Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a key advantage of using the median cubital vein for venipuncture?
What is a key advantage of using the median cubital vein for venipuncture?
- It can be accessed without any training.
- It has a higher sensitivity in the skin layer.
- It lies deep beneath multiple layers of tissue.
- It is less likely to displace during the procedure. (correct)
Which vein is typically the second choice for venipuncture if the median cubital vein is not visible?
Which vein is typically the second choice for venipuncture if the median cubital vein is not visible?
- Femoral vein
- Medial vein
- Cephalic vein (correct)
- Basilic vein
What characteristic makes the basilic vein a less desirable choice for venipuncture?
What characteristic makes the basilic vein a less desirable choice for venipuncture?
- It is always located close to the skin's surface.
- It has a greater risk of damaging nearby nerves and arteries. (correct)
- It is often less prominent in elderly individuals.
- It is surrounded by less connective tissue.
Which layer of the vein wall is responsible for the strength and elasticity of arteries and veins?
Which layer of the vein wall is responsible for the strength and elasticity of arteries and veins?
What is a primary function of the tunica intima in veins?
What is a primary function of the tunica intima in veins?
Flashcards
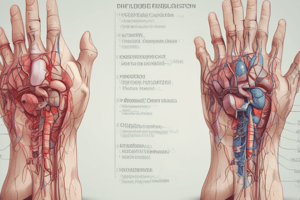
Median Cubital Vein
Median Cubital Vein
A vein near the skin's surface, easily accessible and less likely to move during venipuncture.
Cephalic Vein
Cephalic Vein
A vein on the outer forearm, used only if median cubital vein not found.
Basilic Vein
Basilic Vein
Inner elbow vein, a last option due to fragile nature and proximity to nerves.
Tunica Adventitia
Tunica Adventitia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tunica Media
Tunica Media
Signup and view all the flashcards