Podcast
Questions and Answers
Where is the renal pelvis located?
Where is the renal pelvis located?
- On the medial side of the kidney
- Inside the renal sinus (correct)
- At the lateral side of the kidney
- Directly under the cortex
Which structure of the kidney houses the renal pyramids?
Which structure of the kidney houses the renal pyramids?
- Renal pelvis
- Renal sinus
- Medulla (correct)
- Cortex
What is the function of the hilus of the kidney?
What is the function of the hilus of the kidney?
- Store urine temporarily
- Allow veins and arteries to enter and exit (correct)
- Produce erythropoietin and renin
- Filter plasma
In what region of the body are the kidneys located?
In what region of the body are the kidneys located?
Which part of the urinary tract receives urine from the renal pelvis?
Which part of the urinary tract receives urine from the renal pelvis?
What surrounds the kidneys?
What surrounds the kidneys?
Which side of the kidney has a convex shape?
Which side of the kidney has a convex shape?
What does the renal sinus house?
What does the renal sinus house?
Where does the urethra open in females?
Where does the urethra open in females?
What is not a function of the uterine tube?
What is not a function of the uterine tube?
Where are the ovaries located in females?
Where are the ovaries located in females?
Which part of the ovary contains nerves and vessels?
Which part of the ovary contains nerves and vessels?
What connects the abdominal wall and uterus to the ovaries?
What connects the abdominal wall and uterus to the ovaries?
In males, what is the name of the urethra that leads towards the penis?
In males, what is the name of the urethra that leads towards the penis?
What is a unique feature of the male urethra compared to the female urethra?
What is a unique feature of the male urethra compared to the female urethra?
Which structure catches the oocyte during ovulation?
Which structure catches the oocyte during ovulation?
What is the primary function of the infundibulum?
What is the primary function of the infundibulum?
What is the shape of the uterus?
What is the shape of the uterus?
Which part of the uterus is located within the pelvic cavity?
Which part of the uterus is located within the pelvic cavity?
What is the primary function of the uterus?
What is the primary function of the uterus?
What is the function of the cervix?
What is the function of the cervix?
What is the primary function of the vestibule?
What is the primary function of the vestibule?
What is the relationship between the vagina and the vestibule?
What is the relationship between the vagina and the vestibule?
What is the true statement regarding the broad ligament?
What is the true statement regarding the broad ligament?
What is the shape of the dorsal commissure of the vulva?
What is the shape of the dorsal commissure of the vulva?
What is the purpose of the placenta?
What is the purpose of the placenta?
How many zones are present in the zonary placenta of a bitch?
How many zones are present in the zonary placenta of a bitch?
What is the function of the mammary glands?
What is the function of the mammary glands?
Where are the 5 pairs of mammary glands located in a bitch?
Where are the 5 pairs of mammary glands located in a bitch?
What statement about the clitoris is correct?
What statement about the clitoris is correct?
Which lymph nodes drain the mammary glands?
Which lymph nodes drain the mammary glands?
Where is the location of the pigmented zone in the placenta?
Where is the location of the pigmented zone in the placenta?
What is the primary function of the ureters?
What is the primary function of the ureters?
Which statement about the urinary bladder is correct?
Which statement about the urinary bladder is correct?
What is the primary function of the detrusor muscle in the urinary bladder?
What is the primary function of the detrusor muscle in the urinary bladder?
Which statement about the urethra is correct?
Which statement about the urethra is correct?
What is the function of the urethral muscles?
What is the function of the urethral muscles?
What is the significance of visible ureteral orifices in the urinary bladder?
What is the significance of visible ureteral orifices in the urinary bladder?
Which condition can lead to both fecal and urinary incontinence?
Which condition can lead to both fecal and urinary incontinence?
Study Notes
Urogenital Apparatus
- Consists of the kidneys and urinary tract
- Urinary tract composed of ureters, urethra, urinary bladder, and renal pelvis
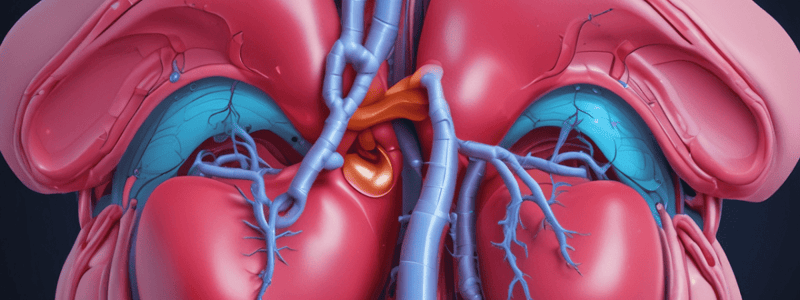
Kidneys
- Right kidney is more cranial than the left
- Surrounded by fat, located in the lumbar region, attached to the ceiling of the abdominal cavity
- Peritoneum covers the ventral aspect of the kidneys but not the dorsal aspect
- Functions: filtering plasma, endocrine function (erythropoietin, renin)
- External features: bean-shaped, hilus medially orientated, medial side concave, lateral side convex
- Structure: cortex, medulla, renal pyramids, renal crest, renal sinus
Renal Pelvis
- Collects urine from the renal crest and passes it to the ureters
- Located inside the renal sinus and the expanding part of the ureter
Urethra
- Females: pelvic urethra only, located at the neck of the urinary bladder, caudally in the pelvic cavity, opens at the vaginal and vestibule junction
- Males: pelvic urethra, longer than females, leads towards the penis, receives ducti deterrents, has a penile urethra
Female Reproductive Viscera
- Composed of ovaries, uterine tube, uterus with cervix, vagina, vestibula, and vulva
- Ovaries: located in the dorsal part of the abdomen, within the lumbar region, close to the tips of the horns of the uterus, functions: female gametogenesis, endocrine function
- Ovary structure: ovoid, composed of two layers (medulla and cortex), containing a reserve of follicles
Uterine Tube
- Functions: catching the oocyte during ovulation, being the site of fertilization, delivering the fertilized ova to the uterine horn
- Structure: infundibulum, funnel-shaped part that covers the ovary to capture the oocyte
Uterus
- Y-shaped organ, located in the abdomen, functions: being the site of gestation, ensuring the physiological exchange between fetus and mom
- Structure: endometrium (mucosa), myometrium (muscle), perimetrium, broad ligament
- Cervix: controls access to and from the vagina, partially projects into the vaginal lumen, includes cervical canal, internal uterine orifice, external uterine orifice
Vagina and Vestibule
- Copulatory organs, used as the birthing canal, urethral orifice separates the vagina from the vestibule
- Vestibule combines reproductive and urinary functions, allows the penis to enter the vagina during sexual intercourse
Vulva
- Ventral commissure has a pointed shape, houses the clitoris and clitoridis, dorsal commissure has a rounded shape
Placenta
- Temporary organ used for gestation, structure varies per species
- A bitch has a zonary placenta with 3 zones: transfer zone, pigmented zone, relatively non-vascular zone
Mammary Glands
- Modified sweat glands, used for lactation, number of pairs varies per species
- Bitches normally have 5 pairs, lymphatic drainage important during surgical removal of tumors
Ureters
- Emerge from the renal hilus, run caudally towards the dorsal aspect of the urinary bladder, function: drain urine
- Compressed if intravesical pressure rises
Urinary Bladder
- Functions: deposits urine between micturition, position of the bladder depends on its plentitude
- External features: apex, body, neck, no visible sphincter, but the urethral muscles keep the urethra constricted
- Structure: outer layer: adventitia, middle layer: detrusor muscle, inner layer: mucosa with urothelium
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge on the urogenital apparatus, including the composition of kidneys and urinary tract. Learn about the location, structure, and functions of the kidneys in the human body.