Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of intervertebral discs in a typical vertebra?
What is the function of intervertebral discs in a typical vertebra?
- Facilitate articulation with ribs
- House the spinal cord
- Connect adjacent vertebral bodies (correct)
- Anchor the vertebrae to the sternum
Which of the following is NOT a part of the vertebral arch of a typical vertebra?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the vertebral arch of a typical vertebra?
- Laminae
- Pedicles
- Intervertebral discs (correct)
- Spinous process
Where are the spinal nerves and blood vessels typically located in relation to the vertebrae?
Where are the spinal nerves and blood vessels typically located in relation to the vertebrae?
- In between the spinous processes
- Within the intervertebral foramen (correct)
- Around the articular processes
- Within the vertebral canal
What is the main function of epaxial muscles in the axial skeleton?
What is the main function of epaxial muscles in the axial skeleton?
In a typical vertebra, what is the main function of articular processes?
In a typical vertebra, what is the main function of articular processes?
What is the main difference between hypaxial and epaxial muscles?
What is the main difference between hypaxial and epaxial muscles?
What is the primary function of the nucleus pulposus?
What is the primary function of the nucleus pulposus?
Which ligament is a cranial extension of the supraspinous ligament?
Which ligament is a cranial extension of the supraspinous ligament?
Where is the dorsal longitudinal ligament located?
Where is the dorsal longitudinal ligament located?
Which ligament is described as broad bands between the spinous processes and between the transverse processes?
Which ligament is described as broad bands between the spinous processes and between the transverse processes?
Where is the ventral longitudinal ligament located?
Where is the ventral longitudinal ligament located?
What is the function of the transverse processes of the thoracic vertebrae?
What is the function of the transverse processes of the thoracic vertebrae?
Which of the following statements about the sacrum is correct?
Which of the following statements about the sacrum is correct?
What is the purpose of the hemal arch in the caudal vertebrae?
What is the purpose of the hemal arch in the caudal vertebrae?
Which of the following statements about the intervertebral disc is incorrect?
Which of the following statements about the intervertebral disc is incorrect?
What is the function of the spinous processes of the lumbar vertebrae?
What is the function of the spinous processes of the lumbar vertebrae?
Which of the following statements about the anulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc is correct?
Which of the following statements about the anulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc is correct?
Which vertebra has a prominent spinous process and articulates with the atlas via the dens?
Which vertebra has a prominent spinous process and articulates with the atlas via the dens?
Which joint allows only extension and flexion (nodding "yes") movement?
Which joint allows only extension and flexion (nodding "yes") movement?
Which ligament holds the dens against the atlas?
Which ligament holds the dens against the atlas?
Which vertebra has a costal fovea for articulation with the first rib?
Which vertebra has a costal fovea for articulation with the first rib?
How many sternebrae (segments of the sternum) are present in the dog?
How many sternebrae (segments of the sternum) are present in the dog?
For which ribs does the head articulate with the vertebral body cranial to that rib?
For which ribs does the head articulate with the vertebral body cranial to that rib?
What is the function of the sacral promontory?
What is the function of the sacral promontory?
Which of the following statements about the anulus fibrosus is correct?
Which of the following statements about the anulus fibrosus is correct?
What is the primary function of the hemal arch in the caudal vertebrae?
What is the primary function of the hemal arch in the caudal vertebrae?
Which of the following statements about the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae is correct?
Which of the following statements about the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae is correct?
What is the function of the ventral sacral foramina?
What is the function of the ventral sacral foramina?
Which of the following statements about the caudal vertebrae is correct?
Which of the following statements about the caudal vertebrae is correct?
What is the primary function of the atlantoaxial joint?
What is the primary function of the atlantoaxial joint?
Which of the following statements about the atlas (C1) vertebra is correct?
Which of the following statements about the atlas (C1) vertebra is correct?
Which of the following statements about the thoracic vertebrae is incorrect?
Which of the following statements about the thoracic vertebrae is incorrect?
For which ribs does the head articulate with the vertebral body of the same number?
For which ribs does the head articulate with the vertebral body of the same number?
Which of the following vertebrae has a costal fovea for articulation with the first rib?
Which of the following vertebrae has a costal fovea for articulation with the first rib?
How many pairs of ribs are present in the dog?
How many pairs of ribs are present in the dog?
What is the primary function of the nucleus pulposus?
What is the primary function of the nucleus pulposus?
Which ligament courses dorsally along the spinous processes of the thoracic and cervical vertebrae?
Which ligament courses dorsally along the spinous processes of the thoracic and cervical vertebrae?
In which animal species is the nuchal ligament not present?
In which animal species is the nuchal ligament not present?
What is the primary function of the ventral longitudinal ligament?
What is the primary function of the ventral longitudinal ligament?
Which ligaments are described as broad bands between the spinous processes and between the transverse processes?
Which ligaments are described as broad bands between the spinous processes and between the transverse processes?
What is the vertebral formula for the dog?
What is the vertebral formula for the dog?
What are the distinguishing features of the atlas (C1) vertebra?
What are the distinguishing features of the atlas (C1) vertebra?
What is the purpose of the transverse processes in the thoracic vertebrae?
What is the purpose of the transverse processes in the thoracic vertebrae?
Which of the following statements about the intervertebral foramen is correct?
Which of the following statements about the intervertebral foramen is correct?
What is the primary function of the intervertebral discs?
What is the primary function of the intervertebral discs?
What is the main difference between epaxial and hypaxial muscles in the axial skeleton?
What is the main difference between epaxial and hypaxial muscles in the axial skeleton?
What is the vertebral formula for the dog?
What is the vertebral formula for the dog?
What is the main function of the transverse processes in the thoracic vertebrae?
What is the main function of the transverse processes in the thoracic vertebrae?
What is the primary function of the atlantoaxial joint?
What is the primary function of the atlantoaxial joint?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the vertebral arch of a typical vertebra?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the vertebral arch of a typical vertebra?
What is the main difference between epaxial and hypaxial muscles in the axial skeleton?
What is the main difference between epaxial and hypaxial muscles in the axial skeleton?
What is the primary function of the intervertebral discs?
What is the primary function of the intervertebral discs?
What type of movement is allowed at the atlanto-occipital joint?
What type of movement is allowed at the atlanto-occipital joint?
Which vertebra has transverse foramina in the transverse processes for the vertebral artery, vein, and nerve?
Which vertebra has transverse foramina in the transverse processes for the vertebral artery, vein, and nerve?
What is the function of the costal fovea present in C7 vertebra?
What is the function of the costal fovea present in C7 vertebra?
At which joint can rotary movement along the long axis occur?
At which joint can rotary movement along the long axis occur?
What is the distinguishing feature of thoracic vertebrae when comparing spinous and transverse processes?
What is the distinguishing feature of thoracic vertebrae when comparing spinous and transverse processes?
How many pairs of ribs are typically present in a dog's thoracic region?
How many pairs of ribs are typically present in a dog's thoracic region?
What is the primary function of the nucleus pulposus?
What is the primary function of the nucleus pulposus?
Which ligament is a cranial extension of the supraspinous ligament?
Which ligament is a cranial extension of the supraspinous ligament?
In which animal species is the nuchal ligament not present?
In which animal species is the nuchal ligament not present?
Where is the ventral longitudinal ligament located?
Where is the ventral longitudinal ligament located?
Which ligaments are described as broad bands between the spinous processes and between the transverse processes?
Which ligaments are described as broad bands between the spinous processes and between the transverse processes?
What is the primary function of the tubercles of the ribs?
What is the primary function of the tubercles of the ribs?
Which of the following statements about the sacrum is correct?
Which of the following statements about the sacrum is correct?
What is the primary function of the intervertebral discs?
What is the primary function of the intervertebral discs?
Which of the following statements about the anulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc is correct?
Which of the following statements about the anulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc is correct?
What is the function of the ventral sacral foramina?
What is the function of the ventral sacral foramina?
Which of the following statements about the caudal vertebrae is correct?
Which of the following statements about the caudal vertebrae is correct?
Flashcards
Vertebral formula for a dog
Vertebral formula for a dog
The sequence of vertebrae in a dog: C7 T13 L7 S3 Ca 20-23
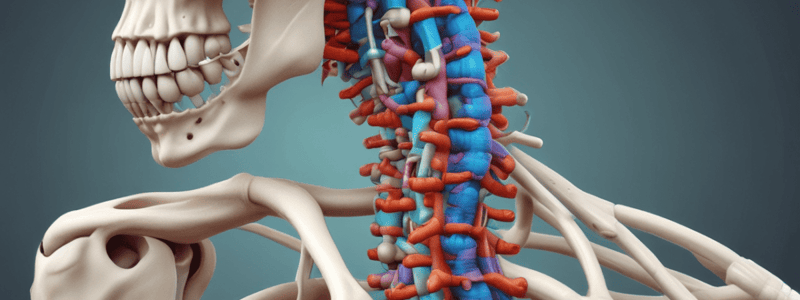
Typical vertebra structure
Typical vertebra structure
Contains a vertebral body, arch (pedicles & laminae), vertebral foramen, and processes (spinous & transverse).
Intervertebral discs
Intervertebral discs
Fibrocartilaginous pads between vertebral bodies, except C1-C2 and sacrum.
Atlas (C1)
Atlas (C1)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axis (C2)
Axis (C2)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervical vertebrae (C3-C6)
Cervical vertebrae (C3-C6)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervical Vertebrae (C7)
Cervical Vertebrae (C7)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T13)
Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T13)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L7)
Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L7)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sacrum (S1-S3)
Sacrum (S1-S3)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Caudal (Coccygeal) Vertebrae
Caudal (Coccygeal) Vertebrae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anulus fibrosus
Anulus fibrosus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleus pulposus
Nucleus pulposus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse ligament of the atlas
Transverse ligament of the atlas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Supraspinous ligament
Supraspinous ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nuchal ligament
Nuchal ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interspinous ligaments
Interspinous ligaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intertransverse ligaments
Intertransverse ligaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atlanto-occipital joint
Atlanto-occipital joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atlantoaxial joint
Atlantoaxial joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Axial Skeleton
- Vertebral formula for the dog: C7 T13 L7 S3 Ca 20-23
- Features of a typical vertebra:
- Vertebral body
- Intervertebral discs are located between adjacent bodies
- Vertebral arch consists of pedicles (walls) and laminae (roof)
- Vertebral foramen surrounded by arch and dorsal surface of body
- Processes: spinous process, transverse processes, articular processes
Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C7)
- C1 (Atlas):
- Large transverse processes (wings)
- No spinous process
- C2 (Axis):
- Prominent spinous process
- Dens articulates with atlas
- C3-C6:
- More typical vertebrae
- Short spinous processes
- Transverse foramen present in transverse processes of C1-C6
- C7:
- No transverse foramen
- Has a costal fovea for articulation with the 1st rib
Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T13)
- Long spinous processes
- Short transverse processes due to articulation with ribs
- Costal foveae on bodies and transverse processes for articulation with ribs
Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L7)
- Large bodies
- Large transverse processes
- Prominent spinous processes
Sacrum (S1-S3)
- Fused S1-S3 vertebrae
- Articulates with ilium
- Cranial ventral lip of the body is called the sacral promontory
- Fused transverse processes
- Sacral foramen for nerves instead of intervertebral foramina
Caudal/Coccygeal Vertebrae (Ca1-Ca20-23)
- First few caudal vertebrae look like typical vertebrae
- Then become more rod-shaped
- Hemal arch located on Ca4-Ca6 - Protects tail vessels
Intervertebral Disc
- Located between vertebral bodies (except at C1-C2 and in the sacrum)
- Fibrocartilaginous structure
- Two parts:
- Anulus fibrosus (outer circumferential collagenous fibers)
- Nucleus pulposus (inner gelatinous core)
Ligaments Associated with the Atlas and Axis
- Transverse ligament of the atlas - holds dens against the atlas
- Supraspinous ligament - courses dorsally along the spinous processes of T1-Ca3 vertebrae
- Nuchal ligament - cranial extension of the supraspinous ligament
- Interspinous and intertransverse ligaments
Joints and Ligaments Associated with the Vertebrae
- Atlanto-occipital joint (between occipital condyles of skull and atlas (C1)) - allows extension and flexion only
- Atlantoaxial joint (between atlas (C1) and axis (C2)) - rotary movement along the long axis
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.