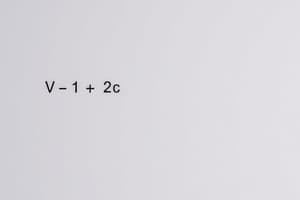Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the term for streams of raw facts?
What is the term for streams of raw facts?
- Information
- Knowledge
- Wisdom
- Data (correct)
What is the result of shaping data into a meaningful and useful form?
What is the result of shaping data into a meaningful and useful form?
- Intelligence
- Wisdom
- Knowledge
- Information (correct)
Which activity is NOT a basic function of an information system?
Which activity is NOT a basic function of an information system?
- Output
- Input
- Processing
- Storage (correct)
What does information systems literacy include?
What does information systems literacy include?
Which term focuses mostly on knowledge of IT?
Which term focuses mostly on knowledge of IT?
What does MIS (Management Information Systems) focus on?
What does MIS (Management Information Systems) focus on?
An information system provides a solution to what?
An information system provides a solution to what?
What do organizations use to coordinate work?
What do organizations use to coordinate work?
What is a key role of managers regarding information systems?
What is a key role of managers regarding information systems?
Computer hardware is a component of which dimension of information systems?
Computer hardware is a component of which dimension of information systems?
What is 'operational excellence' primarily related to?
What is 'operational excellence' primarily related to?
Investing in IT may be driven by what?
Investing in IT may be driven by what?
Which of these is an example of a business driver for information systems around keeping up with competitors?
Which of these is an example of a business driver for information systems around keeping up with competitors?
What are businesses doing when they invest in IT to achieve six important business objectives?
What are businesses doing when they invest in IT to achieve six important business objectives?
What is necessary to use information systems effectively?
What is necessary to use information systems effectively?
Which of the following is an advantage achieved through competitive advantage?
Which of the following is an advantage achieved through competitive advantage?
What factor improves managers' ability to make decisions?
What factor improves managers' ability to make decisions?
What is the result of close relationships with suppliers?
What is the result of close relationships with suppliers?
What is the role of an environmenal actor such as 'customers'?
What is the role of an environmenal actor such as 'customers'?
How does data from a supermarket checkout counter become useful?
How does data from a supermarket checkout counter become useful?
Flashcards
What is data?
What is data?
Raw, unorganized facts that need processing.
What is information?
What is information?
Data shaped into meaningful and useful form.
What is information technology (IT)?
What is information technology (IT)?
The hardware and software a business uses to achieve objectives.
What is an information system?
What is an information system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are IS activities?
What are IS activities?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are organizations?
What are organizations?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are business processes?
What are business processes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is needed from people?
What is needed from people?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is IT infrastructure?
What is IT infrastructure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is operational excellence?
What is operational excellence?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is innovation?
What is innovation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is customer intimacy?
What is customer intimacy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is improved decision-making?
What is improved decision-making?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is competitive advantage?
What is competitive advantage?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Technology: What is survival?
Technology: What is survival?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is IS literacy?
What is IS literacy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is computer literacy?
What is computer literacy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are management information systems?
What are management information systems?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is feedback?
What is feedback?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Information systems vs computers?
Information systems vs computers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
van der Waals Equation: Motivation
- The ideal gas law ($PV = nRT$) fails at high pressures and low temperatures.
- Ideal gas law assumptions: gas molecules have no volume and do not interact.
- The van der Waals equation modifies the ideal gas law, accounting for molecular volume and interaction.
van der Waals Equation: Formula
- The van der Waals equation is: $\left(P + a\left(\frac{n}{V}\right)^2\right)(V-nb) = nRT$
- a and b are empirical constants specific to each gas.
van der Waals Equation: Volume Correction
- The term $nb$ corrects for the volume of gas molecules.
- b is the van der Waals volume, representing the excluded volume per mole of gas.
- The available volume for gas molecules is calculated as $V-nb$.
van der Waals Equation: Pressure Correction
- The term $a\left(\frac{n}{V}\right)^2$ corrects for attractive forces between gas molecules.
- Attractive forces reduce pressure by pulling molecules inward, away from container walls.
- a is the van der Waals attraction parameter measuring the strength of attractive forces.
- The actual pressure of the gas is then $P + a\left(\frac{n}{V}\right)^2$.
van der Waals Constants: Significance
- Constant a: represents the strength of intermolecular attractions.
- High a values relate to stronger attractions.
- Constant b: represents the excluded volume per mole of gas.
- Larger molecules have larger b values.
Virial Expansion
- The virial expansion accounts for non-ideal behavior of real gases.
- Formula: $Z = \frac{PV_m}{RT} = 1 + \frac{B}{V_m} + \frac{C}{V_m^2} +...$
- Z is the compression factor.
- $V_m$ is the molar volume.
- B, C, etc., are virial coefficients which are temperature-dependent, and account for molecular interactions.
Relation to van der Waals Equation
- Second virial coefficient B is given by $B = b - \frac{a}{RT}$
Example Calculation
- Calculating the pressure exerted by 2.4 mol of $N_2$ gas in a 10.0 L vessel at 298 K can be done using 2 formulas:
- Using the ideal gas law: $P = \frac{nRT}{V} = \frac{2.4 \text{ mol} \cdot 0.08206 \frac{\text{L atm}}{\text{mol K}} \cdot 298 \text{ K}}{10.0 \text{ L}} = 5.87 \text{ atm}$
- Using the van der Waals equation ($a = 1.39 \text{ L}^2 \text{ atm mol}^{-2}$, $b = 0.0391 \text{ L mol}^{-1}$): $P = \frac{2.4 \text{ mol} \cdot 0.08206 \frac{\text{L atm}}{\text{mol K}} \cdot 298 \text{ K}}{10.0 \text{ L} - 2.4 \text{ mol} \cdot 0.0391 \text{ L mol}^{-1}} - 1.39 \text{ L}^2 \text{ atm mol}^{-2} \left(\frac{2.4 \text{ mol}}{10.0 \text{ L}}\right)^2= 5.74 \text{ atm}$
- The corrected pressure using van der Waals is lower than the pressure using the ideal gas law.
Summary: Ideal Gas Law vs. van der Waals Equation
- Molecular Volume: Ideal Gas Law says No, van der Waals says Yes (b)
- Intermolecular Force: Ideal Gas Law says No, van der Waals says Yes (a)
- Equation: Ideal Gas Law is $PV = nRT$, van der Waals Equation is $\left(P + a\left(\frac{n}{V}\right)^2\right)(V-nb) = nRT$
Quantum Mechanics: Wave-Particle Duality
- Light and matter exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties.
- de Broglie wavelength relates a particle's momentum (p) to its wavelength ($\lambda$): $\lambda = \frac{h}{p}$, where h is Planck's constant.
Quantum Mechanics: Uncertainty Principle
- Heisenberg's uncertainty principle dictates the impossibility of knowing both position and momentum with perfect accuracy.
- Formula: $\Delta x \Delta p \geq \frac{\hbar}{2}$
- $\Delta x$ and $\Delta p$ represent uncertainties in position and momentum, respectively.
- $\hbar = \frac{h}{2\pi}$ is the reduced Planck constant.
Quantum Mechanics: Wave Functions
- Quantum system state is described by a wave function, $\Psi(r, t)$.
- $\Psi(r, t)$ contains all information about the system.
- Probability density of finding a particle is given by $|\Psi(r, t)|^2$.
- Wave function must satisfy the Schrödinger Equation.
Quantum Mechanics: Schrödinger Equation
- The time-dependent Schrödinger equation describes how the wave function evolves: $i\hbar \frac{\partial \Psi}{\partial t} = \hat{H}\Psi$
- $\hat{H}$ is the Hamiltonian operator, representing total system energy.
- The time-independent Schrödinger equation is for stationary states: $\hat{H}\psi = E\psi$, where Eis the energy of the state.
Quantum Mechanics: Quantum Numbers
- Quantum numbers describe atomic orbital properties.
- They distinguish one electron from another.
- Types of quantum numbers: Principal (n), Angular Momentum (l), Magnetic (m_l), and Spin (m_s).
- Principal Quantum Number (n): describes the energy level of an electron.
- Angular Momentum or Azimuthal Quantum Number (l): describes the shape of the electron's orbital and the number of angular nodes.
- Magnetic Quantum Number (m_l): describes the orientation of the orbital in space.
- Spin Quantum Number (m_s): describes the intrinsic angular momentum of the electron.
Quantum Mechanics: Operators
- In quantum mechanics, physical quantities are represented by operators.
- Momentum operator in one dimension: $\hat{p} = -i\hbar \frac{\partial}{\partial x}$
- Expected value of an operator $\hat{A}$ for a system in state $\Psi$: $\langle A \rangle = \int \Psi^* \hat{A} \Psi d\tau$
Poisson Process: Definition
- N(t) counts events in [0, t].
- {N(t), t ≥ 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ > 0 if: N(0) = 0, has independent increments, and the number of events in any interval of length t follows a Poisson distribution with mean λt.
- $P{N(t+s) - N(s) = n} = e^{-\lambda t} \frac{(\lambda t)^n}{n!}, \quad n = 0, 1, \dots$
Poisson Process: Properties
- Memoryless Property: the process "forgets" past events.
- Arrival Times: $T_i$ is the time of the i-th event; $T_1, T_2, \dots$ are arrival times.
- Interarrival Times: $X_i = T_i - T_{i-1}$ is the time between (i-1)-th and i-th event, $T_0 = 0$.
- $X_1, X_2, \dots$ are interarrival times.
- Interarrival times $X_i$ are iid exponential random variables with mean $1/\lambda$.
Poisson Process: Variations
- The Non-Homogeneous Poisson Process has a rate λ that varies with time: λ(t).
- Expected number of events in $[0, t]$ is $m(t) = \int_0^t \lambda(s) ds$.
- Number of events in (s, t] is Poisson($m(t) - m(s)$).
- The Compound Poisson Process has a random size per event.
- $Y_i$ is the size of the i-th event.
- $S(t) = \sum_{i=1}^{N(t)} Y_i$, $N(t)$ is a Poisson process.
Poisson Process: Applications
- Arrivals in queueing systems
- Reliability analysis
- Finance
Partial Differential Equations: Separation of Variables for Heat Equation
- Heat equation: $\frac{\partial u}{\partial t} = k \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2} \quad 0 0$
- Case 1: $\lambda = 0$
- Solutions are $X(x) = c_1x + c_2$.
- Applying $X(0) = 0$ yields $c_2 = 0$.
- Applying $X(L) = 0$ yields $c_1 = 0$.
- Thus, $X(x) = 0$ (Trivial Solution).
- Case 2: $\lambda < 0$, set $\lambda = -\alpha^2, \alpha > 0$.
- Solutions are $X(x) = c_1e^{\alpha x} + c_2e^{-\alpha x}$.
- Applying $X(0) = 0$ yields $c_2 = -c_1$.
- Applying $X(L) = 0$ yields $c_1 = 0$, so $X(x) = 0$ (Trivial Solution).
- Case 3: $\lambda > 0$, set $\lambda = \alpha^2, \alpha > 0$.
- Solutions are $X(x) = c_1 cos(\alpha x) + c_2 sin(\alpha x)$.
- Applying $X(0) = 0$ yields $c_1 = 0$.
- Applying $X(L) = 0$ requires $sin(\alpha L) = 0$ for non-trivial solutions.
- $\alpha_n = \frac{n\pi}{L}, \quad n = 1, 2, 3,...$
- $\lambda_n = \alpha_n^2 = (\frac{n\pi}{L})^2, \quad n = 1, 2, 3,...$
- Eigenfunctions: $X_n(x) = sin(\frac{n\pi}{L}x), \quad n = 1, 2, 3,...$
- Solve $T'(t) + k\lambda T(t) = 0$:
- $T_n(t) = e^{-k(\frac{n\pi}{L})^2t}, \quad n = 1, 2, 3,...$
- Thus, $u_n(x,t) = X_n(x)T_n(t) = sin(\frac{n\pi}{L}x)e^{-k(\frac{n\pi}{L})^2t}, \quad n = 1, 2, 3,...$
- Superposition Principle:
- $u(x,t) = \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} b_n sin(\frac{n\pi}{L}x)e^{-k(\frac{n\pi}{L})^2t}$
- Initial Condition & Fourier Coefficients:
- $u(x,0) = f(x) = \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} b_n sin(\frac{n\pi}{L}x)$
- $b_n = \frac{2}{L} \int_{0}^{L} f(x) sin(\frac{n\pi}{L}x) dx, \quad n = 1, 2, 3,...$
Linear Algebra: Vectors - Definition
- Vectors are math entities defined by direction, sense, and magnitude.
Linear Algebra: Vectors - Representations
- Vectors in n-dimensional space consist of n ordered real numbers: $\vec{v} = (v_1, v_2,..., v_n) \in \mathbb{R}^n$
Linear Algebra: Vectors - Operations, Addition
- Addition of vectors $\vec{u}$ and $\vec{v}$: $\vec{u} + \vec{v} = (u_1 + v_1, u_2 + v_2,..., u_n + v_n)$
Linear Algebra: Vectors - Operations, Scalar Multiplication
- Multiplication of vector $\vec{v}$ by a scalar c: $c\vec{v} = (cv_1, cv_2,..., cv_n)$
Linear Algebra: Vectors - Dot Product
- Dot product of vectors $\vec{u}$ and $\vec{v}$: $\vec{u} \cdot \vec{v} = \sum_{i=1}^{n} u_i v_i = u_1v_1 + u_2v_2 +... + u_nv_n$
Linear Algebra: Vectors - Norm
- Norm (magnitude) of vector $\vec{v}$: $||\vec{v}|| = \sqrt{\vec{v} \cdot \vec{v}} = \sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^{n} v_i^2}$
Linear Algebra: Vectors - Distance
- Distance between vectors $\vec{u}$ and $\vec{v}$: $d(\vec{u}, \vec{v}) = ||\vec{u} - \vec{v}||$
Linear Algebra: Matrices - Definition
- Matrices are rectangular arrays of real numbers organized into m rows and n columns: $\qquad A = \begin{bmatrix} a_{11} & a_{12} & \cdots & a_{1n} \ a_{21} & a_{22} & \cdots & a_{2n} \ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \ a_{m1} & a_{m2} & \cdots & a_{mn} \end{bmatrix}$
Linear Algebra: Matrices - Operations, Addition
- Addition of matrices A and B (same dimensions): $(A + B){ij} = A{ij} + B_{ij}$
Linear Algebra: Matrices - Operations, Scalar Multiplication
- Multiplication of matrix A by scalar c: $(cA){ij} = cA{ij}$
Linear Algebra: Matrices - Operations, Matrix Multiplication
- Multiplication of matrix A ($m \times p$) by matrix B ($p \times n$): $(AB){ij} = \sum{k=1}^{p} A_{ik}B_{kj}$
Linear Algebra: Matrices - Transposition
- Transpose of matrix A: $(A^T){ij} = A{ji}$
Linear Algebra: Matrices - Identity Matrix
- The identity matrix I is a square matrix with 1s on the diagonal and 0s elsewhere.
Linear Algebra: Matrices - Inverse
- The Inverse of matrix A (if it exists) is a matrix $A^{-1}$ such that: $\qquad AA^{-1} = A^{-1}A = I$
Linear Algebra: Matrices - Determinant
- The determinant of a square matrix A, noted det(A) or |A|, is a scalar.
Linear Algebra: Matrices - Rank
- Rank of matrix A is the maximum number of linearly independent columns (or rows).
Linear Algebra: Systems of Linear Equations - Representation
- A system of linear equations can be represented in matrix form: $Ax = b$
- A is the coefficient matrix
- x is the unknown vector
- b is the constant vector
Linear Algebra: Systems of Linear Equations - Resolution
- Resolution of linear equations refers to finding the vector x that satisfies the equation Ax = b.
Linear Algebra: Systems of Linear Equations - Methods
- Gauss Elimination
- LU Factorization
- Cramer's Rule
Linear Algebra: Vector Spaces - Definition
- A vector space is a set of objects (vectors) with two operations that satisfy certain properties (addition and scalar multiplication).
Linear Algebra: Vector Spaces - Subspace
- A subspace is a subset of a vector space that is itself a vector space.
Linear Algebra: Vector Spaces - Basis
- A basis of a vector space is a set of linearly independent vectors that span the vector space.
Linear Algebra: Vector Spaces - Dimension
- The dimension of a vector space is the number of vectors in a basis of that vector space.
Linear Algebra: Linear Transformations
- A linear transformation between vector spaces preserves addition and scalar multiplication.
Linear Algebra: Linear Transformations - Matrix Representation
- A linear transformation can be represented by a matrix.
Linear Algebra: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- An eigenvector v of matrix A satisfies $Av = \lambda v$, where $\lambda$ is an eigenvalue of A.
Thermodynamics: Zeroth Law
- If two thermodynamic systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
- It allows the definition of temperature.
Thermodynamics: First Law
- Energy is conserved; it can only change forms.
- In any process, the total energy of the universe remains the same.
- For a thermodynamic cycle the net heat supplied to the system equals the net work done by the system.
- Formula: $\Delta U = Q - W$
- U = internal energy of the system
- Q = heat exchanged between system & surroundings
- W = work done by the system
Thermodynamics: Second Law
- The entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will tend to increase over time, approaching a maximum value at equilibrium.
- Formula: $\Delta S \geq 0$
- S = the entropy of the system.
Thermodynamics: Third Law
- As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a minimum or zero value.
- $T \to 0, S \to 0$
- It allows for the definition of absolute entropy.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.