synapse at the paravertebral chain before reaching the diaphragm
The R & L phrenic nerve will synapse at the paravertebral chain before reaching the diaphragm
What is the only nerve that supplies somatic motor innervation to the diaphragm?
What is the only nerve that supplies somatic motor innervation to the diaphragm?
The R & L recurrent laryngeal nerves can be seen lying next to the trachea, and contains pre-synaptic fibers at that level
The R & L recurrent laryngeal nerves can be seen lying next to the trachea, and contains pre-synaptic fibers at that level
In the canine, the heart lies at an angle between intercostal spaces 3-6.
In the canine, the heart lies at an angle between intercostal spaces 3-6.
which of the following represents the correct flow of blood in the heart?
which of the following represents the correct flow of blood in the heart?
Papillary muscles are attached to the AV valve via the
Papillary muscles are attached to the AV valve via the
What is the name of the funnel shaped part of the right ventricle?
What is the name of the funnel shaped part of the right ventricle?
What is the nutritional blood supply to the heart?
What is the nutritional blood supply to the heart?
Patent ductus arteriosus occurs when the foramen ovals fails to close after birth, forming a “common atrium” in the adult.
Patent ductus arteriosus occurs when the foramen ovals fails to close after birth, forming a “common atrium” in the adult.
Match to the appropriate description
Match to the appropriate description
The bronchial tree is supplied by the __________
The bronchial tree is supplied by the __________
The vertebral arch is formed by the ________ and __________
The vertebral arch is formed by the ________ and __________
The transverse foramina is noted between ____ and _______ for vertebral VANS to pass through
The transverse foramina is noted between ____ and _______ for vertebral VANS to pass through
Where does the spinal cord reside?
Where does the spinal cord reside?
The spinal nerves, veins and arteries go through this structure.
The spinal nerves, veins and arteries go through this structure.
Which of the following characteristics about the atlas is FALSE.
Which of the following characteristics about the atlas is FALSE.
What part of the axis articulates with the atlas?
What part of the axis articulates with the atlas?
Match the following ligaments and/or joints to correct definition.
Match the following ligaments and/or joints to correct definition.
What articulation on C7 articulates with the first ribs?
What articulation on C7 articulates with the first ribs?
The ___________ of each rib articulates with the ___________ process of the ___________ number vertebrae
The ___________ of each rib articulates with the ___________ process of the ___________ number vertebrae
The deep inguinal ring is made of 3 out of 4 abdominal muscles.
The deep inguinal ring is made of 3 out of 4 abdominal muscles.
What are the 3 abdominal muscles that make up the deep inguinal ring?
What are the 3 abdominal muscles that make up the deep inguinal ring?
The inguinal ligament is made by the ____________
The inguinal ligament is made by the ____________
The rectus abdominal doesn’t always contribute to the prepubic tendon.
The rectus abdominal doesn’t always contribute to the prepubic tendon.
The statement DRESS to inspire allows us to remember that the muscles for inspiration are ______________
The statement DRESS to inspire allows us to remember that the muscles for inspiration are ______________
The statement SIT And breathe out allow us to remember that the muscles for expiration are ___________
The statement SIT And breathe out allow us to remember that the muscles for expiration are ___________
Where does the right coronary artery arise from?
Where does the right coronary artery arise from?
What structures run through the aortic hiatus? Select all that apply
What structures run through the aortic hiatus? Select all that apply
Flashcards
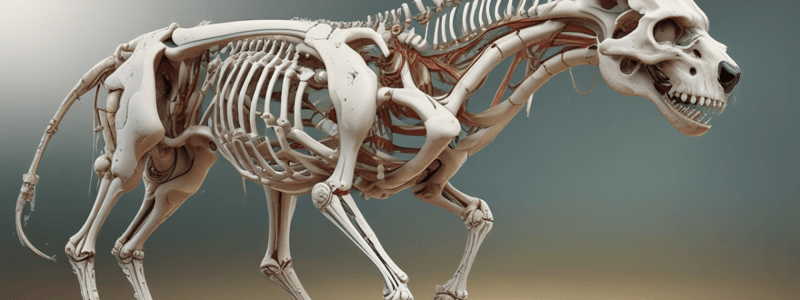
Axial Skeleton
Axial Skeleton
The skeletal elements located along the axis of the body, including the skull, vertebral column, and thorax (sternum and ribs).
Vertebral Formula
Vertebral Formula
The vertebral formula describes the number of vertebrae in each region of the vertebral column.
Vertebral Body
Vertebral Body
The main body of a vertebra, which bears weight and is connected to adjacent vertebrae by intervertebral discs.
Vertebral Arch
Vertebral Arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pedicles
Pedicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laminae
Laminae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Costal Cartilage
Costal Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Manubrium
Manubrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Xiphoid Process
Xiphoid Process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atlanto-occipital Joint
Atlanto-occipital Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atlantoaxial Joint
Atlantoaxial Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse Ligament of the Atlas
Transverse Ligament of the Atlas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apical and Alar Ligaments of the Dens
Apical and Alar Ligaments of the Dens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intervertebral Discs
Intervertebral Discs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Annulus Fibrosus
Annulus Fibrosus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleus Pulposus
Nucleus Pulposus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Supraspinous Ligament
Supraspinous Ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nuchal Ligament
Nuchal Ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epaxial Muscles
Epaxial Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypaxial Muscles
Hypaxial Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Origin of Sympathetic Nervous System
Origin of Sympathetic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pre-ganglionic Axons of Sympathetic Nervous System
Pre-ganglionic Axons of Sympathetic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathway of Pre-ganglionic Axons
Pathway of Pre-ganglionic Axons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synapse of Pre-ganglionic Axons
Synapse of Pre-ganglionic Axons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-ganglionic Fibers
Post-ganglionic Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pre-ganglionic Neuron Cell Bodies of Parasympathetic Nervous System
Pre-ganglionic Neuron Cell Bodies of Parasympathetic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pre-ganglionic Fibers from Sacral Spinal Cord
Pre-ganglionic Fibers from Sacral Spinal Cord
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pre-ganglionic Fibers from Brain
Pre-ganglionic Fibers from Brain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dorsal Vagal Trunk
Dorsal Vagal Trunk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic Ganglia
Parasympathetic Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Axial Musculoskeletal Structures and Body Wall
Bones and Joints of the Axial Skeleton
- Axial skeleton: skeletal elements located along the axis of the body, includes bones of the skull, vertebral column, and thorax (sternum and ribs)
- Vertebral formula:
- Dog and cat: C7 T13 L7 S3 Cd ~20
- Horse: C7 T18 L6 S5 Cd ~20
- Ox: C7 T13 L6 S5 Cd ~20
Typical Features of Vertebrae
- Vertebral body:
- Cranial articular surface is convex
- Caudal articular surface is concave
- Adjacent vertebral bodies, except C1 and C2, are connected via intervertebral discs
- Vertebral arch:
- Arches dorsally from the vertebral body to cover the spinal cord and create the vertebral foramen
- Consists of right and left pedicles (lateral walls of the vertebral foramen) and laminae (roof of the vertebral foramen)
Ribs and Sternum
- Ribs:
- Dogs, cats, and ox have 13 pairs of ribs; horses have 18 pairs
- Each rib has a head, neck, tubercle, and body
- The bony part of a rib has a costochondral junction, where the cartilaginous part (costal cartilage) extends ventrally and articulates with the sternum
- Sternum:
- Comprised of eight sternebrae joined by cartilages
- Manubrium (first sternebra) and xiphoid process (last sternebra) are easily palpable landmarks
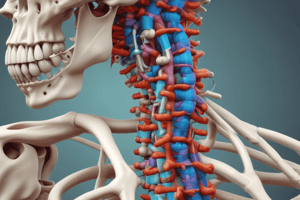
Joints and Ligaments of the Vertebral Column
- Atlanto-occipital joint:
- Between the occipital bone of the skull and the atlas
- Responsible for "Yes" head movement
- Atlantoaxial joint:
- Between the atlas and axis
- Fovea dentis of the atlas and dens of the axis are involved in this joint
- Transverse ligament of the atlas:
- Attaches to the internal wall of the vertebral foramen of the atlas on both sides
- Passes dorsal to the dens and stabilizes it within the fovea dentis
- Apical and alar ligaments of the dens:
- Support the dens within the fovea dentis
- Intervertebral discs:
- Between bodies of adjacent vertebrae
- Composed of an annulus fibrosus (outer circumferential collagenous fibers) and a nucleus pulposus (inner gelatinous core)
Ligaments of the Vertebral Column and Ribs
- Supraspinous ligament:
- Connects the apices of all spinous processes from T1 to the caudal vertebrae
- Nuchal ligament:
- Cranial continuation of the supraspinous ligament
- Extends from the spinous process of thoracic vertebra 1 (T1) to the caudal aspect of the spine of the axis (C2) in the dog
- In large animals, extends to the nuchal crest of the occipital bone of the skull
Epaxial and Hypaxial Musculature
- Epaxial muscles:
- Three systems: splenius, semispinalis capitis, and transversospinalis
- Action: flex or extend the vertebral column
- Location: medial, intermediate, and lateral regions along the vertebral column
- Hypaxial muscles:
- Location: ventral to the vertebral bodies and vertebral transverse processes
- Action: compare size, location, and actions to epaxial muscles
Origin of Sympathetic Nervous System
- Originates from the thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord, not the brain or sacral region.
Pathway of Pre-Ganglionic Axons
- Pre-ganglionic axons extend from neuron cell bodies located in the lateral horn of the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord.
- These axons course to the sympathetic trunk/chain of ganglia via the rami communicantes (communicating branches).
Synapse of Pre-Ganglionic Axons
- Pre-ganglionic axons synapse at one of the sympathetic ganglia, which may include:
- One of the ganglia along the sympathetic chain.
- Cranial cervical ganglion (located at the base of the skull).
- Cervicothoracic ganglion.
- Middle cervical ganglion.
- Celiac, cranial mesenteric, or caudal mesenteric ganglia (located in the abdomen).
Post-Ganglionic Fibers
- Post-ganglionic fibers/axons travel to the target organ, which can be:
- Smooth muscle.
- Cardiac muscle.
- Gland.
Pre-ganglionic Neuron Cell Bodies
- Located in one of two places: brain or lateral region of sacral segment of spinal cord
- Example of brain location: origin of cranial nerve X (vagus nerve)
Pre-ganglionic Fibers
- Exiting sacral spinal cord:
- Course in ventral root of sacral spinal nerve
- Join the pelvic nerve
- Exiting brain:
- Course in Cranial Nerve X (vagus nerve)
- Form right and left vagosympathetic trunks
- Form right and left vagus nerves
- Form right and left recurrent laryngeal nerves (mostly somatic fibers)
- Form dorsal and ventral branches of vagus nerves
- Form dorsal and ventral vagal trunks that travel with esophagus through esophageal hiatus into abdominal cavity
Dorsal Vagal Trunk
- Gives off celiac branch (pre-synaptic parasympathetic fibers) to celiacomesenteric plexus
Parasympathetic Ganglia and Post-ganglionic Nerves
- Not visible with the naked eye in this course
- Synapse and post-synaptic cell located within target organ
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.