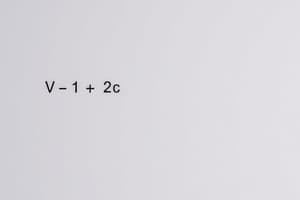Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is an isotherm in the context of real gases?
What is an isotherm in the context of real gases?
- A diagram illustrating the molecular structure of gases
- A curve representing pressure vs. volume at constant temperature (correct)
- A graph showing the relationship between temperature and entropy
- A relationship describing the viscosity of gases at varying pressures
How do van der Waals isotherms differ from those of real gases?
How do van der Waals isotherms differ from those of real gases?
- They are applicable only for ideal gases.
- They are always linear regardless of conditions.
- They account for molecular interactions and volume considerations. (correct)
- They predict gas behavior only at low temperatures.
What characteristic does the isotherm for a real gas typically exhibit compared to an ideal gas?
What characteristic does the isotherm for a real gas typically exhibit compared to an ideal gas?
- It demonstrates a hysteresis effect due to real gas behavior.
- It remains unchanged across different temperatures.
- It shows a perfect linear relationship between pressure and volume.
- It reflects deviations from the ideal behavior at high pressures and low temperatures. (correct)
What significance do van der Waals constants have in the van der Waals equation?
What significance do van der Waals constants have in the van der Waals equation?
In real gases, which factor primarily causes deviations from the ideal gas law?
In real gases, which factor primarily causes deviations from the ideal gas law?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Isotherms
- An isotherm is a graph that plots the pressure of a gas against its volume at a constant temperature.
Real Gases vs Ideal Gases Isotherms
- Isotherms for real gases typically exhibit a characteristic "S" shape at low temperatures.
- The "S" shape reflects the fact that real gases deviate from ideal gas behavior at high pressures and low temperatures.
- Ideal gas isotherms, in contrast, are always hyperbolic, meaning the pressure and volume are inversely proportional.
Van der Waals Equation Isotherms
- The van der Waals equation accounts for intermolecular forces and finite molecular size, which are not considered in the ideal gas law.
- The van der Waals isotherm is a more realistic representation of the behavior of real gases at low temperatures and high pressures.
Van der Waals Constants
- The van der Waals constants "a" and "b" are empirical parameters that reflect the strength of intermolecular forces and the volume occupied by the gas molecules, respectively.
- These constants are unique for each gas.
Deviations from Ideal Gas Law
- The primary factor causing deviations from the ideal gas law in real gases is the presence of intermolecular forces, which are attractive forces between gas molecules.
- These forces become more significant at low temperatures and high pressures, where molecules are closer together.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.